个人学习笔记,如有错误欢迎指正。。
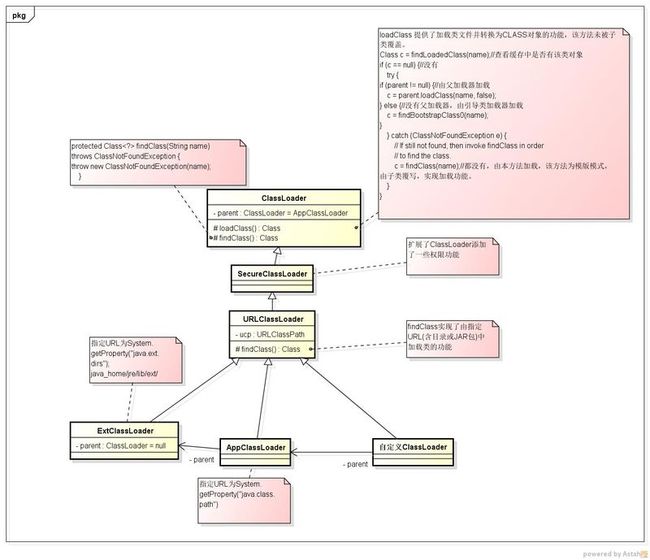
Java ClassLoader用于加载Class文件生成Class对象。
jvm 默认启动的ClassLoader:
1.Bootstrap 引导类加载器 java_home/jre/lib下的固定的几个jar包,如rt.jar 等
2.sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader 扩展类加载器 加载 java_home/jre/lib/ext/下(java.ext.dirs参数指定目录下)的所有jar
3.sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader 系统类加载器 加载ClassPath下的所有JAR
类图:
sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader 和sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader 都扩展了 java.net.URLClassLoader,并使用java.net.URLClassLoader的loadClass方法来加载类( loadClass属于公共方法,并未被子类覆盖)。
看一下loadClass源码:
//name参数是类的全名 如"java.lang.StringBuffer"
protected synchronized Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
// 首先从缓存中查找类是否加载
Class c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {//缓存中没有
try {
if (parent != null) {//有父 类加载器则从父类加载器中加载
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClass0(name);//没有父类加载器,从引导类加载器中加载。
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
c = findClass(name);//没有找到则调用findClass 加载,这个方法是空的,可以由子类覆写这个方法,实现类的加载
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
程序默认当前ClassLoader 是sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader ,它负责从ClassPath中加载程序中需要类,它的父ClassLoader是sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader
public class TestDefaultClassLoader {
public static void main(String args []){
TestDefaultClassLoader testDefaultClassLoader = new TestDefaultClassLoader();
System.out.println(testDefaultClassLoader.getClass().getClassLoader());
//输出:sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@19821f
System.out.println(testDefaultClassLoader.getClass().getClassLoader().getParent());
//输出:sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@1cde100
}
}
类的加载顺序(如果缓存中没有):
1.首先由Bootstrap 引导类加载器从java_home/jre/lib下加载,没有找到进2
2.ExtClassLoader 扩展类加载器从java_home/jre/lib/ext/下加载,没有找到进3
3.AppClassLoader 系统类加载器 从ClassPath路径中加载,没有找到报错ClassNotFoundException
URLClassLoader类通过覆盖findClass方法,实现了如果在上述路径不能加载类时,通过指定的URL加载:
示例 :
1.在另一eclipse工程上新建类 ProductA和B和C,并打jar包 product.jar放到放到F盘下(非ClassPath下):
public class ProductA {
static {
System.out.println("ProductA version 1.0, static code ran");
}
public void printClassLoader(){
System.out.println(" this is ProductA ,version 1.0. classLoader="+this.getClass().getClassLoader());
}
public static void staticPrint(){
System.out.println(" this is ProductA ,version 1.0. static method called ");
}
public void CallB(){
B b = new B();
b.print();
}
}
public class B {
public void print(){
System.out.println("B.classLoader="+this.getClass().getClassLoader());
}
}
public class C {
public void print(){
System.out.println("C.classLoader="+this.getClass().getClassLoader());
}
}
2.当前eclipse 项目中新建测试 URLClassLoader类:
public class TestURLClassLoader {
public static void main(String args []){
try{
File filePath = new File("F:/product.jar");
URL urs [] = new URL[] {filePath.toURI().toURL()};//指定类所在URL
URLClassLoader urlClassLoader = new URLClassLoader(urs);
// 由于类ProductA类所在的jar包 product.jar 未在当前类路径下,因此不能直接NEW (编译器会通不过)或 Class.forName(当前类路径无该类报错:ClassNotFoundException)
// 可以通过指定的类加载器loadClass
Class productAClass = urlClassLoader.loadClass("test.temp.ProductA");//输出"ProductA version 1.0, static code ran",说明loadClass 时 类的静态代码块被执行了
Method method = productAClass.getMethod("staticPrint", null);
method.invoke(null, null);//调用静态方法,不需要对象实例 输出 " this is ProductA ,version 1.0. static method called "
Object obj = productAClass.newInstance();//实例化类
method = productAClass.getMethod("printClassLoader", null);
method.invoke(obj, null);//调用非静态方法,需要对象实例 输出 " this is ProductA ,version 1.0. classLoader=java.net.URLClassLoader@c17164"
method = productAClass.getMethod("CallB", null);
method.invoke(obj, null);
//CallB 方法中直接使用 new B,并调用B的print方法:输出"B.classLoader=java.net.URLClassLoader@c17164"
method = productAClass.getMethod("CallC", null);
method.invoke(obj, null);
//CallC 方法中使用Class.forName()加载C类,newInstance()方法实例化C,并调用C的print方法,输出:"C.classLoader=java.net.URLClassLoader@c17164"
//由一个类加载器L加载的类A,由类A代码调用产生的类实例或Class(new 或 Class.forName()),均由类加载器L加载,因此B类没有报ClassNotFoundException
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
以上代码说明:
1.使用非ClassPath下的类需要使用 指定类加载器手工加载,URLClassLoader.loadClass()
2.非ClassPath下的类加载后,需要使用反射方式调用方法(还有接口方式调用,下面介绍)。
3.类完成加载过程后,static代码块已执行。
4.static 方法和static成员变量 存在Class中,因此反射时不需类的实例。
Class只有一个,类的实例可以有多个,因些可以使用 a.getClass() == b.getClass() 来判断a和b是否为同 一个Class产生的实例.
