- Ubuntu32/64位arm/aarch64交叉编译总结
新潮技术研究社
linux开源项目百万案例之路生活有技术armarm开发嵌入式硬件交叉编译
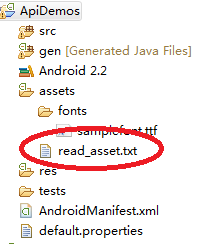
交叉编译,做过Linux的同学应该都不陌生,经常见到的,就是,我的电脑上有一个VMwareUbuntu的虚拟机,然后在Ubuntu系统下,我要将程序移植到某个arm的板子上,就是放到板子上去运行,譬如,放到手机上运行,放到平板上运行,只不过有些平板的系统也是Ubuntu,不是所有的平板都是Android的嘛,还有苹果系统,华为系统,WinCE,无界面系统等等。这时候,有几种方式将程序放到目标设备上
- 美团Android开发200道面试题及参考答案(上)
大模型大数据攻城狮
android开发安卓面经大厂招聘https协议Ddos攻击手撕代码八股文
http三次握手/四次挥手具体过程,信号量的变化,只有两次握手行不行三次握手过程:第一次握手:客户端向服务器发送一个SYN(同步)标志位为1的TCP报文段,其中包含客户端的初始序列号(ISN),此时客户端进入SYN_SENT状态,表示客户端请求建立连接。第二次握手:服务器收到客户端的SYN报文段后,会向客户端发送一个SYN和ACK(确认)标志位都为1的TCP报文段,其中包含服务器的初始序列号和对客
- Android开发网络编程,使用API获取网络数据
浩宇软件开发
androidokhttpjavaAndroid开发网络编程AndroidStudio
文章目录1.实现步骤2.开发环境3.运行效果图4.视频教程1.实现步骤阅读API接口使用文档使用okhttp获取网络数据使用gson将json数据转为数据实体类安装GsonFormatPlus插件使用glide加载网络图片2.开发环境开发工具:Androidstudio开发语言:Javabuild.gradle下导入相关依赖//数据解析implementation'com.google.code.
- Android开发,待办事项提醒App的设计与实现(个人中心页)
浩宇软件开发
androidAndroid开发androidstudio
文章目录1.编写UI布局2.实现逻辑3.运行效果图3.关于作者其它项目视频教程介绍Android开发,待办事项提醒App的设计与实现:https://blog.csdn.net/jky_yihuangxing/article/details/145277956?spm=1001.2014.3001.55011.编写UI布局fragment_mine.xml2.实现逻辑MineFragment.ja
- React Native 0.77发布,新样式特性,Android 16KB页面支持,Swift模板
ReactNative0.77版本发布:新特性、改进与迁移说明2025年1月21日,ReactNative0.77正式发布,此版本带来诸多新特性、对Android的支持增强、社区模板更新以及一些重要变更。一、新特性亮点(一)CSS新特性助力布局、尺寸与混合效果display:contents简化布局逻辑:该属性使元素自身在布局结构中“消失”,但子元素仍正常渲染,就像直接作为父元素的子元素一样。在构
- 通过python对excel进行数据分析和可视化
新叶猫长那么可爱干什么
python的学习python
importpandasaspdimportmatplotlib.pyplotaspltimportseabornassnsfile_path="C:\\Users\\86138\\Desktop\\book_list-计算机-机器学习-linux-android-数据库-互联网.xlsx"data=pd.read_excel(file_path)need_data=data[['书名','评分'
- Android Studio 备忘录(简单)实现
松醪
javasqliteandroidgithub编辑器
项目简介AndroidStudio环境下,备忘录(简单)的实现,功能有:添加,单个查询,删除全部内容,并可获取当前时间存储在SqlLite中。所用到的显示控件为ScrollView,EditText,TextView,ImageButton.图片展示首页添加页添加后的页面Acticity_main.xml代码展示Acativity_add.xml(添加)代码展示MainActivity.java代
- AndroidStudio简单计算器的实现
松醪
javaandroidstudio
项目简介首先此项目是本人学校安卓开发的一次作业,用AndroidStudio开发一个简单的计算器,这个计算器正常的功能为带括号的加减乘除多项式计算!界面展示废话不多说先展示一下界面!(模仿了小米计算器),有两种方式添加控件,一种为动态添加,一种为直接添加。这里使用了EditText(1),TextView(1),Button(19)”activity_main.xml“展示部分AndroidStu
- Android 在后台无法启动Activity
屈佳俊
android移动开发
前言前几天接触的一个闹钟APP项目,闹钟触发从后台启动一个activity,执行之后的响铃操作,但是却失效了,闹钟并没有按时响铃。最后发现是系统拦截了从后台启动的Activity。具体原因一、AndroidQ从后台启动Activity的限制Android10(API级别29)及更高版本对后台应用可启动Activity进行限制。Android10中,当App的Activity不在前台时,其启动Act
