Android 启动流程
SystemServer的启动
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java: run()
其中调用ActivityManagerService.installSystemProviders(),
最终会调用到frameworks/base/packages/SettingsProvider/src/com/android/providers/settings/下
的各个content providers的onCreate()函数,初始化数据库内容。。。
android 启动流程
other ref:http://www.cnblogs.com/jacktu/archive/2010/07/02/1769939.html
Android从Linux系统启动有4个步骤;
(1) init进程启动
(2) Native服务启动
(3) System Server,Android服务启动
(4) Home启动
总体启动框架图如:
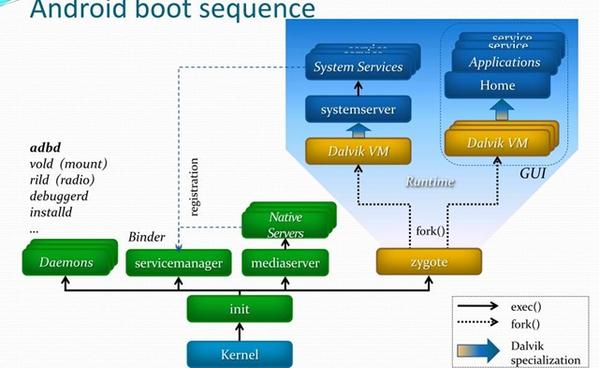
android 启动流程
第一步:initial进程(system\core\init)
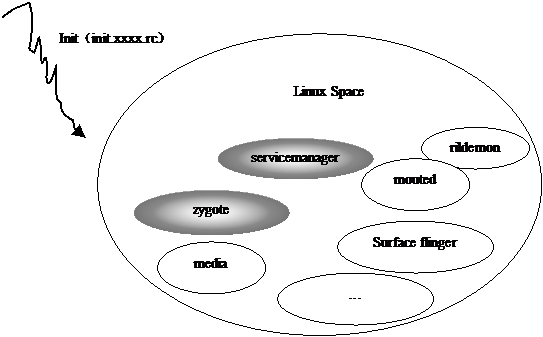
init进程,它是一个由内核启动的用户级进程。内核自行启动(已经被载入内存,开始运行,并已初始化所有的设备驱动程序和数据结构等)之后,就通过启动一个用户级程序init的方式,完成引导进程。init始终是第一个进程.
Init.rc
Init.marvell.rc
android 启动流程
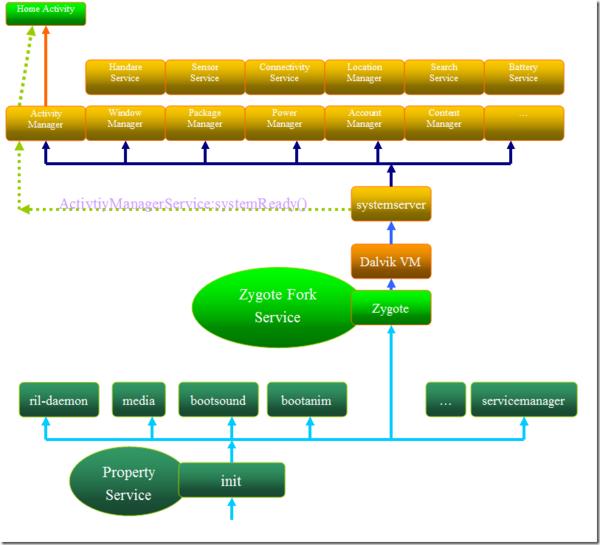
Init进程一起来就根据init.rc和init.xxx.rc脚本文件建立了几个基本的服务:
* servicemanamger
* zygote
。。。
最后Init并不退出,而是担当起property service的功能。
1.1脚本文件
init@System/Core/Init
Init.c: parse_config_file(Init.rc)
@parse_config_file(Init.marvel.rc)
解析脚本文件:Init.rc和Init.xxxx.rc(硬件平台相关)
Init.rc是Android自己规定的初始化脚本(Android Init Language, System/Core/Init/readme.txt)
该脚本包含四个类型的声明:
* Actions
* Commands
* Services
* Options.
1.2 服务启动机制
我们来看看Init是这样解析.rc文件开启服务的。
(1)打开.rc文件,解析文件内容@ system\core\init\init.c
将service信息放置到service_list中。@ system\core\init parser.c
(2)restart_service()@ system\core\init\init.c
service_start
execve(…).建立service进程。
第二步 Zygote
Servicemanager和zygote进程就奠定了Android的基础。Zygote这个进程起来才会建立起真正的Android运行空间,初始化建立的Service都是Navtive service.在.rc脚本文件中zygote的描述:
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
所以Zygote从main(…)@frameworks\base\cmds\app_process\app_main.cpp开始。
(1) main(…)@frameworks\base\cmds\app_process\app_main.cpp
* 建立Java Runtime
* runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", startSystemServer);
(2) runtime.start@frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
* 建立虚拟机:startVM(...)