5.由一个类加载器L加载的类A,由类A代码调用产生的类实例或Class(new 或 Class.forName()),均由类加载器L加载(对于非ClassPath下的jar包中的类中功能,入口时需要反射调用,最好能提供一个总的入口(可以使用门面模式),被调用时反射一次就可以了,如果分散成多个入口,需要反射多次)。
上面提到由于当前ClassPath下没有对应的类,所以需要反射调用调用自定义加载的类,那么新建ProductA和B放到类路径下,编译就能通过了,但是URLClassLoader会优先加载ClassPath下的类,我想要调用的类没有被加载:
示例:(新建的ClassPath下的类)
public class ProductA {
static {
System.out.println("ProductA version 2.0, static code ran");
}
public void printClassLoader(){
System.out.println(" this is ProductA ,version 2.0. classLoader="+this.getClass().getClassLoader());
}
public static void staticPrint(){
System.out.println(" this is ProductA ,version 2.0. static method called ");
}
public void CallB(){
B b = new B();
b.print();
}
}
加载类:
public static void main(String args []){
try{
File filePath = new File("F:/product.jar");
URL urs [] = new URL[] {filePath.toURI().toURL()};//指定类所在URL
URLClassLoader urlClassLoader = new URLClassLoader(urs);
Class productAClass = urlClassLoader.loadClass("test.temp.ProductA");//输出"ProductA version 2.0, static code ran",说明loadClass 加载的是ClassPath下的类
ProductA productA = (ProductA)productAClass.newInstance();
productA.printClassLoader();
//输出" this is ProductA ,version 2.0. classLoader=sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@19821f"
//说明URLClassLoader的优先加载ClassPath下的类
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
因此需要自定义ClassLoader,覆盖loadClass方法,实现优先从非ClassPath中加载:
public class CustomClassLoader extends URLClassLoader{
public CustomClassLoader(URL[] urls) {
super(urls);
}
@Override
protected synchronized Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Class c = customFindClass(name);
if(c != null){
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
}else {
c = super.loadClass(name, resolve);
}
return c;
}
private final Class DEFAULT_CLASS = Object.class;
private Class<?> customFindClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Map<String,Class> classMap = getClassMap();
Class classz = null;
if(classMap.containsKey(name)){
classz = classMap.get(name);
if(classz == DEFAULT_CLASS){
try{
classz = super.findClass(name);
classMap.put(name, classz);
}catch(ClassNotFoundException e){
classMap.remove(name);
}
}
}
return classz;
}
private volatile Map<String,Class> classMap = null;
private Map<String,Class> getClassMap() throws ClassNotFoundException{
Map<String,Class> tempClassMap = classMap;
if(null == tempClassMap){
tempClassMap = initClassMap();
}
return tempClassMap;
}
private synchronized Map<String,Class> initClassMap() throws ClassNotFoundException{
if(classMap==null){
Map<String,Class> tempClassMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String,Class>();
URL urls [] = this.getURLs();
if(urls != null && urls.length>0){
for(int i=0;i<urls.length;i++){
URL url = urls[i];
String fileName = url.getFile();
if(fileName != null ){
List<String> classNameList = getClassNameList(fileName);
if(classNameList != null && classNameList.size()>0){
for(String className:classNameList){
tempClassMap.put(className, DEFAULT_CLASS);
System.out.println(className);
}
}
}
}
}
classMap= tempClassMap;
}
return classMap;
}
private List<String> getClassNameList(String fileName) throws ClassNotFoundException{
List<String> classNameList = null;
File file = new File(fileName);
if(file.exists()){
if(file.getName().endsWith("jar") && file.isFile()){
classNameList = getClassNameFromJar(file);
}else if(file.isDirectory()){
classNameList = getClassNameFromDir("",file);
}
}
return classNameList;
}
private List<String> getClassNameFromJar(File file) throws ClassNotFoundException{
List<String> classNameList = new ArrayList();
try{
JarFile jarFile = null;
jarFile = new JarFile(file);
Enumeration<JarEntry> enumeration = jarFile.entries();
