X.509Token
BinarySecurityToken
在WS-Security规范出现之前,针对Web Service或者其他的分布式技术并不是没有安全协议来保证它们的安全。只是这些协议一旦跨越了企业边界往往会受到防火墙的影响,而不再起作用。在WS-Security中,并没有抛弃这些现有的协议,而是将这些Binary的Security Token通过Encoding的方式集成到XML元素中,从而在Web Service中仍然能使用这些经典的安全协议,并利用SOAP消息穿越防火墙的特性,使它们适用于新的环境。这类Security Token在WS-Security中被称为BinarySecurityToken,目前仅支持X509v3 Certificate和Kerberos两种,但是利用XML的高度扩展性,用户可以定义自己的BinarySecurityToken。
下面是BinarySecurityToken的标准格式:
<wsse:BinarySecurityToken wsu:Id=...
EncodingType=...
ValueType=...>
...Binary Data ...
<wsse:BinarySecurityToken/>
其中EncodingType属性指定将Binary数据Encoding到XML中的方法(常用Base64); ValueType属性指定BinarySecurityToken的类型(比如X509v3); 元素内容则是经过Encoding的BinaryToken的内容。
X.509Token
使用X.509 Token来保证消息安全在介绍UsernameToken的文章最后已经提到。如果把UsernameToken从那个例子中去除,就变成了WSE中已经实现了的AnonymousForCertificate。
下图就是AnonymousForCertificate对SOAP Envelop的扩展结构。
可以看出它和UsernameForCertificate非常相似,仅仅缺少了被加密的UsernameToken元素. 这点也正如它的名字所描述的一致,即使用这种方式的用户对于Service来说是匿名的,也就没有用户鉴别的概念. 这恰好适用于那些仅仅需要保证消息安全而不需要验证用户身份的应用. 在介绍UsernameForCertificate的时候,并没有详细说明对X509Certificate Token的引用, 这里做一些补充. 先来回顾一下之前在是如何引用X509Certificate Token. 从示意图上我们也可以看出X509Certificate Token并没有象UsernameToken那样被包含在Request Security Head中, 为什么? 原因很简单, 因为这里的X509证书并不是Client自己的证书,而是Service的证书(根据对称密钥的原理,加密需要使用消息接受方的公钥). 以下是采用KeyIdentifier来引用Service的证书的方式.
<xenc:EncryptedKey wsu:id="userSysmetricKey">
…
<ds:KeyInfo>
<wsse:SecurityTokenReference>
<wsse:KeyIdentifier
ValueType="...oasis-wss-soap-message-security-1.1#ThumbPrintSHA1">
LKiQ/CmFrJDJqCLFcjlhIsmZ/+0=
</wsse:KeyIdentifier>
</wsse:SecurityTokenReference>
</ds:KeyInfo>
…
</xenc:EncryptedKey>
对于这种使用消息接受方X509证书加密的应用场景, 在WS-Security1.1规范中还定义了另一种引用证书的方法---X509IssuerSerial.
<xenc:EncryptedKey wsu:id="userSysmetricKey">
…
<ds:KeyInfo>
<wsse:SecurityTokenReference>
<ds:X509Data>
<ds:X509IssuerSerial>
<ds:X509IssuerName>
DC=ACMECorp, DC=com
</ds:X509IssuerName>
<ds:X509SerialNumber>12345678</ds:X509SerialNumber>
</ds:X509IssuerSerial>
</ds:X509Data>
</wsse:SecurityTokenReference>
</ds:KeyInfo>
….
</xenc:EncryptedKey>
使用AnonymousForCertificate的方法最大的缺陷就是无法实现用户的身份鉴别, 然而在大多数的应用中这个功能是不可豁缺的. 使用UsernameForCertificate可以达到鉴别用户身份的目的, 不过它一般用于保证个人用户和企业之间的安全. 而企业与企业之间常采用X509证书来达到互相的信任.一方面因为使用X509证书的安全性要高于Username&Password, 另一方面从现实的角度你不可能为每个企业分配一个用户名密码. 于是就会在SOAP Head中出现两个X509证书, 从而实现相互认证. 这也是WSE中MutualCertificate所要实现的功能.
