HashMap实现原理之我的理解
HashMap[键值对存储]和ArrayList[顺序存储]是Java集合中使用频率最高的两个集合。经常我们都会自然的使用它们来存放数据,然后用Java JDK自带方法来操作他们(添加,修改,删除,迭代等)来实现我们的业务逻辑。
在多线程环境下,需要考虑数据安全性,应该优先考虑其同步类,如HashTable和Vector。ConcurrentHashMap也值得推荐。但是如果不涉及修改和删除,仅有只读的情况下,使用HashMap将会使性能大大提升。
一.HashMap的数据结构。
数组的特点是:寻址容易,插入和删除困难;而链表的特点是:寻址困难,插入和删除容易。HashMap则是数组和链表的综合体,具有两者的优点,被称为链表的数组。
哈希算法是为了能够进行快速查找定位所使用的的一种技术。
哈希表是一个以空间换时间的数据结构。
下图描述了HashMap底层的存储结构,为一个默认长度为16的数组,数组的每个元素存放的是一个链表。例如496%16=0,则存放在index=0的第一个位置,而896%16=0,也是存放在数组index=0的位置,由于第一个位置已经被496占据了,则存放在第二个位置,依次链式存储。【链地址法:java中解决hash冲突的方法】 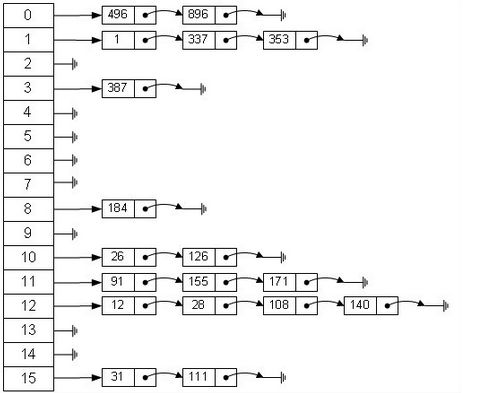
还有个办法可以很清晰的看到HashMap内部结构。在Eclipse下写个测试类Debug下,inspect查看map对象,可看到各个属性的值。默认长度为16,加载因子为0.75,当前存放4个键值对。
map默认打印enrySet中键值对情况。
而选中table属性,更可以看到键值对的散列情况。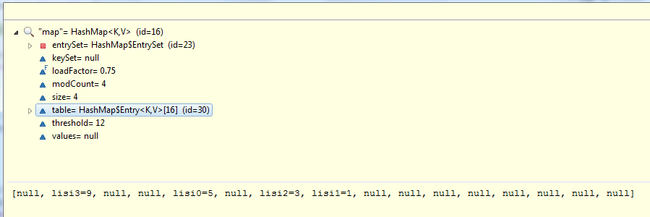
二.HashMap如何存放数据。
查看JDK中源码:
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
可以看到,当map键值对put进来的时候,如果key为空,则直接放在table[0]处。
不为空,则根据hash(key.hashCode())与table的长度(默认16)的模。来确定该键值对所在table中的索引。然后遍历该索引处table[i]所对应的Entry链表,根据key的二次hash值和key的equals()的值,来判断是否已经存在该键值对。如果存在则覆盖原键值对的value,如果没有则添加至链表的最后。
三.HashMap如何读取数据。
查看JDK中源码:
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null :
* key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise
* it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* <p>A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i>
* indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also
* possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}.
* The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to
* distinguish these two cases.
*
* @see #put(Object, Object)
*/
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
可以看到,map在通过key来get对应的value时,和存储时很类似。当key为null时,直接去table[0]的链表去获得key为null的value。不为空则根据二次hash值找到对应的索引,再在索引所在的链表中,通过先前的二次hash值和key的equal方法来确定链表节点,如果找到,则返回该value。
四.一些常见问题。
1. 两个对象比较equals()为true,则hashCode也相同吗? 反之呢?
