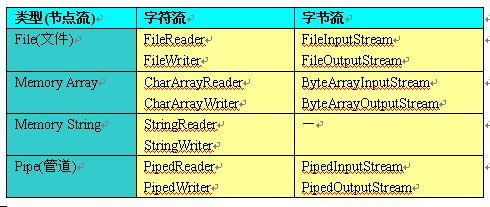
Java文件读写数据流
数据流可分节点流(想象成一管子直接接文件或内存等上),处理流(套在节点流之外使用).
一、理解数据流:
流一般分为输入流Input Stream和输出流Output Stream.
Java的标准数据流:
指在字符方式下,程序与系统进行交互的方式.标准输入studin,对象是键盘.标准输出stdout,对象是屏幕.标准错误输出stderr,对象是屏幕.
例:
本例用System.in.read(buffer)从键盘输入一行字符,存储在缓冲区buffer中,count保存实际读入的字节个数,再以整数和字符两种方式输出buffer中的值.
import java.io.*;
public class Input1
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
System.out.println("Input: ");
byte buffer[]=new byte[512]; //输入缓冲区
int count=System.in.read(buffer); //读取标准输入流
System.out.println("Output: ");
for (int i=0;i<count;i++) //输出buffer元素值
{
System.out.print(" "+buffer[i]);
}
System.out.println();
for (int i=0;i<count;i++) //按字符方式输出buffer
{
System.out.print((char)buffer[i]);
}
System.out.println("count="+count);
}
}
程序中,main方式采用throws子句抛出IOException异常交由系统处理.
字节流:
从InputStream和OutputStream派生出来的一系列类.这类流以字节byte为基本处理单位
FileInputStream FileOutputStream
PipedInputStream PipedOutputStream
ByteArrayInputStream ByteArrayOutputStream
FilterInputStream FilterOutputStream
DataInputStream DataOutputStream
BufferedInputStream BufferedOutputStream
字符流:
从Reader和Writer派生出来的一系列类,以16位的Unicode码表示的字符为基本处理单位
InputStreadmReader OutputStreadmWriter
FileReader FileWriter
CharArrayReader CharArrayWriter
PipedReader PipedWriter
FilterReader FilterWriter
BufferedReader BufferedWriter
StringReader StringWriter
字节流初步:
read() // 从流中读入数据 skip() // 跳过流中若干字节数 available() // 返回流中可用字节数 mark() // 在流中标记一个位置 reset() // 返回标记过得位置 markSupport() // 是否支持标记和复位操作 close() write() // 输出到流 flush() // 刷空输出流
例:
本例以FileInpuStream的read(buffer)方法,每次从源程序文件OpenFile.java中读取512个字节,存储在缓冲区buffer中,再将以buffer中的值构造的字符串new String(buffer)显示在屏幕上
import java.io.*;
public class OpenFile
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
try
{
FileInputStream rf=new FileInputStream("OpenFIle.java");
int n=512;
byte buffer[]=new byte[n];
while ((rf.read(buffer,0,n)!=1)&&(n>0))
{
System.out.print(new String(buffer));
}
System.out.println();
rf.close();
}
catch(IOException ioe)
{ System.out.println(ioe); }
catch(Exception e)
{ System.out.println(e); }
}
}
例:写入文件
本例用System.in.read(buffer)从键盘输入一行字符,存储在缓冲区buffer中,再以FileOutStream的writer(buffer)方法,将buffer中内容写入文件中.
