另:Java多线程(6)之Deque与LinkedBlockingDeque深入分析(转)
ArrayDeque类实现Queue,Deque接口。
对于数组实现的Deque来说,数据结构上比较简单,只需要一个存储数据的数组以及头尾两个索引即可。由于数组是固定长度的,所以很容易就得到数组的头和尾,那么对于数组的操作只需要移动头和尾的索引即可。
特别说明的是ArrayDeque并不是一个固定大小的队列,每次队列满了以后就将队列容量扩大一倍(doubleCapacity()),因此加入一个元素总是能成功,而且也不会抛出一个异常。也就是说ArrayDeque是一个没有容量限制的队列。
同样继续性能的考虑,使用System.arraycopy复制一个数组比循环设置要高效得多。
ArrayDeque不是线程安全的。
ArrayDeque不可以存取null元素,因为系统根据某个位置是否为null来判断元素的存在。
当作为栈使用时,性能比Stack好;
当作为队列使用时,性能比LinkedList好。
因为栈Stack继承了Vector,是线程安全的
总结:
1、队列满了后自动扩容,因此新增总会成功
2、head 为第一个元素的索引
tail 为下个要添加元素的位置,为末尾元素的索引 + 1
因此,首元素为element[head],未元素为element[tail-1]
3、
头部添加元素e时:
head = (head - 1)
elements[head】 = e
尾部添加元素e时:
是将e 赋值给elements[tail] 即elements[tail] = e;
tail = (tail + 1) ,指向下个要添加元素的位置
添加完之后都需要判断是否需要扩容。
头部删除元素时:
elements[head] = null;
head = (head + 1)
尾部删除元素时:
int t = (tail - 1) // 处理临界情况(当tail为0时),与后的结果为elements.length - 1。
elements[t] = null;
tail = t
看了ArrayDeque类的源码。有以下几点总结:
1)ArrayDeque有两个类属性,head和tail,两个指针。
2)ArrayDeque通过一个数组作为载体,其中的数组元素在add等方法执行时不移动,发生变化的只是head和tail指针,而且指针是循环变化,数组容量不限制。
3)offer方法和add方法都是通过其中的addLast方法实现,每添加一个元素,就把元素加到数组的尾部,此时,head指针没有变化,而tail指针加一,因为指针是循环加的,所以当tail追上head((this.tail = this.tail + 1 & this.elements.length - 1) == this.head)时,数组容量翻一倍,继续执行。
4)remove方法和poll方法都是通过其中的pollFirst方法实现,每移除一个元素,该元素所在位置变成null,此时,tail指针没有变化,而head指针加一,当数组中没有数据时,返回null。
5)因为ArrayDeque不是线程安全的,所以,用作堆栈时快于 Stack,在用作队列时快于 LinkedList。
1. 两个重要的索引:head和tail
- // 第一个元素的索引
- private transient int head;
- // 下个要添加元素的位置,为末尾元素的索引 + 1
- private transient int tail;
2. 构造方法
- public ArrayDeque() {
- elements = (E[]) new Object[16]; // 默认的数组长度大小
- }
- public ArrayDeque(int numElements) {
- allocateElements(numElements); // 需要的数组长度大小
- }
- public ArrayDeque(Collection<? extends E> c) {
- allocateElements(c.size()); // 根据集合来分配数组大小
- addAll(c); // 把集合中元素放到数组中
- }
3. 分配合适大小的数组
- private void allocateElements(int numElements) {
- int initialCapacity = MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
- // 找到大于需要长度的最小的2的幂整数。
- // Tests "<=" because arrays aren't kept full.