* 运行:com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit:main函数。
(3)main()@com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit//正真的Zygote。
* registerZygoteSocket();//登记Listen端口
* startSystemServer();
* 进入Zygote服务框架。
经过这几个步骤,Zygote就建立好了,利用Socket通讯,接收ActivityManangerService的请求,Fork应用程序。
第三步 System Server
上fork了一个进程: com.android.server.SystemServer.于是 SystemServer@(SystemServer.java)就建立了。Android的所有服务循环框架都是建立 SystemServer@(SystemServer.java)上。在SystemServer.java中看不到循环结构,只是可以看到建立了 init2的实现函数,建立了一大堆服务,并AddService到service Manager。
main() @ com/android/server/SystemServer
init1();
Init1()是在Native空间实现的(com_andoird_server_systemServer.cpp)。我们一看这个函数就知道了,init1->system_init() @System_init.cpp
在system_init()我们看到了循环闭合管理框架。
Call "com/android/server/SystemServer", "init2"
…..
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
init2()@SystemServer.java中建立了Android中所有要用到的服务。
这个init2()建立了一个线程,来New Service和AddService来建立服务
第三步 Home启动
后半段,我们可以看到系统在启动完所有的Android服务后,做了这样一些动作:
(1) 使用xxx.systemReady()通知各个服务,系统已经就绪。
(2) 特别对于ActivityManagerService.systemReady(回调)
Widget.wallpaper,imm(输入法)等ready通知。
Home就是在ActivityManagerService.systemReady()通知的过程中建立的。下面是ActivityManagerService.systemReady()的伪代码:
systemReady()@ActivityManagerService.java
resumeTopActivityLocked()
startHomeActivityLocked();//如果是第一个则启动HomeActivity。
startActivityLocked(。。。)CATEGORY_HOME android 启动流程
In this topic you will learn some information about Android process management. First let’s take a look at the launched processes during Android booting.
USER PID PPID VSIZE RSS WCHAN PC NAME
root 1 0 264 176 c00acc6c 0000c36c S /init
root 28 1 724 308 c0051354 afe0c4cc S /system/bin/sh
system 30 1 796 248 c026516c afe0b74c S /system/bin/servicemanager
root 31 1 1824 316 ffffffff afe0b50c S /system/bin/mountd
root 32 1 652 248 c02976e0 afe0c0bc S /system/bin/debuggerd
radio 33 1 5344 664 ffffffff afe0bdbc S /system/bin/rild
root 34 1 71028 18828 c00ad308 afe0b874 S zygote
media 37 1 16812 3456 ffffffff afe0b74c S /system/bin/mediaserver
root 39 1 788 288 c02f9ae4 afe0b50c S /system/bin/installd
system 86 34 187756 21836 ffffffff afe0b74c S system_server
radio 118 34 103476 13896 ffffffff afe0c824 S com.android.phone
app_4 124 34 117848 19248 ffffffff afe0c824 S android.process.acore
app_5 139 34 98672 11516 ffffffff afe0c824 S com.android.mms
app_3 151 34 92096 10976 ffffffff afe0c824 S com.android.alarmclock
app_6 161 34 94436 12616 ffffffff afe0c824 S com.android.calendar
app_9 173 34 93248 11728 ffffffff afe0c824 S android.process.media
app_15 182 34 91848 9764 ffffffff afe0c824 S com.android.voicedialer
app_16 190 34 94524 10812 ffffffff afe0c824 S android.process.im
They can be divided into three kinds.
Root Process
init is the first process after kernel booting. The major task it performs:
l Parser and execute init.rc and init.%hardware%.rc
l Automatically generate device node under /dev
l Start log and property service
l Monitor for device, property set and child process exit events
Native Application Process
According to init.rc, init will fork the following native application process.
console: star a shell.
servicemanager: start binder IPC service manager.
mountd: mount all fs defined in /system/etc/mountd.conf if started, receive commands through local socket to mount any fs.
debuggerd: start debug system.
rild: start radio interface layer daemon.
zygote: start Android Java VM Runtime and start system server. It’s the most important process.
mediaserver: start AudioFlinger, MediaPlayerService and CameraService.
installd: start install package daemon.