- android presentation
weixin_33725126
移动开发ui
对于双屏异显(lcd和hdmi的双屏异显),android框架已经支持,但是底层接口功能还是要自己去实现,且需要底层驱动支持。使用presentation去画第二个display就好了。1MediaRoutermediaRouter=(MediaRouter)context.getSystemService(Context.MEDIA_ROUTER_SERVICE);2MediaRouter.Ro
- android-Presentation双屏异显
勘察加熊人
android
最近碰到一个智能硬件,有两块屏幕,主屏幕和小屏幕,主界面执行各种操作流程,然后小屏幕展示数据,然后做一下数据交互主要技术是Presentation+eventbusstep1:清单文件注册权限step2:首页主界面packagecom.example.user.mathgame;importandroid.os.Bundle;importandroid.support.v4.app.Fragmen
- Android Rxjava3 使用场景
2401_89760309
android
Observable>>hotKey=ApiManager.getInstance().getApiService().getHotKey();Observable.just(articleList).subscribeOn(Schedulers.io()).observeOn(AndroidSchedulers.mainThread()).map(newFunction,Observable>>
- Android 内核开发之—— repo 使用教程
ByteSaid
Android开发androidgit
前言repo是一个用于管理多个Git仓库的工具,特别适用于管理大型项目如Android的源码。它是由Google开发的,用于解决多个Git仓库的同步、管理和代码审查等问题。因此,做Android内核开发,首先要了解repo是什么,它是如何使用的?1repo的概念repo是一种代码版本管理工具,它是由一系列的Python脚本组成,封装了一系列的Git命令,用来统一管理多个Git仓库。2repo的作用
- Android AIDL 使用教程
ByteSaid
Android开发androidipcaidl
AIDL(AndroidInterfaceDefinitionLanguage)是一种IDL语言,用于生成可以在Android设备上两个进程之间进行进程间通信(IPC)的代码。通过AIDL,可以在一个进程中获取另一个进程的数据和调用其暴露出来的方法,从而满足进程间通信的需求。通常,暴露方法给其他应用进行调用的应用称为服务端,调用其他应用的方法的应用称为客户端,客户端通过绑定服务端的Service来
- Android系统开发(十六):从许可名单到角色分配,Android权限机制访问
刘争Stanley
Framework框架大师Android开发巅峰之路android
引言欢迎来到《没权限别搞事》的世界!今天我们聊的是Android权限系统。权限这玩意儿,既是开发者的伙伴,也是绊脚石。一不小心,系统不给面子,直接宕机;稍有疏漏,敏感数据泄露用户信任跑光光。为什么选择这个主题?因为权限管理已经从简单的“允许/拒绝”进化到高深莫测的角色配置。而我们程序猿,不仅要懂,还要会用。来吧,一起解锁Android权限的全新世界!一、权限角色Android权限系统是守护用户隐私
- Android15音频进阶之音效sessionId(一百零四)
Android系统攻城狮
AndroidAudio工程师进阶系列音视频Android15音效Visualizer处理audiosessionId
简介:CSDN博客专家、《Android系统多媒体进阶实战》一书作者新书发布:《Android系统多媒体进阶实战》优质专栏:Audio工程师进阶系列【原创干货持续更新中……】优质专栏:多媒体系统工程师系列【原创干货持续更新中……】优质视频课程:AAOS车载系统+AOSP14系统攻城狮入门视频实战课
- 原生开发vs混合开发
甘光宗
c++
原生开发(NativeDevelopment)和混合开发(HybridDevelopment)是两种常见的移动应用开发方式,各有其优缺点。以下是它们的详细对比:1.原生开发(NativeDevelopment)定义:原生开发指的是使用平台特定的编程语言和工具(如Android使用Java/Kotlin,iOS使用Swift/Objective-C)来开发应用程序。这些应用直接与操作系统交互,能够使
- Flutter核心原理(Flutter UI 框架(Framework)+Element、BuildContext和RenderObject )
彳饕餮亍
flutter
什么是UI框架?UI框架是在特定平台上实现快速开发图形用户界面(GUI)的框架。它解决了如何基于基础的图形API(如Canvas)来封装一套高效创建UI的工具集的问题。每个平台的UI框架实现原理基本相通,无论是Android还是iOS,它们将用户界面展示到屏幕的流程都是类似的。UI框架的作用是简化开发人员在特定平台上创建GUI的过程,提供高效且易于使用的工具和组件,使开发者能够快速构建各种用户界面