在采用两个X509证书来实现相互认证中, 比AnonymousForCertificate方式多出了用户的X509证书. 而加入它的原因就是要利用用户的私钥来签名消息, 从而让Service通过证书来鉴别用户的身份.下图就是MutualCertificate11对SOAP Envelop的扩展结构。

从中可以看出变化比较小,仅仅多出了一个用户X509 Certificate,并用它对原来的ds:Signature元素做了一次签名. 对应这副图的Soap Envelop如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope"
xmlns:ds="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#"
xmlns:xenc="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc"
xmlns:wsu="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2002/07/utility">
<SOAP-ENV:Header>
<wsse:Security
xmlns:wsse="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2002/secext">
<wsse:BinarySecurityToken
wsu:Id="userX509Cert"
ValueType="…#X509v3"
EncodingType="…#Base64Binary">
MIIEZzCCA9CgAwIBAgIQEmtJZc0…
</wsse:BinarySecurityToken>
<xenc:EncryptedKey wsu:id="userSysmetricKey">
<xenc:EncryptionMethod
Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#rsa-1_5"/>
<ds:KeyInfo>
<wsse:SecurityTokenReference>
<wsse:KeyIdentifier
ValueType="...oasis-wss-soap-message-security-1.1#ThumbPrintSHA1">
LKiQ/CmFrJDJqCLFcjlhIsmZ/+0=
</wsse:KeyIdentifier>
</wsse:SecurityTokenReference>
</ds:KeyInfo>
<xenc:CipherData>
<xenc:CipherValue>G2wDCq24FsgBGerE...</xenc:CipherValue>
</xenc:CipherData>
<xenc:ReferenceList>
<xenc:DataReference URI="#DiscountResponse"/>
</xenc:ReferenceList>
</xenc:EncryptedKey>
<ds:Signature wsu:id="originSignature">
<ds:SignedInfo>
<ds:CanonicalizationMethod
Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2001/10/xml-exc-c14n#"/>
<ds:SignatureMethod
Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#hmac-sha1"/>
<ds:Reference URI="#DiscountedBookingForPartnersResponse">
<ds:DigestMethod Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#sha1"/>
<ds:DigestValue>JwFsd3eQc0iXlJm5PkLh7...</ds:DigestValue>
</ds:Reference>
</ds:SignedInfo>
<ds:SignatureValue>BSxlJbSiFdm5Plhk...</ds:SignatureValue>
<ds:KeyInfo>
<wsse:SecurityTokenReference>
<wsse:Reference URI="#userSysmetricKey"
ValueType="...oasis-wss-soap-message-security-1.1#EncryptedKey"/>
</wsse:SecurityTokenReference>
</ds:KeyInfo>
</ds:Signature>
<ds:Signature>
<ds:SignedInfo>
...