- if (numElements >= initialCapacity) {
- initialCapacity = numElements;
- initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 1);
- initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 2);
- initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 4);
- initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 8);
- initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 16);
- initialCapacity++;
- if (initialCapacity < 0) // Too many elements, must back off
- initialCapacity >>>= 1;// Good luck allocating 2 ^ 30 elements
- }
- elements = (E[]) new Object[initialCapacity];
- }
4. 扩容
- // 扩容为原来的2倍。
- private void doubleCapacity() {
- assert head == tail;
- int p = head;
- int n = elements.length;
- int r = n - p; // number of elements to the right of p
- int newCapacity = n << 1;
- if (newCapacity < 0)
- throw new IllegalStateException("Sorry, deque too big");
- Object[] a = new Object[newCapacity];
- // 既然是head和tail已经重合了,说明tail是在head的左边。
- System.arraycopy(elements, p, a, 0, r); // 拷贝原数组从head位置到结束的数据
- System.arraycopy(elements, 0, a, r, p); // 拷贝原数组从开始到head的数据
- elements = (E[])a;
- head = 0; // 重置head和tail为数据的开始和结束索引
- tail = n;
- }
- // 拷贝该数组的所有元素到目标数组
- private <T> T[] copyElements(T[] a) {
- if (head < tail) { // 开始索引大于结束索引,一次拷贝
- System.arraycopy(elements, head, a, 0, size());
- } else if (head > tail) { // 开始索引在结束索引的右边,分两段拷贝
- int headPortionLen = elements.length - head;
- System.arraycopy(elements, head, a, 0, headPortionLen);
- System.arraycopy(elements, 0, a, headPortionLen, tail);
- }
- return a;
- }
5. 添加元素
- public void addFirst(E e) {
- if (e == null)
- throw new NullPointerException();
- // 本来可以简单地写成head-1,但如果head为0,减1就变为-1了,和elements.length - 1进行与操作就是为了处理这种情况,这时结果为elements.length - 1。
- elements[head = (head - 1) & (elements.length - 1)] = e;
- if (head == tail) // head和tail不可以重叠
- doubleCapacity();
- }
- public void addLast(E e) {
- if (e == null)
- throw new NullPointerException();
- // tail位置是空的,把元素放到这。
- elements[tail] = e;
- // 和head的操作类似,为了处理临界情况 (tail为length - 1时),和length - 1进行与操作,结果为0。
- if ( (tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)) == head)
- doubleCapacity();
- }
- public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
- addFirst(e);
- return true;
- }
- public boolean offerLast(E e) {
- addLast(e);
- return true;
- }
6. 删除元素
删除首尾元素:
- public E removeFirst() {
- E x = pollFirst();
- if (x == null)
- throw new NoSuchElementException();
- return x;
- }
- public E removeLast() {
- E x = pollLast();
- if (x == null)
- throw new NoSuchElementException();
- return x;
- }
- public E pollFirst() {
- int h = head;
- E result = elements[h]; // Element is null if deque empty
- if (result == null)
- return null;
- // 表明head位置已为空
- elements[h] = null; // Must null out slot
- head = (h + 1) & (elements.length - 1); // 处理临界情况(当h为elements.length - 1时),与后的结果为0。
- return result;
- }
- public E pollLast() {
- int t = (tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1); // 处理临界情况(当tail为0时),与后的结果为elements.length - 1。
- E result = elements[t];
- if (result == null)
- return null;
- elements[t] = null;
- tail = t; // tail指向的是下个要添加元素的索引。
- return result;
- }
删除指定元素:
- public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
- if (o == null)
- return false;
- int mask = elements.length - 1;
- int i = head;
- E x;
- while ( (x = elements[i]) != null) {
- if (o.equals(x)) {
- delete(i);
- return true;
- }
- i = (i + 1) & mask; // 从头到尾遍历
- }
- return false;
- }
- public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
- if (o == null)
- return false;
- int mask = elements.length - 1;
- int i = (tail - 1) & mask; // 末尾元素的索引
- E x;
- while ( (x = elements[i]) != null) {
- if (o.equals(x)) {
- delete(i);
- return true;
- }
- i = (i - 1) & mask; // 从尾到头遍历
- }
- return false;
- }
- private void checkInvariants() { // 有效性检查
- assert elements[tail] == null; // tail位置没有元素
- assert head == tail ? elements[head] == null :
- (elements[head] != null &&
- elements[(tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1)] != null); // 如果head和tail重叠,队列为空;否则head位置有元素,tail-1位置有元素。
- assert elements[(head - 1) & (elements.length - 1)] == null; // head-1的位置没有元素。
- }
- private boolean delete(int i) {
- checkInvariants();
- final E[] elements = this.elements;
- final int mask = elements.length - 1;
- final int h = head;
- final int t = tail;
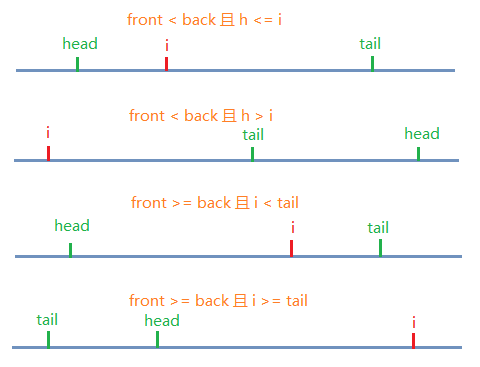
- final int front = (i - h) & mask; // i前面的元素个数
- final int back = (t - i) & mask; // i后面的元素个数
- // Invariant: head <= i < tail mod circularity
- if (front >= ((t - h) & mask)) // i不在head和tail之间
- throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
- // Optimize for least element motion
- if (front < back) { // i的位置靠近head,移动开始的元素,返回false。
- if (h <= i) {
- System.arraycopy(elements, h, elements, h + 1, front);
- } else { // Wrap around
- System.arraycopy(elements, 0, elements, 1, i);
- elements[0] = elements[mask]; // 处理边缘元素
- System.arraycopy(elements, h, elements, h + 1, mask - h);
