之前我们讲解了如何让启动mule工程,单是那种启动方式,不利于跟踪日志、调试程序,下面讲一下如果用代码启动程序,先看一下效果:
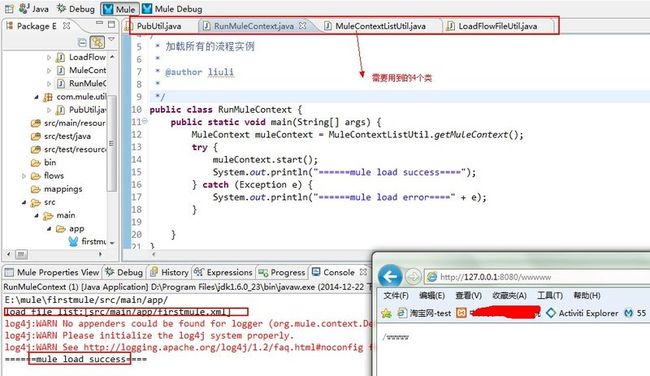
这种启动方式可以很方便的产看日志,调成程序,要实现这种启动方式,你需要了解2个对象:
DefaultMuleContextFactory 和 SpringXmlConfigurationBuilder
具体代码如下:
import org.mule.api.MuleContext;
/**
* 加载所有的流程实例
*
* @author liuli
*
*/
public class RunMuleContext {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MuleContext muleContext = MuleContextListUtil.getMuleContext();
try {
muleContext.start();
System.out.println("======mule load success====");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("======mule load error====" + e);
}
}
}
单例模式加载类:
import org.mule.api.MuleContext;
import org.mule.config.spring.SpringXmlConfigurationBuilder;
import org.mule.context.DefaultMuleContextFactory;
/**
* 单例模式 用于加载mule配置文件
* @author liuli
*
*/
public final class MuleContextListUtil {
private static MuleContext muleContextList = null;
private static String[] confing =LoadFlowFileUtil.arrayFile();
private MuleContextListUtil() {
}
static {
try {
DefaultMuleContextFactory muleContextFactory = new DefaultMuleContextFactory();
SpringXmlConfigurationBuilder configBuilder = new SpringXmlConfigurationBuilder(confing);
muleContextList = muleContextFactory.createMuleContext(configBuilder);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
public static MuleContext getMuleContext() {
return muleContextList;
}
}
获取配置文件辅助类:
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import com.mule.util.PubUtil;
/**
* mule 自动获取要加载的文件
* @author liuli
*
*/
public class LoadFlowFileUtil {
/**
* 获取要加载的文件列表
*
* @return
*/
public static ArrayList<String> getFileArray() {
ArrayList<String> fileArray = new ArrayList<String>();;// 存放最终的文件集合
String path = "src/main/app/";// 文件前缀
String filePath = PubUtil.getRealPath() + "/" + path;
System.out.println(filePath);
File rootFile = new File(filePath.replace("/", "\\"));
File[] fs = rootFile.listFiles();
//System.out.println(rootFile);
int i = 0;
if (fs != null) {
for (File f : fs) {
if (f.getName().endsWith(".xml")) {//只加载xml文件
fileArray.add(path+f.getName());
}
i++;
}
} else {
System.out.println("no file load");
}
return fileArray;
}
/**
* 获取要加载的文件
* @return
*/
public static String[] arrayFile(){
ArrayList<String> fileArray = getFileArray();
String[] arrayFile =new String[fileArray.size()];
fileArray.toArray(arrayFile);
System.out.println("load file list:"+fileArray);
return arrayFile;
}
}
获取配置文件辅助类:
package com.mule.util;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.security.CodeSource;
import java.security.ProtectionDomain;
/**
* 系统公共方法
* @author liuli
*
*/
public class PubUtil {
/**
* 获取classes文件路径
* @return
*/
public static String getClassesPath() {
try {
return getFullPathRelateClass("../../..", PubUtil.class);
} catch (IOException ex) {
return "Error!getFilePath Fail!";
}
}
/**
* 获取工程的绝对路径
* @return
*/
public static String getRealPath() {
try {
return getFullPathRelateClass("../../../../..", PubUtil.class);
} catch (IOException ex) {
return "Error!getFilePath Fail!";
}
}
/**
* 这个方法可以通过与某个类的class文件的相对路径来获取文件或目录的绝对路径。 通常在程序中很难定位某个相对路径,特别是在B/S应用中。
* 通过这个方法,我们可以根据我们程序自身的类文件的位置来定位某个相对路径。
* 比如:某个txt文件相对于程序的Test类文件的路径是../../resource/test.txt,
* 那么使用本方法Path.getFullPathRelateClass("../../resource/test.txt",Test.class)
* 得到的结果是txt文件的在系统中的绝对路径。
*
* @param relatedPath
* 相对路径
* @param cls
* 用来定位的类
* @return 相对路径所对应的绝对路径
* @throws IOException
* 因为本方法将查询文件系统,所以可能抛出IO异常
*/
public static String getFullPathRelateClass(String relatedPath, Class cls)
throws IOException {
String path = null;
if (relatedPath == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
String clsPath = getPathFromClass(cls);
File clsFile = new File(clsPath);
String tempPath = clsFile.getParent() + File.separator + relatedPath;
File file = new File(tempPath);
path = file.getCanonicalPath();
return path;
}
/**
* 获取一个类的class文件所在的绝对路径。 这个类可以是JDK自身的类,也可以是用户自定义的类,或者是第三方开发包里的类。
* 只要是在本程序中可以被加载的类,都可以定位到它的class文件的绝对路径。
*
* @param cls
* 一个对象的Class属性
* @return 这个类的class文件位置的绝对路径。 如果没有这个类的定义,则返回null。
*/
public static String getPathFromClass(Class cls) throws IOException {
String path = null;
if (cls == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
URL url = getClassLocationURL(cls);
if (url != null) {
path = url.getPath();
if ("jar".equalsIgnoreCase(url.getProtocol())) {
try {
path = new URL(path).getPath();
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
}
int location = path.indexOf("!/");
if (location != -1) {
path = path.substring(0, location);
}
}
File file = new File(path);
path = file.getCanonicalPath();
}
return path;
}
/**
* 获取类的class文件位置的URL。这个方法是本类最基础的方法,供其它方法调用。
*/
private static URL getClassLocationURL(final Class cls) {
if (cls == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("null input: cls");
URL result = null;
final String clsAsResource = cls.getName().replace('.', '/').concat(".class");
final ProtectionDomain pd = cls.getProtectionDomain();
if (pd != null) {
final CodeSource cs = pd.getCodeSource();
if (cs != null)
result = cs.getLocation();
if (result != null) {
if ("file".equals(result.getProtocol())) {
try {
if (result.toExternalForm().endsWith(".jar")|| result.toExternalForm().endsWith(".zip"))
result = new URL("jar:".concat(result.toExternalForm()).concat("!/").concat(clsAsResource));
else if (new File(result.getFile()).isDirectory())
result = new URL(result, clsAsResource);
} catch (MalformedURLException ignore) {
}
}
}
}
if (result == null) {
final ClassLoader clsLoader = cls.getClassLoader();
result = clsLoader != null ? clsLoader.getResource(clsAsResource): ClassLoader.getSystemResource(clsAsResource);
}
return result;
}
}
有了这写以后调试程序就非常方便了。接下来要告诉你如何调试......