import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.jbpm.api.Configuration;
import org.jbpm.api.ExecutionService;
import org.jbpm.api.HistoryService;
import org.jbpm.api.ManagementService;
import org.jbpm.api.ProcessDefinition;
import org.jbpm.api.ProcessEngine;
import org.jbpm.api.ProcessInstance;
import org.jbpm.api.RepositoryService;
import org.jbpm.api.TaskService;
public class Test {
ProcessEngine processEngine;
RepositoryService repositoryService;
ExecutionService executionService;
TaskService taskService;
HistoryService historyService;
ManagementService managementService;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test t=new Test();
t.process();
}
public void process() {
processEngine=Configuration.getProcessEngine();
repositoryService=processEngine.getRepositoryService();
executionService=processEngine.getExecutionService();
//定义流程processEngine repositoryService
String deploymentId=repositoryService.createDeployment().addResourceFromClasspath("hellworld.jpdl.xml").deploy();
String deploymentId1=repositoryService.createDeployment().addResourceFromClasspath("hellworld.jpdl.xml").deploy();
List<ProcessDefinition> list=repositoryService.createProcessDefinitionQuery().list();
System.out.println("11111111111111111111111流程定义");
String processId=null;//后面用到processId
for(ProcessDefinition processDefinition:list){
if (null==processId) {//后面用到processId
processId=processDefinition.getId();//后面用到processId
}
System.out.println("流程定义:"+processDefinition.getId());
System.out.println("流程部署:"+processDefinition.getDeploymentId());
}
//删除流程deploymentId1
System.out.println("222222222222222222222222流程删除");
// repositoryService.deleteDeploymentCascade(deploymentId1);
list=repositoryService.createProcessDefinitionQuery().list();
for(ProcessDefinition processDefinition:list){
System.out.println("流程定义:"+processDefinition.getId());
System.out.println("流程部署:"+processDefinition.getDeploymentId());
}
/**
//建立流程实例
System.out.println("333333333333333333333333333流程实例");
// ProcessInstance processInstance=executionService.startProcessInstanceByKey("hellworld");
ProcessInstance processInstance=executionService.startProcessInstanceById(processId);//用到processId
List<ProcessInstance> list1=executionService.createProcessInstanceQuery().list();
String processInstanceId=null;//后面用到processInstanceId
for (ProcessInstance processInstance1 : list1) {
if (null==processInstanceId) {
processInstanceId=processInstance1.getId();//后面用到processInstanceId
}
System.out.println("流程实例key:"+processInstance1.getKey());
System.out.println("流程实例Id:"+processInstance1.getId());
System.out.println("流程定义Id:"+processInstance1.getProcessDefinitionId());
}
System.out.println("333333333333333333333333333删除流程实例");
executionService.deleteProcessInstanceCascade(processInstanceId);//用到processInstanceId
list1=executionService.createProcessInstanceQuery().list();
for (ProcessInstance processInstance1 : list1) {
System.out.println("流程实例key:"+processInstance1.getKey());
System.out.println("流程实例Id:"+processInstance1.getId());
System.out.println("流程定义Id:"+processInstance1.getProcessDefinitionId());
}
System.out.println("4444444444444444444444444结束流程实例");
executionService.endProcessInstance(processInstanceId, "结束流程实例");
list1=executionService.createProcessInstanceQuery().list();
for (ProcessInstance processInstance1 : list1) {
System.out.println("流程实例key:"+processInstance1.getKey());
System.out.println("流程实例Id:"+processInstance1.getId());
System.out.println("流程定义Id:"+processInstance1.getProcessDefinitionId());
}
*/
System.out.println("555555555555555555555555结束流程实例");
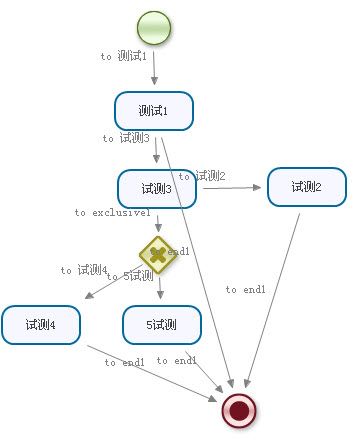
ProcessInstance processInstance=executionService.startProcessInstanceByKey("hellworld");