JAVA Application Process
Every JAVA application process is forked from zygote process. system_server is a special JAVA process, which is directly forked from zygote.. Other JAVA process is created from ActivityManagerService(run in system_server process) like this.
int pid = Process.start("android.app.ActivityThread",
mSimpleProcessManagement ? app.processName : null, uid, uid,
gids, ((app.info.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_DEBUGGABLE) != 0), null);
While Process.java use UNIX domain socket to communicate with zygote. So the overall picture is shown as following.
android 启动流程
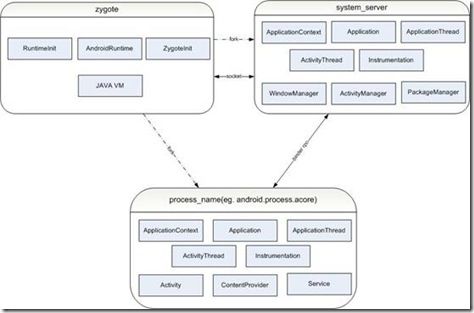

System Server
It’s the first JAVA application launched by zygote. It starts the core Android services, e.g. ActivityManager, WindowManager, PackageManager etc. It’s the Android core engine.
Persistent Application
During booting, ActivityManagerService.systemReady will start all persistent applications.
List apps = ActivityThread.getPackageManager().
getPersistentApplications(PackageManager.GET_SHARED_LIBRARY_FILES);
if (apps != null) {
int N = apps.size();
int i;
for (i=0; i<N; i++) {
ApplicationInfo info
= (ApplicationInfo)apps.get(i);
if (info != null &&
!info.packageName.equals("android")) {
addAppLocked(info);
}
}
Currently only Phone application is registered as a persistent app in AndroidManifest.xml like this.
<application android:name="PhoneApp"
android:persistent="true"
android:label="@string/dialerIconLabel"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher_phone">
So during booting, only phone application is automatically launched. It’s the “com.android.phone” process.
The First Activity
The first activity is launched by senting Intent.CATEGORY_HOME intent from ActivityManagerService.
Intent intent = new Intent(
mTopAction,
mTopData != null ? Uri.parse(mTopData) : null);
intent.setComponent(mTopComponent);
if (mFactoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME);
}
ActivityInfo aInfo =
intent.resolveActivityInfo(mContext.getPackageManager(),
PackageManager.GET_SHARED_LIBRARY_FILES);
if (aInfo != null) {
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(
aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, aInfo.name));
// Don't do this if the home app is currently being
// instrumented.
ProcessRecord app = getProcessRecordLocked(aInfo.processName,
aInfo.applicationInfo.uid);
if (app == null || app.instrumentationClass == null) {
intent.setFlags(intent.getFlags() | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
startActivityLocked(null, intent, null, null, 0, aInfo,
null, null, 0, 0, 0, false);
}
It’s the “android.process.acore” process. (The process name is defined in AndroidManifest.xml)
Auto-launched Application After Booting
When activity idle is detected in ActivityManagerService, it will broadcast ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED intent at the first time.
if (mFactoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
// Tell anyone interested that we are done booting!
synchronized (this) {
broadcastIntentLocked(null, null,
new Intent(Intent.ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED, null),
null, null, 0, null, null,
android.Manifest.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED,
false, false, MY_PID, Process.SYSTEM_UID);
}
Currently, MMS, AlarmClock, Calendar, MediaProvider, VoiceDialer and IM have registered as a receiver for ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED intent in their AndroidManifest.xml. So they will be automatically launched. (This explains the remained JAVA process.)
Email also registers as a receiver for ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED intent in its AndroidManifest.xml, but it defines android:enable=”false”. So it won’t be launched.
<receiver android:name=".service.BootReceiver"
android:enabled="false"
>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.DEVICE_STORAGE_LOW" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.DEVICE_STORAGE_OK" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
DownloadProvider also registers as a receiver for ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED intent in its AndroidManifest.xml, but it defines android:exported=”false”. So it won’t be launched.
<receiver android:name=".DownloadReceiver" android:exported="false">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED" />
<action android:name="android.net.conn.CONNECTIVITY_CHANGE" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
Behind the JAVA process
system_server is a special case. It calls ActivityThread.java’s systemMain static function, which creates an instance of ActivityThread. ActivityThread then creates an instance of ApplicationThread, Application and ApplicationContext.
Every other JAVA process works in a different way. It’s controlled by system_server while forked by zygote. When any JAVA process other than system_server is forked from zygote, it automatically calls ActivityThread.java’s main static function(See Process.java and the following code snippet).
try {
ZygoteInit.invokeStaticMain(cloader, className, mainArgs);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logAndPrintError (newStderr, "Error starting. ", ex);
}
The ActivityThread.java’s main function creates an instance of ActivityThread. ActivityThread then creates an instance of ApplicationThread. The ApplicationThread will work as an IBinder object to interact with ActivityManagerService in system_server. The new process does nothting at this time other than waiting IPC call from system_server. The Application and ApplicationContext object won’t be created at this time. Actually it’s deferred to when the process really works, eg. start an activity, receive intent or start a service.
