Source from: Finagle: A Protocol-Agnostic RPC System
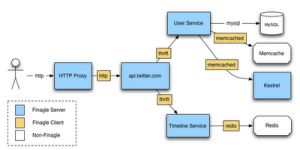
Rendering even the simplest web page on twitter.com requires the collaboration of dozens of network services speaking many different protocols. For example, in order to render the home page, the application issues requests to the Social Graph Service, Memcached, databases, and many other network services. Each of these speaks a different protocol: Thrift, Memcached, MySQL, and so on. Additionally, many of these services speak to other services — they are both servers and clients. The Social Graph Service, for instance, provides a Thrift interface but consumes from a cluster of MySQL databases.
In such systems, a frequent cause of outages is poor interaction between components in the presence of failures; common failures include crashed hosts and extreme latency variance. These failures can cascade through the system by causing work queues to back up, TCP connections to churn, or memory and file descriptors to become exhausted. In the worst case, the user sees a Fail Whale.
CHALLENGES OF BUILDING A STABLE DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM
Sophisticated network servers and clients have many moving parts: failure detectors, load-balancers, failover strategies, and so on. These parts need to work together in a delicate balance to be resilient to the varieties of failure that occur in a large production system.
This is made especially difficult by the many different implementations of failure detectors, load-balancers, and so on, per protocol. For example, the implementation of the back-pressure strategies for Thrift differ from those for HTTP. Ensuring that heterogeneous systems converge to a stable state during an incident is extremely challenging.
OUR APPROACH
We set out to develop a single implementation of the basic components of network servers and clients that could be used for all of our protocols. Finagle is a protocol-agnostic, asynchronous Remote Procedure Call (RPC) system for the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) that makes it easy to build robust clients and servers in Java, Scala, or any JVM-hosted language. Finagle supports a wide variety of request/response- oriented RPC protocols and many classes of streaming protocols.
Finagle provides a robust implementation of:
Additionally, Finagle makes it easier to build and deploy a service that
We believe our work has paid off — we can now write and deploy a network service with much greater ease and safety.
FINAGLE AT TWITTER
Today, Finagle is deployed in production at Twitter in several front- and back-end serving systems, including our URL crawler and HTTP Proxy. We plan to continue deploying Finagle more widely.
HOW FINAGLE WORKS
Finagle is flexible and easy to use because it is designed around a few simple, composable primitives: Futures, Services, and Filters.
Future objects
In Finagle, Future objects are the unifying abstraction for all asynchronous computation. A Future represents a computation that may not yet have completed and that can either succeed or fail. The two most basic ways to use a Future are to:
Composing Futures
Futures can be combined and transformed in interesting ways, leading to the kind of compositional behavior commonly seen in functional programming languages. For instance, you can convert a Future[String] to a Future[Int] by using map:
Similarly, you can use flatMap to easily pipeline a sequence of Futures:
In this example, User.authenticate() is performed asynchronously;Tweet.findAllByUser() is invoked on its eventual result. This is alternatively expressed in Scala, using the for statement:
Handling errors and exceptions is very easy when Futures are pipelined using flatMapor the for statement. In the above example, if User.authenticate()asynchronously raises an exception, the subsequent call to Tweet.findAllByUser()never happens. Instead, the result of the pipelined expression is still of the typeFuture[Seq[Tweet]], but it contains the exceptional value rather than tweets. You can respond to the exception using the onFailure callback or other compositional techniques.
A nice property of Futures, as compared to other asynchronous programming techniques (such as the continuation passing style), is that you an easily write clear and robust asynchronous code, even with more sophisticated operations such as scatter/gather:
Service objects
A Service is a function that receives a request and returns a Future object as a response. Note that both clients and servers are represented as Service objects.
To create a Server, you extend the abstract Service class and listen on a port. Here is a simple HTTP server listening on port 10000:
Building an HTTP client is even easier:
Filter objects
Filters are a useful way to isolate distinct phases of your application into a pipeline. For example, you may need to handle exceptions, authorization, and so forth before your Service responds to a request.
A Filter wraps a Service and, potentially, converts the input and output types of the Service to other types. In other words, a Filter is a Service transformer. Here is a filter that ensures an HTTP request has valid OAuth credentials that uses an asynchronous authenticator service:
A Filter then decorates a Service, as in this example:
Finagle is an open source project, available under the Apache License, Version 2.0. Source code and documentation are available on GitHub.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Finagle was originally conceived by Marius Eriksen and Nick Kallen. Other key contributors are Arya Asemanfar, David Helder, Evan Meagher, Gary McCue, Glen Sanford, Grant Monroe, Ian Ownbey, Jake Donham, James Waldrop, Jeremy Cloud, Johan Oskarsson, Justin Zhu, Raghavendra Prabhu, Robey Pointer, Ryan King, Sam Whitlock, Steve Jenson, Wanli Yang, Wilhelm Bierbaum, William Morgan, Abhi Khune, and Srini Rajagopal.