<ds:Reference URI="#originSignature">
<ds:DigestMethod Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#sha1"/>
<ds:DigestValue>FeGre4lWv1lY2Kn4LJkg9...</ds:DigestValue>
</ds:Reference>
</ds:SignedInfo>
<ds:SignatureValue>ADfkTeYsGen5Re4L...</ds:SignatureValue>
<ds:KeyInfo>
<wsse:SecurityTokenReference>
<wsse:Reference URI="#userX509Cert"
</wsse:SecurityTokenReference>
</ds:KeyInfo>
</ds:Signature>
</wsse:Security>
</SOAP-ENV:Header>
<SOAP-ENV:Body wsu:Id="DiscountedBookingForPartnersResponse">
<s:GetSpecialDiscountedBookingForPartnersResponse
xmlns:s="http://www.MyHotel.com/partnerservice ">
<xenc:EncryptedData
wsu:Id="DiscountResponse"
type="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#Element">
<xenc:EncryptionMethod
Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#aes256-cbc "/>
<CipherData>
<CipherValue>XD6sFa0DrWsHdehrHdhcW0x...</CipherValue>
</CipherData>
</xenc:EncryptedData>
</s:GetSpecialDiscountedBookingForPartnersResponse>
</SOAP-ENV:Body>
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
和加密引用证书一样, 在WS-Security1.1中为签名也定义了3种引用方式.第一种就是上述的引用BinarySecurityToken. 第二种同加密所用的第二种方法一样采用X509IssuerSerial.第三种是KeyIdentifier, 只不过与加密所用的KeyIdentifier的类型不同,下面是使用KeyIdentifier做签名的引用的示例:
<ds:Signature
…
<ds:KeyInfo>
<wsse:SecurityTokenReference>
<wsse:KeyIdentifier EncodingType="...#Base64Binary"
ValueType="...#X509SubjectKeyIdentifier">
MIGfMa0GCSq…
</wsse:KeyIdentifier>
</wsse:SecurityTokenReference>
</ds:KeyInfo>
</ds:Signature>
看到如此多的引用方式,读者可能会对此产生一些疑惑。主要可能会有如下三个问题:
1.为什么要支持如此多的引用方式?
2.为什么加密不支持引用BinarySecurityToken的方式?
3.为什么同为KeyIdentifier方式, 在加密和签名中信息的类型却不同?
在解答以上疑问之前,首先需要明白WS-Security中使用X509Token和SSL有一点不同的就是: SSL中Server端的X509证书用户能够在协议中动态的获得,而WS-Security中使用X509Token却需要用户在消息传递前获得Server端得X509证书(静态方式)。在了解了这个前提后,让我们依次解答上述得问题。
1.虽然表面看来有3种引用方式,实际上可以分为包含式和标识式。所谓包含式就是将X509证书包含到消息中,然后引用包含它的XML元素(引用BinarySecurityToken就是此种方式)。而标识式并不将X509证书包含到消息中,仅仅包含某些属性从而让消息的发送方和接受方能够通过它们在本地的证书库中定位到相应的证书。以上两种方式各自有其应用场景。当我们利用Server的证书加密消息的时候自然会使用标识式,因为Server端显然保存有自己的证书,能够通过标识定位到相应的证书就足够了。 而当用户使用与自己证书对应的私钥签名消息的时候,自然希望能同时将自己的证书传送给消息的接受方(Server),以便它利用证书的公钥验证签名,此时就会采用了包含式的引用。当然如果Server端已经获得了用户的证书并保存到本地(比如通过第一次包含式的消息传递后),自然也可以使用标识式引用。
2. 由于加密使用的是Server的证书,用户显然没必要采用包含式的引用向证书的拥有者传递证书。
3. 同样是因为签名和加密所使用的证书的拥有者不同的原因。签名使用的是用户的证书,所以需要传递完整的信息,以方便Server去其他地方查找。而加密使用的是Server的证书,server端本地已经拥有该证书,只需要定位到即可,所以利用摘要(SHA)一方面可以减少数据传输量,另一方面可以增强安全性。
同时使用Client和Service的X509证书, 可以在保证消息安全的同时实现Client与Service的身份鉴别. 与UsernameForCertificate用于个人与企业之间的安全不同的是MutualCertificate通常用于保障企业与企业之间的安全.
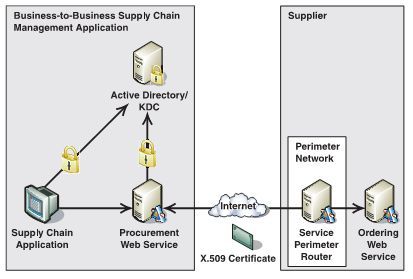
应用场景:
B2B供应链, 在物资需求方的企业内部使用Kerberos协议来保障个人或各个部门的安全, 而在物资需求方和供应方之间采用X509 Certification.
参考资料:
OASIS X509 Token Profile 1.1
Protect Your Web Services Through The Extensible Policy Framework In WSE 3.0