System.out.println(processInstance.isActive("测试1"));
System.out.println(processInstance.getId());
processInstance = executionService.signalExecutionById(processInstance.getId(),"to 试测3" );
Map hashmap=new HashMap();
hashmap.put("var1", 5);
processInstance = executionService.signalExecutionById(processInstance.getId(),"to exclusive1",hashmap);
System.out.println(processInstance.isEnded());
}
}
基础知识
流程定义引擎:
ProcessEngine processEngine;
获取:
| processEngine=Configuration.getProcessEngine(); |
重要的几个接口:
| RepositoryService repositoryService; ExecutionService executionService; TaskService taskService; HistoryService historyService; ManagementService managementService; |
获取:
| repositoryService=processEngine.getRepositoryService(); executionService=processEngine.getExecutionService(); taskService=processEngine.getTaskService(); historyService=processEngine.getHistoryService(); managementService=processEngine.getManagementService(); |
说明:
RepositoryService主要用来管理和发布流程定义,发布流程定义、删除流程定义、查看流程定义。
流程定义发布:
| repositoryService.createDeployment().addResourceFromClasspath("demo.jpdl.xml").deploy(); |
注:此方法表示从classpath路径加载一个流程定义文件,并发布,上例中demo.jpdl.xml文件位于src(classpath)路径下,若流程定义文件放置与包中,则需要使用包名+jpdl文件名。如com/jbpm/demo.jpdl.xml
查看流程定义:
| repositoryService.createDeployment().addResourceFromClasspath("test1.jpdl.xml").deploy(); List<ProcessDefinition> list=repositoryService.createProcessDefinitionQuery().list(); for (ProcessDefinition processDefinition : list) { System.out.println("流程定义Id:"+processDefinition.getId()); System.out.println("流程部署Id:"+processDefinition.getDeploymentId()); } |
删除流程定义:
| String deploymentId=repositoryService.createDeployment().addResourceFromClasspath("test1.jpdl.xml").deploy(); repositoryService.deleteDeploymentCascade(deploymentId); |
deploymentId为流程定义部署Id
ExecutionService主要用来操作流程实例,启动流程实例、查看流程实例、删除流程实例、结束流程实例。
其前提条件是发布了流程定义
启动流程实例:
| repositoryService.createDeployment().addResourceFromClasspath("demo.jpdl.xml").deploy(); ProcessInstance processInstance=executionService.startProcessInstanceByKey("demo"); |
使用executionService.startProcessInstanceByKey("demo");方法来启动一个流程实例。其中startProcessInstanceByKey就表示以key的方式来启动流程实例,key为流程定义文件中process节点的key属性,若未明确给出key属性,则默认key属性的值与name属性的值相同。
同样也可以使用executionService.startProcessInstanceById(processDefinitionId)的方式来启动流程实例。此方法是用流程定义文件中process节点的id属性来启动流程实例。
其Id属性由两部分组成流程定义的key和流程定义的版本来组成。形如key-version
例如:
ProcessInstance processInstance=executionService.startProcessInstanceById("demo-1");
其中demo-1就为流程定义中的流程Id,其key为demo,版本号为1
同样使用此方法可用来启动指定版本号的流程实例。
查看流程实例:
| List<ProcessInstance> list=executionService.createProcessInstanceQuery().list(); for (ProcessInstance processInstance : list) { System.out.println("流程实例Id:"+processInstance.getId()); System.out.println("流程定义Id:"+processInstance.getProcessDefinitionId()); } |
级联删除流程实例:
| executionService.deleteProcessInstanceCascade(processInstance.getId()); |
结束流程实例:
| executionService.endProcessInstance(processInstance.getId(), "结束流程实例"); |
注意:在使用executionService.endProcessInstance()对流程实例进行结束操作后,需要重新查询processInstance才能得到更新后的流程实例,如果流程已结束,则查询结果为null
如:
| executionService.endProcessInstance(processInstance.getId(), "结束流程实例"); System.out.println(processInstance.isEnded()); 此行代码是无意义的,因为此时并未获取到更新后的流程实例,需要重新查询流程实例,所以此处返回为false System.out.println("-----------查询流程实例--------------->"); List<ProcessInstance> list=executionService.createProcessInstanceQuery().list(); for (ProcessInstance processInstance : list) { System.out.println("流程实例Id:"+processInstance.getId()); System.out.println("流程定义Id:"+processInstance.getProcessDefinitionId()); } |
结果:
false
-----------查询流程实例--------------->
使流程向下执行:
在使用executionService启动流程实例后,流程会顺着向下执行(即启动流程实例后,流程会从start节点向下移动),在state或task节点,流程会暂停下来,满足条件后流程会向下继续执行,直到流程end节点,结束流程。
在程序中是流程遵循某一条件,沿着某个方向流动的方法为executionService.signalExecutionById();
该方法有多个重载:
| ProcessInstance signalExecutionById(String executionId); //若在流程定义某一个节点没有分支时(只有一个transition时),调用此方法,可将流程继续向下执行 executionId为流程实例Id ProcessInstance signalExecutionById(String executionId, String signalName); //若在流程定义某一个节点有多个分支时(有多个transition时),调用此方法,可将流程沿着transition所指的方向向下执行 executionId为流程实例Id, signalName为流程定义中transition节点的name属性的值 ProcessInstance signalExecutionById(String executionId, String signalName, Map<String, ?> parameters); 用于将流程沿着signalName方向(transition的name属性所指的方向)向下继续执行,在执行的过程中顺便传递参数parameters ProcessInstance signalExecutionById(String executionId, Map<String, ?> parameters); 用于将流程向下继续执行,在执行的过程中顺便传递参数parameters |
注:当一个节点有多个分支时,若要通过signalExecutionById()方法将流程向下执行必须明确指出signalName即(transition的name属性所指的方向),否则流程不会向下执行,仍会停留在当前节点。因为jbpm不确定流程该流向那个方向。
示例代码:
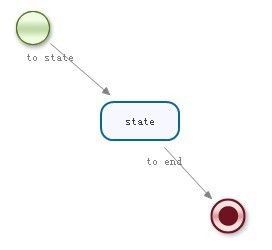
1. 没有分支的state流向
流程定义文件:
| <?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?> <processname="demo"xmlns="http://jbpm.org/4.3/jpdl"> <startname="start"g="87,113,48,48"> <transitionname="to state"to="state"g="-53,-17"/> </start> <statename="state"g="238,236,92,52"> <transitionname="to end"to="end"g="-41,-17"/> </state> <endname="end"g="384,367,48,48"/> </process> |
测试代码:
| import org.jbpm.api.Configuration; import org.jbpm.api.ExecutionService; import org.jbpm.api.ProcessEngine; import org.jbpm.api.ProcessInstance; import org.jbpm.api.RepositoryService; import junit.framework.TestCase; publicclass DemoTest extends TestCase{ ProcessEngine processEngine; RepositoryService repositoryService; ExecutionService executionService; @Override protectedvoid setUp() throws Exception { processEngine=Configuration.getProcessEngine(); repositoryService=processEngine.getRepositoryService(); executionService=processEngine.getExecutionService(); //部署流程定义 repositoryService.createDeployment().addResourceFromClasspath("demo.jpdl.xml").deploy(); } publicvoid testProcessInstance(){ ProcessInstance processInstance=executionService.startProcessInstanceByKey("demo"); System.out.println("流程实例Id:"+processInstance.getId()); System.out.println("流程定义Id:"+processInstance.getProcessDefinitionId()); //判断当前是否位于start节点 System.out.println("是否位于start节点:"+processInstance.isActive("start")); //判断当前是否位于state节点 System.out.println("是否位于state节点:"+processInstance.isActive("state")); //判断流程是否结束 System.out.println("判断流程是否结束:"+processInstance.isEnded()); System.out.println("------------------------>使流程继续向下执行"); //使流程继续向下执行 //ProcessInstance instanceState=executionService.signalExecutionById(processInstance.getId()); //此处也可以这么写 ProcessInstance instanceState=executionService.signalExecutionById(processInstance.getId(),"to end"); //to end为流程定义中用于连接state和end节点之间transition的name属性的值 //判断当前是否位于state节点 System.out.println("是否位于state节点:"+instanceState.isActive("state")); //判断流程是否结束 System.out.println("判断流程是否结束:"+instanceState.isEnded()); } } |
执行结果:
| 流程实例Id:demo1.7 流程定义Id:demo1-1 是否位于start节点:false 是否位于state节点:true 判断流程是否结束:false ------------------------>使流程继续向下执行 是否位于state节点:false 判断流程是否结束:true |
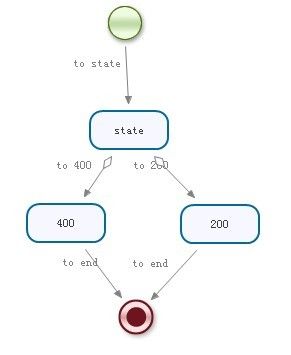
2. 含有分支的state流向
流程定义文件:
| <?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?> <processname="demo"xmlns="http://jbpm.org/4.3/jpdl"> <startg="347,27,48,48"name="start"> <transitiong="-53,-17"name="to state"to="state"/> </start> <stateg="329,132,92,52"name="state"> <transitionname="to 200"to="200"g="-41,-17"/> <transitionname="to 400"to="400"g="-41,-17"/> </state> <endg="358,321,48,48"name="end"/> <statename="200"g="420,226,92,52"> <transitionname="to end"to="end"g="-41,-17"/> </state> <statename="400"g="266,225,92,52"> <transitionname="to end"to="end"g="-41,-17"/> </state> </process> |