- Android 应用逆向与 Hook 技术进阶实战
阿贾克斯的黎明
javaandroid
目录Android应用逆向与Hook技术进阶实战一、课程目标二、变量Hook详解(一)静态变量与实例变量区分(二)静态变量Hook步骤(三)实例变量Hook步骤三、构造函数Hook攻略(一)构造函数识别(二)Hook构造函数方法四、方法主动调用技巧(一)静态方法与实例方法区分及调用原则(二)静态方法调用示例(三)实例方法调用示例五、内部类Hook指南(一)内部类定义与识别(二)Hook内部类方法步
- 什么是 React Native
程序猿经理
reactnativereact.jsjavascript
ReactNative(简称RN)是Facebook于2015年4月开源的跨平台移动应用开发框架,它是Facebook早先开源的JS框架React在原生移动应用平台的衍生产物,支持iOS和安卓两大平台。以下是关于ReactNative的详细介绍:一、基本概述定义:ReactNative是一个使用React和应用平台的原生功能来构建Android和iOS应用的开源框架。起源:由Facebook开发并
- Android 导出CSV文件乱码问题处理
AD钙奶-lalala
android
最近有一个需求,需要在Android端导出CSV文件,自测是用的WPS,没啥问题。可到了测试那边,用Excel直接打开就是乱码,需要在Excel数据里面用【从文件/CSV】打开。这样就显示非常的不方便。解决办法:publicstaticvoidexportToCsv(Listdata,StringfilePath)throwsIOException{FilecsvFolder=newFile(Fi
- React Native 介绍
王睿丶
资讯看点ReactNative移动开发跨平台React王睿丶
文章目录一丶ReactNative惊喜二丶ReactNative简介三丶ReactNative特性四丶ReactNative优点五丶ReactNative局限性六丶构建最简单的应用七丶学习资料一丶ReactNative惊喜ReactNative是一个使用JavaScript和React来编写跨终端移动应用(Android或IOS)的一种解决方案这句话是什么意思呢?即使你不懂如何使用Java或Kot
- 基于ADB Shell 实现的 Android TV、电视盒子万能遥控器 — ADB Remote ATV
sw-code
adbandroid电视盒子tv
OrangePiZero3AndroidTV、电视盒子万能遥控器ADBRemoteATVAndroidTV的遥控器,基于ADBShell命令ADBRemoteATV是一个AndroidTV的遥控器,基于ADBShell命令,泛用性更高。下面的shell命令,是软件的基本原理,通过shell命令可模拟物理遥控器的基本按键,此外还可以快捷启动指定APP、借助手机软键盘输入中/英字符等。#输入事件adb
- 聊聊如何实现Android 放大镜效果
咖啡老师
android
一、前言很久没有更新Android原生技术内容了,前些年一直在做跨端方向开发,最近换工作用重新回到原生技术,又回到了熟悉但有些生疏的环境,真是感慨万分。近期也是因为准备做地图交互相关的需求,功能非常复杂,尤其是交互部分,不过再复杂的交互,只要一点点将它拆解,分而治之,问题还是可以解决,就比如接下来要做的放大镜功能。二、功能设计该功能的场景是在操作地图时,对于边缘的精细化操作(像素级别的)需要在放大
- 【Java】Android解析apk文件中的AndroidManifest.xml
Mr_EvanChen
JavaJava解析apk获取apk版本号
该ApkUtil的主要功能是通过解析AndroidManifest.xml,获取apk的版本号(即versionCode)和名字(versionName)。importandroid.util.TypedValue;importbrut.androlib.res.decoder.AXmlResourceParser;importorg.slf4j.Logger;importorg.slf4j.Lo
- android material 组件 - ShapeableImageView
2401_89210258
androidgitee
android:padding=“1dp”android:scaleType=“centerCrop”android:src=“@mipmap/ic_img”app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf=“parent”app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf=“parent”app:layout_constraintStart_toStar
- 【Flutter】webview_flutter使用详解
Jzin
flutter
文章目录前言一、如何使用前言webview_flutter是Flutter官方推出的一款用于Flutter上的webview插件,该插件在iOS用的是WKWebView支持;在Android上用的是系统WebView。插件地址:https://pub.dev/packages/webview_flutter一、如何使用第一步:在项目根目录下运行如下命令配置依赖flutterpubaddwebvie
