K-means算法Java实现
K-means算法Java实现
算法设计 1》什么是K-means算法
step1 从数据中随机抽取K个点作为初始聚类的中心。
step2 计算数据中所有的点到这K个点的距离,将点归到离其最近的聚类里。
step3 调整聚类中心。
step4 重复step2,直到误差小于阈值或者聚类中心及聚类成员不在改变。
2》java实现
| Point.java |
| package cn.edu.shu.kmeans; public class Point { int x;//坐标 int y; int id; //名称 public Point(int id, int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.id = id; } public int getX() { return x; } public void setX(int x) { this.x = x; } public int getY() { return y; } public void setY(int y) { this.y = y; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } @Override public String toString() { return "P"+id+"("+x+","+y+")"; } } |
| Cluster.java |
| package cn.edu.shu.kmeans; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Cluster { double error=0.0;//聚类内部误差 int center;//聚类中心point的id ArrayList<Point> ofCluster = new ArrayList<Point>();//属于这个聚类的点的集合 public double getError() { return error; } public void setError(double error) { this.error = this.error+ error; } public int getCenter() { return center; } public void setCenter(int center) { this.center = center; } public ArrayList<Point> getOfCluster() { return ofCluster; } public void setOfCluster(ArrayList<Point> ofCluster) { this.ofCluster = ofCluster; } public void addPoints(Point point){ if(!(this.ofCluster.contains(point))) this.ofCluster.add(point); } } |
| Distence.java |
| package cn.edu.shu.kmeans; public class Distence { int dest; int source; double dist; public int getDest() { return dest; } public void setDest(int dest) { this.dest = dest; } public int getSource() { return source; } public void setSource(int source) { this.source = source; } public double getDist() { return dist; } public void setDist(double dist) { this.dist = dist; } public Distence(int dest, int source, double dist) { super(); this.dest = dest; this.source = source; this.dist = dist; } public Distence() { } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if(obj!=null){ Distence d = (Distence)obj; if(this.dest==d.dest&&this.source==d.source&&this.dist==d.dist){ return true; } else{ return false; } } return false; } } |
| Kmeans.java |
| package cn.edu.shu.kmeans; import java.io.*; import java.util.*; public class Kmeans { int K; //聚类参数,聚成几个类。 int Generation=100;//聚类次数,聚类结束条件之一。 double E=7.1;//误差参数,聚类结束的条件之一。 static ArrayList<Point> allPoints = new ArrayList<Point>();//参与聚类的所有点 int totalNumber = 0;//聚类的点的个数 //初始化数据 //data.txt //2 //1 1 //2 2 //4 4 //5 5 //8 8 public void prepare() throws IOException { File file = new File("D:\\eclipse\\workspace\\algorithm\\db\\data.txt"); FileReader fr = new FileReader(file); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr); String data = "0"; int x = 0; int y = 0; String[] temp = null; Point p = null; K = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); while ((data = br.readLine()) != null) { temp = data.split(" "); x = Integer.parseInt(temp[0]); y = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]); p = new Point(totalNumber++, x, y); allPoints.add(p); } } // 第一次随机选取聚类中心 public Set<Integer> firstChoose() { Set<Integer> center = new HashSet<Integer>();//聚类中心的点的id,采用set保证不会有重复id Random ran = new Random(); int roll = ran.nextInt(totalNumber); while (center.size() < K) { roll = ran.nextInt(totalNumber); center.add(roll); } return center; } //根据聚类中心初始化聚类信息 public ArrayList<Cluster> beforCP(Set<Integer> center) { ArrayList<Cluster> cluster = new ArrayList<Cluster>();//存放几个类的信息 Iterator<Integer> it = center.