import java.io.*;
public class Writer
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
System.out.print("Input: ");
int count,n=512;
byte buffer[]=new byte[n];
count=System.in.read(buffer);
FileOuputStream wf=new FileOutputStream("Writer.txt");
wf.write(buffer,0,count);
wf.close();
}
catch(Exception e)
{ System.out.print(e); }
}
import java.io.*;
public class FileStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("Myhello.txt");
out.write("Welcome to 香巴拉空间~".getBytes());
out.close();
byte [] buf=new byte[1024];
File f=new File("Myhello.txt");
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(f);
int len=in.read(buf);
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
in.close();
}
}
字符流: Reader Writer
FileReader 、FileWriter应用示例:
public class FileStream2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// FileStream2 filestream2 = new FileStream2();
FileWriter out=new FileWriter("File_tmp2.txt");
out.write("欢迎来到香巴拉空间~ , FileWriter");
out.close();
char [] buf=new char[1024];
FileReader in=new FileReader("File_tmp2.txt");
int len=in.read(buf);
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
}
}
例: 文件编辑器
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.io.*;
public class EditFile1 extends WindowAdapter implements ActionListener,TextListener
{
Frame f;
TextArea ta1;
Panel p1;
TextField tf1;
Button b1,b2,b3;
FileDialog fd;
File file1=null;
public static void main(String args[])
{
(new EditFile1()).display();
}
public void display()
{
f = new Frame("EditFile");
f.setSize(680,400);
f.setLocation(200,140);
f.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
f.addWindowListener(this);
tf1 = new TextField();
tf1.setEnabled(false);
tf1.setFont(new Font("Dialog",0,20)); //设置文本行的初始字体
f.add(tf1,"North");
ta1 = new TextArea();
ta1.setFont(new Font("Dialog",0,20)); //设置文本区的初始字体
f.add(ta1);
ta1.addTextListener(this); //注册文本区的事件监听程序
p1 = new Panel();
p1.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
b1 = new Button("Open");
b2 = new Button("Save");
b3 = new Button("Save As");
p1.add(b1);
p1.add(b2);
p1.add(b3);
b2.setEnabled(false);
b3.setEnabled(false);
b1.addActionListener(this); //注册按钮的事件监听程序
b2.addActionListener(this);
b3.addActionListener(this);
f.add(p1,"South");
f.setVisible(true);
}
public void textValueChanged(TextEvent e)
{ //实现TextListener接口中的方法,对文本区操作时触发
b2.setEnabled(true);
b3.setEnabled(true);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
if (e.getSource()==b1) //单击[打开]按钮时
{
fd = new FileDialog(f,"Open",FileDialog.LOAD);
fd.setVisible(true); //创建并显示打开文件对话框
if ((fd.getDirectory()!=null) && (fd.getFile()!=null))
{
tf1.setText(fd.getDirectory()+fd.getFile());
try //以缓冲区方式读取文件内容
{
file1 = new File(fd.getDirectory(),fd.getFile());
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file1);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String aline;
while ((aline=br.readLine()) != null)//按行读取文本
ta1.append(aline+"\r\n");
fr.close();
br.close();
}
catch (IOException ioe)
{
System.out.println(ioe);
}
}
}
if ((e.getSource()==b2) || (e.getSource()==b3))
{ //单击[保存]按钮时
if ((e.getSource()==b3) ||(e.getSource()==b2)&&(file1==null))
{ //单击[SaveAs]按钮时,或单击[Save]按钮且文件对象为空时
fd = new FileDialog(f,"Save",FileDialog.SAVE);
if (file1==null)
fd.setFile("Edit1.txt");
else
fd.setFile(file1.getName());
fd.setVisible(true); //创建并显示保存文件对话框
if ((fd.getDirectory()!=null) && (fd.getFile()!=null))
{
tf1.setText(fd.getDirectory()+fd.getFile());
file1 = new File(fd.getDirectory(),fd.getFile());
save(file1);
}
}
else
save(file1);
}
}
public void save(File file1)
{
try //将文本区内容写入字符输出流
{
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file1);
fw.write(ta1.getText());
fw.close();
b2.setEnabled(false);
b3.setEnabled(false);
}
catch (IOException ioe)
{
System.out.println(ioe);
}
}
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
{
System.exit(0);
}
}
文件操作
File类:
File(String pathname) File(File patent,String chile) File(String patent,String child) String getName() // 得到文件名(不含路径) String getPath() // 得到文件路径 String getAbslutePath() // 得到文件绝对路径 String getParent() // 得到文件上一级目录名 String renameTo(File newName) // 将当前文件更名为给定文件的完整路径 boolean exists() // 文件是否存在 boolean canWrite() boolean canRead() boolean isFile() // 是否是文件(而不是目录) boolean isDirectory() long lastModified() long length() boolean delete() // 删除当前文件 boolean mkdir() String list() // 列出当前目录下的文件