- 代码编写java代做c++程序代编程Python代c#设计C语言接单软件定制
matlabgoodboy
javac++c#
您提到的服务涵盖了多种编程语言和软件开发需求,包括Java代码编写、C++程序代编、Python编程代做、C#设计、C语言编程,以及软件定制服务。这些服务在软件开发领域非常常见,且有着广泛的应用。以下是对这些服务更详细的解释和接单时的一些建议:服务详解Java代码编写Java以其跨平台性、面向对象和丰富的API而著称,广泛应用于企业级应用、Android应用开发、Web服务端开发等领域。您可以提供
- Android Kotlin MVP 架构项目教程
常樱沙Vigour
AndroidKotlinMVP架构项目教程android-kotlin-mvp-architectureThisrepositorycontainsadetailedsampleappthatimplementsMVParchitectureinKotlinusingDagger2,Room,RxJava2,FastAndroidNetworkingandPlaceholderView项目地址:
- omfun官方版网页版下载-omofun官方版2024安卓IOS下载
omofun5541
omofun动漫omofun动漫ios动画安卓windows
omofun关于“ROOT苹果手机”的说法实际上是一个误解,omofun动漫因为“ROOT”这个术语通常指的是获取Android设备的超级用户权限,omofun漫画而苹果手机(iPhone)使用的是iOS操作系统,获取超级用户权限的过程被称为“越狱”(Jailbreak)。omfun官方版app最新版本版下载:http://om.aunbaidu.com/下面是一篇关于如何越狱苹果手机的文章,介绍
- Spring的注解积累
yijiesuifeng
spring注解
用注解来向Spring容器注册Bean。
需要在applicationContext.xml中注册:
<context:component-scan base-package=”pagkage1[,pagkage2,…,pagkageN]”/>。
如:在base-package指明一个包
<context:component-sc
- 传感器
百合不是茶
android传感器
android传感器的作用主要就是来获取数据,根据得到的数据来触发某种事件
下面就以重力传感器为例;
1,在onCreate中获得传感器服务
private SensorManager sm;// 获得系统的服务
private Sensor sensor;// 创建传感器实例
@Override
protected void
- [光磁与探测]金吕玉衣的意义
comsci
这是一个古代人的秘密:现在告诉大家
信不信由你们:
穿上金律玉衣的人,如果处于灵魂出窍的状态,可以飞到宇宙中去看星星
这就是为什么古代
- 精简的反序打印某个数
沐刃青蛟
打印
以前看到一些让求反序打印某个数的程序。
比如:输入123,输出321。
记得以前是告诉你是几位数的,当时就抓耳挠腮,完全没有思路。
似乎最后是用到%和/方法解决的。
而今突然想到一个简短的方法,就可以实现任意位数的反序打印(但是如果是首位数或者尾位数为0时就没有打印出来了)
代码如下:
long num, num1=0;
- PHP:6种方法获取文件的扩展名
IT独行者
PHP扩展名
PHP:6种方法获取文件的扩展名
1、字符串查找和截取的方法
1
$extension
=
substr
(
strrchr
(
$file
,
'.'
), 1);
2、字符串查找和截取的方法二
1
$extension
=
substr
- 面试111
文强chu
面试
1事务隔离级别有那些 ,事务特性是什么(问到一次)
2 spring aop 如何管理事务的,如何实现的。动态代理如何实现,jdk怎么实现动态代理的,ioc是怎么实现的,spring是单例还是多例,有那些初始化bean的方式,各有什么区别(经常问)
3 struts默认提供了那些拦截器 (一次)
4 过滤器和拦截器的区别 (频率也挺高)
5 final,finally final
- XML的四种解析方式
小桔子
domjdomdom4jsax
在平时工作中,难免会遇到把 XML 作为数据存储格式。面对目前种类繁多的解决方案,哪个最适合我们呢?在这篇文章中,我对这四种主流方案做一个不完全评测,仅仅针对遍历 XML 这块来测试,因为遍历 XML 是工作中使用最多的(至少我认为)。 预 备 测试环境: AMD 毒龙1.4G OC 1.5G、256M DDR333、Windows2000 Server
- wordpress中常见的操作
aichenglong
中文注册wordpress移除菜单
1 wordpress中使用中文名注册解决办法
1)使用插件
2)修改wp源代码
进入到wp-include/formatting.php文件中找到
function sanitize_user( $username, $strict = false
- 小飞飞学管理-1
alafqq
管理
项目管理的下午题,其实就在提出问题(挑刺),分析问题,解决问题。
今天我随意看下10年上半年的第一题。主要就是项目经理的提拨和培养。
结合我自己经历写下心得
对于公司选拔和培养项目经理的制度有什么毛病呢?
