通过Location获取Address的使用
我们获取Location的目的之一肯定是有获取这个位置的详细地址,而我们有了Location在来获取Address就相对简单多了,因为GoogleApi已经封装好了方法,我们只需呀通过Location获取GeoPoint,然后在通过GeoPoint来获取我们想要的Address.下面是我做的一个简单的Demo.
第一步新建一个Android工程LocationDemo,注意这里选用的是(Google APIs),下面是文件目录结构:
第二步: 修改main.xml(相比第十四节增加了一个address的TextView),代码如下:
第三步:修改LocationDemo.java(增加了两个方法)代码如下:
第四步:最重要一步在AndroidManiefest.xml中导入Google Api(第14行代码)库,代码如下:
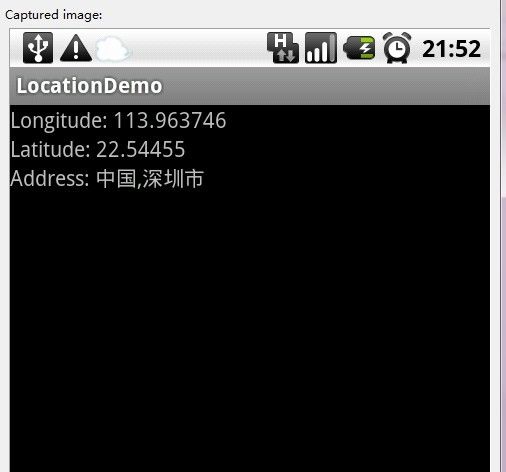
第五步:运行上述工程,效果如下图如示:
本文转自 http://blog.csdn.net/Android_Tutor/archive/2010/06/24/5692517.aspx
第一步新建一个Android工程LocationDemo,注意这里选用的是(Google APIs),下面是文件目录结构:

第二步: 修改main.xml(相比第十四节增加了一个address的TextView),代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/longitude"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="longitude:"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/latitude"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="latitude:"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/address"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</LinearLayout>
第三步:修改LocationDemo.java(增加了两个方法)代码如下:
package com.android.tutor;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Locale;
import com.google.android.maps.GeoPoint;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.location.Address;
import android.location.Geocoder;
import android.location.Location;
import android.location.LocationManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class LocationDemo extends Activity {
private TextView longitude;
private TextView latitude;
private TextView address;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
longitude = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.longitude);
latitude = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.latitude);
address = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.address);
Location mLocation = getLocation(this);
GeoPoint gp = getGeoByLocation(mLocation);
Address mAddress = getAddressbyGeoPoint(this, gp);
longitude.setText("Longitude: " + mLocation.getLongitude());
latitude.setText("Latitude: " + mLocation.getLatitude());
address.setText("Address: " + mAddress.getCountryName()+"," + mAddress.getLocality());
}
//Get the Location by GPS or WIFI
public Location getLocation(Context context) {
LocationManager locMan = (LocationManager) context
.getSystemService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE);
Location location = locMan
.getLastKnownLocation(LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER);
if (location == null) {
location = locMan
.getLastKnownLocation(LocationManager.NETWORK_PROVIDER);
}
return location;
}
//通过Location获取GeoPoint
public GeoPoint getGeoByLocation(Location location) {
GeoPoint gp = null;
try {
if (location != null) {
double geoLatitude = location.getLatitude() * 1E6;
double geoLongitude = location.getLongitude() * 1E6;
gp = new GeoPoint((int) geoLatitude, (int) geoLongitude);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return gp;
}
//通过GeoPoint来获取Address
public Address getAddressbyGeoPoint(Context cntext, GeoPoint gp) {
Address result = null;
try {
if (gp != null) {
Geocoder gc = new Geocoder(cntext, Locale.CHINA);
double geoLatitude = (int) gp.getLatitudeE6() / 1E6;
double geoLongitude = (int) gp.getLongitudeE6() / 1E6;
List<Address> lstAddress = gc.getFromLocation(geoLatitude,
geoLongitude, 1);
if (lstAddress.size() > 0) {
result = lstAddress.get(0);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
}
第四步:最重要一步在AndroidManiefest.xml中导入Google Api(第14行代码)库,代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.android.tutor"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name=".LocationDemo"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<uses-library android:name="com.google.android.maps" />
</application>
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="7" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION"/>
</manifest>
第五步:运行上述工程,效果如下图如示:

本文转自 http://blog.csdn.net/Android_Tutor/archive/2010/06/24/5692517.aspx