测试代码:
| import junit.framework.TestCase; public class Demo2Test extends TestCase{ ProcessEngine processEngine; RepositoryService repositoryService; ExecutionService executionService; @Override protected void setUp() throws Exception { processEngine=Configuration.getProcessEngine(); repositoryService=processEngine.getRepositoryService(); executionService=processEngine.getExecutionService(); //部署流程定义 repositoryService.createDeployment().addResourceFromClasspath("demo.jpdl.xml").deploy(); } public void testProcessInstance(){ ProcessInstance processInstance=executionService.startProcessInstanceByKey("demo"); System.out.println("流程实例Id:"+processInstance.getId()); System.out.println("流程定义Id:"+processInstance.getProcessDefinitionId()); //判断当前是否位于start节点 System.out.println("是否位于start节点:"+processInstance.isActive("start")); //判断当前是否位于state节点 System.out.println("是否位于state节点:"+processInstance.isActive("state")); //判断流程是否结束 System.out.println("判断流程是否结束:"+processInstance.isEnded()); System.out.println("------------------------>使流程继续向下执行"); //不明确指出流动方向,看流程位于那个节点 ProcessInstance instance=executionService.signalExecutionById(processInstance.getId()); //判断当前是否位于state节点 System.out.println("是否位于state节点:"+instance.isActive("state")); //判断流程是否结束 System.out.println("判断流程是否结束:"+instance.isEnded()); } } |
执行结果:
| 流程实例Id:demo.7 流程定义Id:demo-1 是否位于start节点:false 是否位于state节点:true 判断流程是否结束:false ------------------------>使流程继续向下执行 是否位于state节点:true 判断流程是否结束:false |
指明流向节点:
| ProcessInstance processInstance=executionService.startProcessInstanceByKey("demo"); System.out.println("------------------------>使流程继续向下执行"); System.out.println("------------------------>使流程流向200"); ProcessInstance processInstance200=executionService.signalExecutionById(processInstance.getId(), "to 200"); System.out.println("当前流程是否位于200节点---->"+processInstance200.isActive("200")); System.out.println("当前流程是否结束---->"+processInstance200.isEnded()); /*System.out.println("------------------------>使流程流向400"); ProcessInstance processInstance400=executionService.signalExecutionById(processInstance.getId(), "to 400"); System.out.println("当前流程是否位于400节点---->"+processInstance400.isActive("400")); System.out.println("当前流程是否结束---->"+processInstance400.isEnded());*/ |
执行效果:
| ------------------------>使流程继续向下执行 ------------------------>使流程流向200 当前流程是否位于200节点---->true 当前流程是否结束---->false |
上述代码中使用signalExecutionById()方法时,传入的是流程实例的Id,也可以使用以下代码来完成同样的工作:
| ProcessInstance processInstance=executionService.startProcessInstanceByKey("demo"); //查询该流程实例的活动节点 System.out.println(processInstance.findActiveActivityNames()); //因为流程实例启动后,它会自动向下执行,直到遇到state或task等节点时暂停下来,在我们的流程定义文件中紧跟在start后的节点为state,所以流程实例会在state节点暂停下来 Execution execution=processInstance.findActiveExecutionIn("state"); ProcessInstance processInstance200=executionService.signalExecutionById(execution.getId(), "to 200"); System.out.println("当前流程是否位于200节点---->"+processInstance200.isActive("200")); System.out.println("当前流程是否结束---->"+processInstance200.isEnded()); //使流程继续向下执行(结束) System.out.println("-------使流程继续向下执行(结束)------->"); ProcessInstance instance=executionService.signalExecutionById(processInstance200.getId()); System.out.println("当前流程是否结束---->"+instance.isEnded()); |
执行结果:
| [state] 当前流程是否位于200节点---->true 当前流程是否结束---->false -------使流程继续向下执行(结束)-------> 当前流程是否结束---->true |
关于流程实例几个重要的方法:
processInstance.isEnded()判断程实例是否结束结束返回true,否则返回false
processInstance.isActive(“A”)判断当前流程是否处于A节点
谨记executionService.signalExecutionById(String executionId, String signalName)方法中executionId为流程实例Id,signalName为流程向下执行的transition的name属性的值,而不是下一个节点的名称。