1,公司考察,选拔项目经理,只关注技术能力,而很少或没有关注管理方面的经验,能力。
2,公司对项目经理缺乏必要的项目管理知识和技能方面的培训。
3,公司对项目经理的工作缺乏进行指
- IO输入输出部分探讨
百合不是茶
IO
//文件处理 在处理文件输入输出时要引入java.IO这个包;
/*
1,运用File类对文件目录和属性进行操作
2,理解流,理解输入输出流的概念
3,使用字节/符流对文件进行读/写操作
4,了解标准的I/O
5,了解对象序列化
*/
//1,运用File类对文件目录和属性进行操作
//在工程中线创建一个text.txt
- getElementById的用法
bijian1013
element
getElementById是通过Id来设置/返回HTML标签的属性及调用其事件与方法。用这个方法基本上可以控制页面所有标签,条件很简单,就是给每个标签分配一个ID号。
返回具有指定ID属性值的第一个对象的一个引用。
语法:
&n
- 励志经典语录
bijian1013
励志人生
经典语录1:
哈佛有一个著名的理论:人的差别在于业余时间,而一个人的命运决定于晚上8点到10点之间。每晚抽出2个小时的时间用来阅读、进修、思考或参加有意的演讲、讨论,你会发现,你的人生正在发生改变,坚持数年之后,成功会向你招手。不要每天抱着QQ/MSN/游戏/电影/肥皂剧……奋斗到12点都舍不得休息,看就看一些励志的影视或者文章,不要当作消遣;学会思考人生,学会感悟人生
- [MongoDB学习笔记三]MongoDB分片
bit1129
mongodb
MongoDB的副本集(Replica Set)一方面解决了数据的备份和数据的可靠性问题,另一方面也提升了数据的读写性能。MongoDB分片(Sharding)则解决了数据的扩容问题,MongoDB作为云计算时代的分布式数据库,大容量数据存储,高效并发的数据存取,自动容错等是MongoDB的关键指标。
本篇介绍MongoDB的切片(Sharding)
1.何时需要分片
&nbs
- 【Spark八十三】BlockManager在Spark中的使用场景
bit1129
manager
1. Broadcast变量的存储,在HttpBroadcast类中可以知道
2. RDD通过CacheManager存储RDD中的数据,CacheManager也是通过BlockManager进行存储的
3. ShuffleMapTask得到的结果数据,是通过FileShuffleBlockManager进行管理的,而FileShuffleBlockManager最终也是使用BlockMan
- yum方式部署zabbix
ronin47
yum方式部署zabbix
安装网络yum库#rpm -ivh http://repo.zabbix.com/zabbix/2.4/rhel/6/x86_64/zabbix-release-2.4-1.el6.noarch.rpm 通过yum装mysql和zabbix调用的插件还有agent代理#yum install zabbix-server-mysql zabbix-web-mysql mysql-
- Hibernate4和MySQL5.5自动创建表失败问题解决方法
byalias
J2EEHibernate4
今天初学Hibernate4,了解了使用Hibernate的过程。大体分为4个步骤:
①创建hibernate.cfg.xml文件
②创建持久化对象
③创建*.hbm.xml映射文件
④编写hibernate相应代码
在第四步中,进行了单元测试,测试预期结果是hibernate自动帮助在数据库中创建数据表,结果JUnit单元测试没有问题,在控制台打印了创建数据表的SQL语句,但在数据库中
- Netty源码学习-FrameDecoder
bylijinnan
javanetty
Netty 3.x的user guide里FrameDecoder的例子,有几个疑问:
1.文档说:FrameDecoder calls decode method with an internally maintained cumulative buffer whenever new data is received.
为什么每次有新数据到达时,都会调用decode方法?