回答:不一定。在没有重写hashCode方法的前提下,他们比较的Object里的hashCode返回的值,如果重写了,则是使用自定义的hashCode方法的返回值。如果两个String值equals为true则他们hashCode相同,而实际项目中,我们会覆盖hashCode方法来重写我们业务的判断逻辑,这样即使equals相等,hashCode也不同。
反之,hashCode相同,equals比较一定相等。因为equals比较的依据就是hashCode的值。
2. 如何定位一个数值的index。
回答:hashMap的处理方法是,将key二次hash之后的值,与table的长度进行取模运算。F返回值即为当前table的index。
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//。。。。。。
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
3. HashMap存放数据,是否会发生数据冲撞?
回答:会。当他们对象的hashcode相同时,他们会保存在同一个table[i]的同一个索引上,此时发生碰撞。HashMap拥有一个LinkList机制,将发生碰撞的值以链表形式存储在同一table[i]上。
4. hashMap是否会无限存放数据?
回答:会。当table的容量达到当前容量*加载因子(默认的capacity * load factor是16*0.75)是,table的容量会增加一倍,来应对存储量的扩增。
/**
* Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to
* the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this
* method to resize the table if appropriate.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method.
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
5. hashmap如何散列数值的?取模为什么是16,而不是15?
回答:hashmap里的hash算法设计的目的是使元素的排列尽量分散,也就是散列。尽量使得每个位置上的元素数量只有一个。此算法加入了高位计算,防止低位不变,高位变化时,造成的hash冲突。
/**
* Applies a supplemental hash function to a given hashCode, which
* defends against poor quality hash functions. This is critical
* because HashMap uses power-of-two length hash tables, that
* otherwise encounter collisions for hashCodes that do not differ
* in lower bits. Note: Null keys always map to hash 0, thus index 0.
*/
static int hash(int h) {
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
当length总是2的n次方时,h& (length-1)运算等价于对length取模,也就是h%length,但是&比%具有更高的效率。只有是2的n次方,才能保证每次二进制与运算之后的结果笼罩所有的数。
6. 何如合理设计一个hashMap。
五.自己设计一个HashMap。
代码copy至http://www.cnblogs.com/xwdreamer/archive/2012/05/14/2499339.html
基本与JDK源码一致:
Entry.java
public class Entry<K, V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K, V> next;// 下一个结点
// 构造函数
public Entry(K k, V v, Entry<K, V> n) {
key = k;
value = v;
next = n;
}
public final K getKey() {
return key;
}
public final V getValue() {
return value;
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Entry))
return false;
Entry e = (Entry) o;
Object k1 = getKey();
Object k2 = e.getKey();
if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) {
Object v1 = getValue();
Object v2 = e.getValue();
if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2)))
return true;
}
return false;
}
public final int hashCode() {
return (key == null ? 0 : key.hashCode())
^ (value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
}
public final String toString() {
return getKey() + "=" + getValue();
}
}
MyHashMap.java
public class MyHashMap<K, V> {
private Entry[] table;// Entry数组表
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;// 默认数组长度
private int size;
// 构造函数
public MyHashMap() {
table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];
size = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
}
// 获取数组长度
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
// 求index
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h % (length - 1);
}
// 获取元素
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return null;
int hash = key.hashCode();// key的哈希值
int index = indexFor(hash, table.length);// 求key在数组中的下标
for (Entry<K, V> e = table[index]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k = e.key;
if (e.key.hashCode() == hash && (k == key || key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
// 添加元素
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return null;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = indexFor(hash, table.length);
// 如果添加的key已经存在,那么只需要修改value值即可
for (Entry<K, V> e = table[index]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k = e.key;
if (e.key.hashCode() == hash && (k == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
return oldValue;// 原来的value值
}
}
// 如果key值不存在,那么需要添加
Entry<K, V> e = table[index];// 获取当前数组中的e
table[index] = new Entry<K, V>(key, value, e);// 新建一个Entry,并将其指向原先的e
return null;
}
}
MyHashMapTest.java
public class MyHashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyHashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new MyHashMap<Integer, Integer>();
map.put(1, 90);
map.put(2, 95);
map.put(17, 85);
System.out.println(map.get(1));
System.out.println(map.get(2));
System.out.println(map.get(17));
System.out.println(map.get(null));
}
}