在多线程环境下对字符串进行MD5,到底应该使用加锁来共享同一个MessageDigest呢?还是每次新创建一个,个人认为需要 根据程序运行的环境来分别对待。下边是从org.springframework.extensions.surf摘取的一段代码,实现了两种调用方式, 不过到底在何种情况下使用何种方式,目前还不是很清晰,希望通过测试能够得出结论。
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
/**
* The MD5 utility class computes the MD5 digest (aka: "hash") of a block
* of data; an MD5 digest is a 32-char ASCII string.
*
* The synchronized/static function "Digest" is useful for situations where
* lock contention in the application is not expected to be an issue.
*
* The unsynchronized/non-static method "digest" is useful in a
* multi-threaded program that wanted to avoid locking by creating
* an MD5 object for exclusive use by a single thread.
*
*
*
* EXAMPLE 1: Static usage
*
* import org.springframework.extensions.surf.util.MD5;
* String x = MD5.Digest("hello".getBytes());
*
*
* EXAMPLE 2: Per-thread non-static usage
*
* import org.springframework.extensions.surf.util.MD5;
* MD5 md5 = new MD5();
* ...
* String x = md5.digest("hello".getBytes());
*
*
* Email: [email protected]
* User: diwayou
* Date: 13-4-15
* Time: 下午11:18
*/
public class MD5 {
private static final byte[] ToHex_ =
{ '0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7',
'8','9','a','b','c','d','e','f'
};
private MessageDigest md5_ = null;
static private MessageDigest Md5_;
static
{
try { Md5_ = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");} // MD5 is supported
catch ( NoSuchAlgorithmException e ) {}; // safe to swallow
};
/**
* Constructor for use with the unsynchronized/non-static method
* "digest" method. Note that the "digest" function is not
* thread-safe, so if you want to use it, every thread must create
* its own MD5 instance. If you don't want to bother & are willing
* to deal with the potential for lock contention, use the synchronized
* static "Digest" function instead of creating an instance via this
* constructor.
*/
public MD5()
{
try { md5_ = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");} // MD5 is supported
catch ( NoSuchAlgorithmException e ) {}; // safe to swallow
}
/**
* Thread-safe static digest (hashing) function.
*
* If you want to avoid lock contention, create an instance of MD5
* per-thead, anc call the unsynchronized method 'digest' instead.
*/
public static synchronized String Digest(byte[] dataToHash)
{
Md5_.update(dataToHash, 0, dataToHash.length);
return HexStringFromBytes( Md5_.digest() );
}
/**
* Non-threadsafe MD5 digest (hashing) function
*/
public String digest(byte[] dataToHash)
{
md5_.update(dataToHash, 0, dataToHash.length);
return HexStringFromBytes( md5_.digest() );
}
private static String HexStringFromBytes(byte[] b)
{
byte [] hex_bytes = new byte[ b.length * 2 ];
int i,j=0;
for (i=0; i < b.length; i++)
{
hex_bytes[j] = ToHex_[ ( b[i] & 0x000000F0 ) >> 4 ] ;
hex_bytes[j+1] = ToHex_[ b[i] & 0x0000000F ];
j+=2;
}
return new String( hex_bytes );
}
}
下边是闲暇时写的一段测试代码,测试方式考虑因素还是比较少的,只考虑到了竞争线程的数量,代码如下:
package com.diwayou.logq; import com.diwayou.logq.util.MD5; import org.jfree.chart.ChartFactory; import org.jfree.chart.ChartFrame; import org.jfree.chart.JFreeChart; import org.jfree.chart.plot.PlotOrientation; import org.jfree.data.xy.DefaultXYDataset; import org.jfree.data.xy.XYDataset; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; /** * Email: [email protected] * User: diwayou * Date: 13-3-26 * Time: 下午5:48 */ public class LogQ { public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException, InterruptedException { String s = "alibabagogogo"; final byte[] message = s.getBytes("GBK"); int coreNum = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); int scale = 100; System.out.println(String.format("Core size is %d", coreNum)); int TEST_TIMES = 1; long startTime, endTime; DefaultXYDataset xyDataset = new DefaultXYDataset(); double[][] elapse = new double[2][scale]; for (int j = 0; j < scale; j++) { ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(scale); startTime = System.nanoTime(); for (int i = 0; i < TEST_TIMES; i++) { executorService.submit(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { MD5.Digest(message); } }); } executorService.shutdown(); endTime = System.nanoTime(); System.out.println(String.format("Pool size %d, elapse time %d", j, (endTime - startTime))); elapse[0][j] = j; if (j == 0) { elapse[1][j] = 0; } else { elapse[1][j] = endTime - startTime; } } xyDataset.addSeries("Synchronized", elapse); elapse = new double[2][scale]; for (int j = 0; j < scale; j++) { ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(scale); startTime = System.nanoTime(); for (int i = 0; i < TEST_TIMES; i++) { executorService.submit(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { MD5 md5 = new MD5(); md5.digest(message); } }); } executorService.shutdown(); endTime = System.nanoTime(); System.out.println(String.format("Pool size %d, elapse time %d", j, (endTime - startTime))); elapse[0][j] = j; if (j == 0) { elapse[1][j] = 0; } else { elapse[1][j] = endTime - startTime; } } xyDataset.addSeries("NewEveryTime", elapse); displayChart("Synchronized VS NewEveryTime", xyDataset); } private static void displayChart(String title, XYDataset dataset) { JFreeChart xyLineChart = ChartFactory.createXYLineChart(title, "Pool Size", "Elapse Time", dataset, PlotOrientation.VERTICAL, true, true, true); ChartFrame chartFrame = new ChartFrame("Stat Result", xyLineChart); chartFrame.pack(); chartFrame.setVisible(true); } }
运行结果如下:
(1)第一次
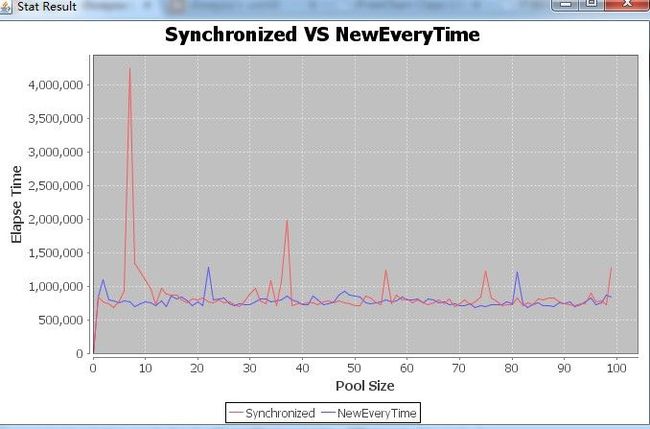
Core size is 8 Pool size 0, elapse time 2012874 Pool size 1, elapse time 839776 .............. (2)第二次
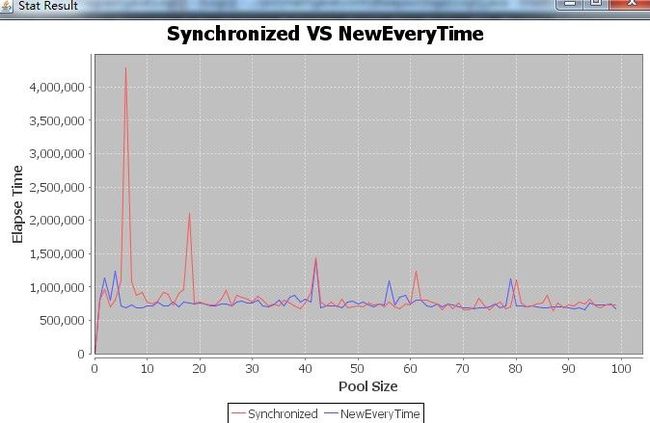
Core size is 8 Pool size 0, elapse time 2256508 Pool size 1, elapse time 795155 Pool size 2, elapse time 968285 ................... 结论:通过测试结果,可以看出每次都new一个新的并不比共享同一个MessageDigest慢,而且不需要锁,这样在服务器高并发的环境下,就不会出现共享锁性能瓶颈 的问题,这样可以减少由于共享锁出现的上下文切换,个人倾向于每次都new一个。 本人菜鸟一个,分析有误还请大家支出,随便批评,这样我才能进步。