例:自动更新文件
本例使用File类对象对指定文件进行自动更新的操作
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Data;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
public class UpdateFile
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
String fname="Write.txt";
String childdir="backup"
new UpdateFile().update(fname,childdir);
}
public void update(String fname,String childdir) throws IOException
{
File f1,f2,child;
f1=new File(fname);
child=new File(childdir)
if (f1.exists())
{
if (!child.exists())child.mkdir(); //如果目录不存在则建立
f2=new File(child,fname);
if (!f2.exists() || f2.exists() && (f1.lastModified()>f2.lastModified())) //如果f2不存在,或存在但日期较f1早
copy(f1,f2)
getinfo(f1);
getinfo(child);
}
else
System.out.println(f1.getName()+" file not found!");
}
public void copy(File f1,FIle f2) throws IOException
{
FileInputStream rf=new FileInputStream(f1);
FileOutputStreadm w=new FileOutputStream(f2);
int count,n=512;
byte buffer[]=new byte[n];
count=rf.read(buffer,0,n);
while(count!=-1)
{
wf.write(buffer,0,count)
count=rf.read(buffer,0,n);
}
System.out.println("CopyFile "+f2.getName()+" !");
rf.close();
wf.close();
}
public static void getinfo(File f1) throws IOException
{
SimpleDateFormat sdf;
sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日hh时mm分);
if (f1.isFile())
System.out.println("<FILE>\t"+f1.getAbsolutePath()+"\t"+f1.lenght()+"\t"+f1.lenght()+"\t"+sdf.format(new Date(f1.lastModified())));
else
{
System.out.println("\t"+f1.getAbsolutePath());
File[] files=f1.listFiles();
for (int i=0;i<FILES.Lenght;i++)
getInfo(files[i]);
}
}
}
文件过滤器
类FilterInputStream和FilterOutputStream分别对其他输入/输出流进行特殊处理,它们在读/写数据的同时可以对数据进行特殊处理.另外还提供了同步机制,使得某一时刻只有一个线程可以访问一个输入/输出流
要使用过滤流,首先必须把它连接到某个输入/输出流上: FilterInputStream(InputStream in); FilterOutputStream(OutputStream out);
例: 列出当前目录中带过滤器的文件名清单
import java.io.*;
public class DirFilter implements FilenameFIlter
{
private String prefix="",suffix="" //文件名的前缀和后缀
public DirFilter(String filterstr)
{
filterstr=filterstr.toLowerCase();
int i=filterstr.indexOf('*');
int j=filterstr.indexOf('.');
if (i>0)
prefix=filterstr.substring(0,i);
if(j>0)
suffix=filterstr.substring(j+1);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
FilenameFIlter filter=new DirFilter("w*abc.txt");
File f1=new File("");
File curdir=new File(f1.getAbsolutePath(),"");
System.out.println(curdir.getAbsolutePath();
String[] str=curdir.list(filter); //列出带过滤器的文件名清单
for (int i=0;i<Str.length,i++)
System.out.println("\t"+str[i]);
}
public boolean accept(File dir,String filename)
{
boolean yes=true;
try
{
filename=filename.toLowerCase();
yes=(filename.startsWith(prefix)) & (filename.endsWidth(suffix));
}
catch(NullPointerExceptin e)
{ }
return yes;
}
}
对于InputStream和OutputStream来说,它们的实例都是顺序访问流.在java中,类RandomAccessFile提供了随机访问文件的方法
public class RandomAccessFile extends Object implements DataInput,DataOutput
类RandomAccessFile允许对文件内容同时进行读写: Datainput DataOutput
int skipBytes(int n) 指针向下移动若干字节
redInt. writeDouble ...
length() 返回文件长度
long getFilePointer() 指针当前位置
void seek(long pos) 指针调到所需位置
void setLenght(long newLenght) 设置文件长度
RandomAccessFile(File file,String mode)
RandomAccessFile(String name,String mode)
r 只读 rw 读写 rws 同步读写 rwd 数据同步读写
例:随机文件操作
import java.io.*;
public class PrimesFIle
{
RandomAccessFile raf;
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
(nw PrimesFile()).createprime(100);
}
public void createprime(int max) throws IOException
{
raf=new RandomAccessFile("primes.bin","rw");
raf.seek(0);
raf.writeInt(2); //写入整形
int k=3;
while (k<=max)
{
if(isPrime(k))
raf.writeInt(k);
k=k+2;
}
output(max);
raf.close();
}
public boolean isPrime(int k) throws IOException
{
int i=0,j;
boolean yes=true;
try
{
raf.seek(0);
int count=(int)(raf.lenght()/4);
while ((i<=count) && yes)
{
if (k % raf.readInt()==0)
yes=false;
else
i++;
raf.seek(i*4);
}
}
catch(EOFExcption e){}
return yes;
}
public void output(int max) throws IOException
{
try
{
raf.seek(0);
System.out.println("[2.."+max+"]中有 "+(raf.lenght()/4)+" 个素数:");
for (int i=0;i<(int)(raf.lenght()/4);i++)
{
raf.seek(i*4);
System.out.print(raf.readInt()+" ");
if ((i+1)%10==0) System.out.println();
}
}
catch(EOFExcption e){}
System.out.println();
}
}