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { Cluster c = new Cluster();//代表一个聚类 c.setCenter(it.next()); cluster.add(c); } return cluster; } //第一次聚类 public ArrayList<Cluster> clusterProcess(ArrayList<Cluster> cluster, Set<Integer> center) { ArrayList<Distence> distence = new ArrayList<Distence>();//存放距离信息 Point source = null; Point dest = null; int id = 0; int id2 = 0; Object[] p = center.toArray(); boolean flag = false; for (int i = 0; i < totalNumber; i++) { distence.clear(); for (int j = 0; j < center.size(); j++) { if (!(center.contains(i))) { flag = true; // 计算距离 source = allPoints.get(i); dest = allPoints.get((Integer) p[j]); distence.add(new Distence((Integer) p[j], i, (Double) Math .sqrt(StrictMath .pow(source.getX() - dest.getX(), 2) + StrictMath.pow(source.getY() - dest.getY(), 2)))); } else { flag = false; } } if (flag == true) { // 排序比较一个点到各个中心的距离的大小 double min = distence.get(0).getDist(); for (int k = 1; k < distence.size(); k++) { if (min > distence.get(k).getDist()) { min = distence.get(k).getDist(); id = distence.get(k).getDest(); id2 = distence.get(k).getSource(); } else { id = distence.get(0).getDest(); id2 = distence.get(0).getSource(); } } for (int n = 0; n < cluster.size(); n++) { if (cluster.get(n).getCenter() == id) { cluster.get(n).setError(min); cluster.get(n).addPoints(allPoints.get(id2)); } } } } return cluster; } // 更新聚类中心 public ArrayList<Cluster> stack(ArrayList<Cluster> cluster) { double te = 0; for (int m = 0; m < Generation; m++) { te = 0; Set<Integer> center = new HashSet<Integer>(); // 重新计算聚类中心 // 方法二:在聚类中,按照距离重新计算聚类中心 Point source = null; Point dest = null; int id = 0; ArrayList<Distence> distence = new ArrayList<Distence>(); for (int j = 0; j < K; j++) { distence.clear(); ArrayList<Point> ps = cluster.get(j).getOfCluster(); ps.add(allPoints.get(cluster.get(j).getCenter())); int size = ps.size(); if (size > 2) {//一个聚类只有1个或2个点就不重新更新聚类中心 // 计算距离 for (int k1 = 0; k1 < size; k1++) { for (int k2 = 0; k2 < size; k2++) { if (k1 != k2) { source = ps.get(k1); dest = ps.get(k2); distence.add(new Distence(dest.getId(), source .getId(), (Double) Math.sqrt(StrictMath .pow(source.getX() - dest.getX(), 2) + StrictMath.pow(source.getY() - dest.getY(), 2)))); } } } // 比较大小 double min = distence.get(0).getDist(); for (int k = 1; k < distence.size(); k++) { if (min > distence.get(k).getDist()) { min = distence.get(k).getDist(); id = distence.get(k).getSource(); } else { id = distence.get(0).getSource(); } } center.add(id); } else { center.add(cluster.get(j).getCenter()); } } // 方法一:采用随机产生新的聚类中心 // center = firstChoose(); // 重新聚类 cluster = clusterProcess(beforCP(center), center); for (int nz = 0; nz < K; nz++) { te = te + cluster.get(nz).getError();//计算误差 } if (te < E) break; } return cluster; } //输出聚类信息 public static void print(ArrayList<Cluster> cs) { double e = 0; for (int i = 0; i < cs.size(); i++) { e = e + cs.get(i).getError(); } System.out.print("---e "); System.out.printf("%8.6f", e); System.out.println("-------------"); for (int i = 0; i < cs.size(); i++) { Cluster c = cs.get(i); System.out.println("center: " +allPoints.get(c.center) + " error: " + c.getError()); ArrayList<Point> p = c.getOfCluster(); for (int j = 0; j < p.size(); j++) { System.out.print(p.get(j)); } System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Kmeans kmeans = new Kmeans(); kmeans.prepare(); Set<Integer> center = kmeans.firstChoose(); ArrayList<Cluster> cs = kmeans.clusterProcess(kmeans.beforCP(center),center); print(cs); ArrayList<Cluster> cs2 = kmeans.stack(cs); print(cs2); } } |
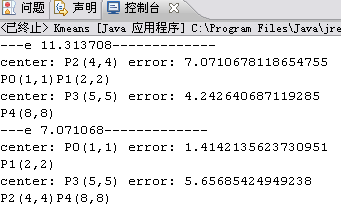
3》结果