2.Dec
- SQL行列转换方法
chicony
行列转换
create table tb(终端名称 varchar(10) , CEI分值 varchar(10) , 终端数量 int)
insert into tb values('三星' , '0-5' , 74)
insert into tb values('三星' , '10-15' , 83)
insert into tb values('苹果' , '0-5' , 93)
- 中文编码测试
ctrain
编码
循环打印转换编码
String[] codes = {
"iso-8859-1",
"utf-8",
"gbk",
"unicode"
};
for (int i = 0; i < codes.length; i++) {
for (int j
- hive 客户端查询报堆内存溢出解决方法
daizj
hive堆内存溢出
hive> select * from t_test where ds=20150323 limit 2;
OK
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
问题原因: hive堆内存默认为256M
这个问题的解决方法为:
修改/us
- 人有多大懒,才有多大闲 (评论『卓有成效的程序员』)
dcj3sjt126com
程序员
卓有成效的程序员给我的震撼很大,程序员作为特殊的群体,有的人可以这么懒, 懒到事情都交给机器去做 ,而有的人又可以那么勤奋,每天都孜孜不倦得做着重复单调的工作。
在看这本书之前,我属于勤奋的人,而看完这本书以后,我要努力变成懒惰的人。
不要在去庞大的开始菜单里面一项一项搜索自己的应用程序,也不要在自己的桌面上放置眼花缭乱的快捷图标
- Eclipse简单有用的配置
dcj3sjt126com
eclipse
1、显示行号 Window -- Prefences -- General -- Editors -- Text Editors -- show line numbers
2、代码提示字符 Window ->Perferences,并依次展开 Java -> Editor -> Content Assist,最下面一栏 auto-Activation
- 在tomcat上面安装solr4.8.0全过程
eksliang
Solrsolr4.0后的版本安装solr4.8.0安装
转载请出自出处:
http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2096478
首先solr是一个基于java的web的应用,所以安装solr之前必须先安装JDK和tomcat,我这里就先省略安装tomcat和jdk了
第一步:当然是下载去官网上下载最新的solr版本,下载地址
- Android APP通用型拒绝服务、漏洞分析报告
gg163
漏洞androidAPP分析
点评:记得曾经有段时间很多SRC平台被刷了大量APP本地拒绝服务漏洞,移动安全团队爱内测(ineice.com)发现了一个安卓客户端的通用型拒绝服务漏洞,来看看他们的详细分析吧。
0xr0ot和Xbalien交流所有可能导致应用拒绝服务的异常类型时,发现了一处通用的本地拒绝服务漏洞。该通用型本地拒绝服务可以造成大面积的app拒绝服务。
针对序列化对象而出现的拒绝服务主要
- HoverTree项目已经实现分层
hvt
编程.netWebC#ASP.ENT
HoverTree项目已经初步实现分层,源代码已经上传到 http://hovertree.codeplex.com请到SOURCE CODE查看。在本地用SQL Server 2008 数据库测试成功。数据库和表请参考:http://keleyi.com/a/bjae/ue6stb42.htmHoverTree是一个ASP.NET 开源项目,希望对你学习ASP.NET或者C#语言有帮助,如果你对
- Google Maps API v3: Remove Markers 移除标记
天梯梦
google maps api
Simply do the following:
I. Declare a global variable:
var markersArray = [];
II. Define a function:
function clearOverlays() {
for (var i = 0; i < markersArray.length; i++ )
- jQuery选择器总结
lq38366
jquery选择器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
- 基础数据结构和算法六:Quick sort
sunwinner
AlgorithmQuicksort
Quick sort is probably used more widely than any other. It is popular because it is not difficult to implement, works well for a variety of different kinds of input data, and is substantially faster t
- 如何让Flash不遮挡HTML div元素的技巧_HTML/Xhtml_网页制作
刘星宇
htmlWeb
今天在写一个flash广告代码的时候,因为flash自带的链接,容易被当成弹出广告,所以做了一个div层放到flash上面,这样链接都是a触发的不会被拦截,但发现flash一直处于div层上面,原来flash需要加个参数才可以。
让flash置于DIV层之下的方法,让flash不挡住飘浮层或下拉菜单,让Flash不档住浮动对象或层的关键参数:wmode=opaque。
方法如下:
- Mybatis实用Mapper SQL汇总示例
wdmcygah
sqlmysqlmybatis实用
Mybatis作为一个非常好用的持久层框架,相关资料真的是少得可怜,所幸的是官方文档还算详细。本博文主要列举一些个人感觉比较常用的场景及相应的Mapper SQL写法,希望能够对大家有所帮助。
不少持久层框架对动态SQL的支持不足,在SQL需要动态拼接时非常苦恼,而Mybatis很好地解决了这个问题,算是框架的一大亮点。对于常见的场景,例如:批量插入/更新/删除,模糊查询,多条件查询,联表查询,