while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
JarEntry jarEntry = enumeration.nextElement();
String name = jarEntry.getName();
if (name.endsWith(".class")) {
String className = name.substring(0, name.length() -6).replace('/', '.').replace('\\', '.');
classNameList.add(className);
}
}
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return classNameList;
}
private List<String> getClassNameFromDir(String path,File dir){
List<String> classNameList = new ArrayList();
File files[] = dir.listFiles();
for(File file:files){
if(file.isFile() && file.getName().endsWith(".class")){
String className = file.getName().substring(0, file.getName().length() -6).replace('/', '.').replace('\\', '.');
if(path.length()>0){
className = path+"."+className;
}
classNameList.add(className);
}else{
String subPath = path;
if(path.length()>0){
subPath+=("."+file.getName());
}
List subClassNameList = getClassNameFromDir(subPath,file);
classNameList.addAll(subClassNameList);
}
}
return classNameList;
}
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
}
}
再测试一下:
public static void main(String args []){
try{
File filePath = new File("F:/product.jar");
URL urs [] = new URL[] {filePath.toURI().toURL()};//指定类所在URL
URLClassLoader urlClassLoader = new CustomClassLoader(urs);//使用自定义ClassLoader ,优先从URL指定的路径加载类
// 由于类ProductA类所在的jar包 product.jar 未在当前类路径下,因此不能直接NEW (编译器会通不过)或 Class.forName(当前类路径无该类报错:ClassNotFoundException)
// 可以通过指定的类加载器loadClass
Class productAClass = urlClassLoader.loadClass("test.temp.ProductA");//输出"ProductA version 1.0, static code ran",说明loadClass 正确加载非ClassPath下的类
Object obj = (Object)productAClass.newInstance();
//这行没有报错?为啥?,因为Object类型不是由自定义ClassLoader加载的,
System.out.println(Object.class.getName()+".classLoader="+Object.class.getClassLoader());//输出"java.lang.Object.classLoader=null"
System.out.println(ProductA.class.getClassLoader());//输出:sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@19821f
System.out.println(productAClass.getClassLoader());//输出:temp.java.CustomClassLoader@1fb8ee3
ProductA productA = (ProductA)productAClass.newInstance();
//这行报错了:java.lang.ClassCastException: test.temp.ProductA cannot be cast to test.temp.ProductA
//at temp.java.TestURLClassLoader1.main(TestURLClassLoader1.java:23)
productA.printClassLoader();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
上面代码中,编译通过了,自定义ClassLoader加载非ClassPath下的类成功了,但类型转换失败了。
可能原因如下:
ProductA (标红的 ProductA )是由系统类加载器加载的,可能是因为明文代码写的,编译时就确定了吧, productAClass 是由自定义类加载的,虽然类全名相同,但jvm不认为它们是相同的。
上面代码中:
Object obj = (Object)productAClass.newInstance();
这行就没有报错,为啥呢? 估计明文写的代码Object是由当前ClassLoader自动加载的()
System.out.println(Object.class.getName()+".classLoader="+Object.class.getClassLoader());//输出"java.lang.Object.classLoader=null"引导类加载器加载的
而自定义类加载器加载了ProductA,ProductA是Object的子类,Object也需要加载,在自定义类加载器中加入输出代码,测试一下 Object是哪个类加载器加载的:
protected synchronized Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Class c = customFindClass(name);
if(c != null){
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
}else {
c = super.loadClass(name, resolve);
}
System.out.println(name+".classLoader="+c.getClassLoader());
return c;
}
输出:java.lang.Object.classLoader=null//引导类加载
test.temp.ProductA.classLoader=temp.java.CustomClassLoader@1fb8ee3//自定义类加载
表明:1.由同一个类加载器加载,可以做类型转换。
2.加载顺序:先加父类或接口,再加载子类
可以在ClassPath类路径上建立父类或接口,由非ClassPath上的类实现,非ClassPath上的类使用:
1.如果ClassPath上没有父类或接口的另一实现版本,使用URLClassLoader就可以加载非ClassPath上的类,并可以做类型转换,转到父类或接口上再调用
2.如果ClassPath上有父类或接口的另一实现版本,需要自定义ClassLoader优先加载非ClassPath上的类,并可以做类型转换,转到父类或接口上再调用
3.非ClassPath上的类没有父类或接口,又或者父类或接口不在ClassPath上,类加载后,需要通过反射调用。
参考资料:http://blog.csdn.net/lovingprince/article/details/4238695
http://jiajun.iteye.com/blog/608564