- }
- elements[h] = null;
- head = (h + 1) & mask; // head位置后移
- return false;
- } else { // i的位置靠近tail,移动末尾的元素,返回true。
- if (i < t) { // Copy the null tail as well
- System.arraycopy(elements, i + 1, elements, i, back);
- tail = t - 1;
- } else { // Wrap around
- System.arraycopy(elements, i + 1, elements, i, mask - i);
- elements[mask] = elements[0];
- System.arraycopy(elements, 1, elements, 0, t);
- tail = (t - 1) & mask;
- }
- return true;
- }
- }
- public E getFirst() {
- E x = elements[head];
- if (x == null)
- throw new NoSuchElementException();
- return x;
- }
- public E getLast() {
- E x = elements[(tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1)]; // 处理临界情况(当tail为0时),与后的结果为elements.length - 1。
- if (x == null)
- throw new NoSuchElementException();
- return x;
- }
- public E peekFirst() {
- return elements[head]; // elements[head] is null if deque empty
- }
- public E peekLast() {
- return elements[(tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1)];
- }
8. 队列操作
- public boolean add(E e) {
- addLast(e);
- return true;
- }
- public boolean offer(E e) {
- return offerLast(e);
- }
- public E remove() {
- return removeFirst();
- }
- public E poll() {
- return pollFirst();
- }
- public E element() {
- return getFirst();
- }
- public E peek() {
- return peekFirst();
- }
9. 栈操作
- public void push(E e) {
- addFirst(e);
- }
- public E pop() {
- return removeFirst();
- }
10. 集合方法
- public int size() {
- return (tail - head) & (elements.length - 1); // 和elements.length - 1进行与操作是为了处理当tail < head时的情况。
- }
- public boolean isEmpty() {
- return head == tail; // tail位置的元素一定为空,head和tail相等,也为空。
- }
- // 向前迭代器
- public Iterator<E> iterator() {
- return new DeqIterator();
- }
- // 向后迭代器
- public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {
- return new DescendingIterator();
- }
- private class DeqIterator implements Iterator<E> {
- private int cursor = head;
- private int fence = tail; // 迭代终止索引,同时也为了检测并发修改。
- private int lastRet = -1; // 最近的next()调用返回的索引。据此可以定位到需要删除元素的位置。
- public boolean hasNext() {
- return cursor != fence;
- }
- public E next() {
- if (cursor == fence)
- throw new NoSuchElementException();
- E result = elements[cursor];
- // This check doesn't catch all possible comodifications,
- // but does catch the ones that corrupt traversal
- if (tail != fence || result == null)
- throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
- lastRet = cursor;
- cursor = (cursor + 1) & (elements.length - 1); // 游标位置加1
- return result;
- }
- public void remove() {
- if (lastRet < 0)
- throw new IllegalStateException();
- if (delete(lastRet)) { // 如果将元素从右往左移,需要将游标减1。
- cursor = (cursor - 1) & (elements.length - 1); // 游标位置回退1。
- fence = tail; // 重置阀值。
- }
- lastRet = -1;
- }
- }
- private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator<E> {
- private int cursor = tail; // 游标开始索引为tail
- private int fence = head; // 游标的阀值为head
- private int lastRet = -1;
- public boolean hasNext() {
- return cursor != fence;
- }
- public E next() {
- if (cursor == fence)
- throw new NoSuchElementException();
- cursor = (cursor - 1) & (elements.length - 1); // tail是下个添加元素的位置,所以要减1才是尾节点的索引。
- E result = elements[cursor];
- if (head != fence || result == null)
- throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
- lastRet = cursor;
- return result;
- }
- public void remove() {
- if (lastRet < 0)
- throw new IllegalStateException();
- if (!delete(lastRet)) { // 如果从左往右移,需要将游标加1。
- cursor = (cursor + 1) & (elements.length - 1);
- fence = head;
- }
- lastRet = -1;
- }
- }
- public boolean contains(Object o) {
- if (o == null)
- return false; // ArrayDeque不可以存储null元素
- int mask = elements.length - 1;
- int i = head;
- E x;
- while ( (x = elements[i]) != null) {
- if (o.equals(x))
- return true;
- i = (i + 1) & mask; // 处理临界情况
- }
- return false;
- }
- public boolean remove(Object o) {
- return removeFirstOccurrence(o);
- }
- public void clear() {
- int h = head;
- int t = tail;
- if (h != t) { // clear all cells
- head = tail = 0; // 重置首尾索引
- int i = h;
- int mask = elements.length - 1;
- do {
- elements[i] = null; // 清除元素
- i = (i + 1) & mask;
- } while (i != t);
- }
- }
- public Object[] toArray() {
- return copyElements(new Object[size()]); // 把所有元素拷贝到新创建的Object数组上,所以对返回数组的修改不会影响该双端队列。
- }
- public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
- int size = size();
- if (a.length < size) // 目标数组大小不够
- a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(
- a.getClass().getComponentType(), size); // 利用反射创建类型为T,大小为size的数组。
- yElements(a); // 拷贝所有元素到目标数组。
- if (a.length > size)
- a[size] = null; // 结束标识
- return a;
- }
11. Object方法
- public ArrayDeque<E> clone() {
- try {
- ArrayDeque<E> result = (ArrayDeque<E>) super.clone();
- result.elements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, elements.length); // 深度复制。
- return result;
- } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
- throw new AssertionError();
- }
- }
来源:http://czj4451.iteye.com/blog/1688693