For example, when start an activity, ActivityManagerService know which process the to-be-launched activity should run in, so it will RPC call ApplicationThread’s scheduleLaunchActivity to launch a new activity in that process. ApplicationThread then post a message to let ActivityThread know it needs to start an activity. ActivityThread then creates Application and ApplicationContext object. After that, it calls Instrumentation, then Instrumentation finally calls JAVA dalvik VM to really create an activity JAVA object.
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java: run()
其中调用ActivityManagerService.installSystemProviders(),
最终会调用到frameworks/base/packages/SettingsProvider/src/com/android/providers/settings/下
的各个content providers的onCreate()函数,初始化数据库内容。。。
android 启动流程
other ref:http://www.cnblogs.com/jacktu/archive/2010/07/02/1769939.html
Android从Linux系统启动有4个步骤;
(1) init进程启动
(2) Native服务启动
(3) System Server,Android服务启动
(4) Home启动
总体启动框架图如:

android 启动流程
第一步:initial进程(system\core\init)
init进程,它是一个由内核启动的用户级进程。内核自行启动(已经被载入内存,开始运行,并已初始化所有的设备驱动程序和数据结构等)之后,就通过启动一个用户级程序init的方式,完成引导进程。init始终是第一个进程.
Init.rc
Init.marvell.rc
android 启动流程

Init进程一起来就根据init.rc和init.xxx.rc脚本文件建立了几个基本的服务:
* servicemanamger
* zygote
。。。
最后Init并不退出,而是担当起property service的功能。
1.1脚本文件
init@System/Core/Init
Init.c: parse_config_file(Init.rc)
@parse_config_file(Init.marvel.rc)
解析脚本文件:Init.rc和Init.xxxx.rc(硬件平台相关)

Init.rc是Android自己规定的初始化脚本(Android Init Language, System/Core/Init/readme.txt)
该脚本包含四个类型的声明:
* Actions
* Commands
* Services
* Options.
1.2 服务启动机制
我们来看看Init是这样解析.rc文件开启服务的。
(1)打开.rc文件,解析文件内容@ system\core\init\init.c
将service信息放置到service_list中。@ system\core\init parser.c
(2)restart_service()@ system\core\init\init.c
service_start
execve(…).建立service进程。
第二步 Zygote
Servicemanager和zygote进程就奠定了Android的基础。Zygote这个进程起来才会建立起真正的Android运行空间,初始化建立的Service都是Navtive service.在.rc脚本文件中zygote的描述:
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
所以Zygote从main(…)@frameworks\base\cmds\app_process\app_main.cpp开始。
(1) main(…)@frameworks\base\cmds\app_process\app_main.cpp
* 建立Java Runtime
* runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", startSystemServer);
(2) runtime.start@frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
* 建立虚拟机:startVM(...)
* 运行:com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit:main函数。
(3)main()@com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit//正真的Zygote。
* registerZygoteSocket();//登记Listen端口
* startSystemServer();
* 进入Zygote服务框架。
经过这几个步骤,Zygote就建立好了,利用Socket通讯,接收ActivityManangerService的请求,Fork应用程序。
第三步 System Server
上fork了一个进程: com.android.server.SystemServer.于是 SystemServer@(SystemServer.java)就建立了。Android的所有服务循环框架都是建立 SystemServer@(SystemServer.java)上。在SystemServer.java中看不到循环结构,只是可以看到建立了 init2的实现函数,建立了一大堆服务,并AddService到service Manager。
main() @ com/android/server/SystemServer
init1();
Init1()是在Native空间实现的(com_andoird_server_systemServer.cpp)。我们一看这个函数就知道了,init1->system_init() @System_init.cpp
在system_init()我们看到了循环闭合管理框架。
Call "com/android/server/SystemServer", "init2"
…..
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
init2()@SystemServer.java中建立了Android中所有要用到的服务。
这个init2()建立了一个线程,来New Service和AddService来建立服务
第三步 Home启动
后半段,我们可以看到系统在启动完所有的Android服务后,做了这样一些动作:
(1) 使用xxx.systemReady()通知各个服务,系统已经就绪。
(2) 特别对于ActivityManagerService.systemReady(回调)
Widget.wallpaper,imm(输入法)等ready通知。
Home就是在ActivityManagerService.systemReady()通知的过程中建立的。下面是ActivityManagerService.systemReady()的伪代码:
systemReady()@ActivityManagerService.java
resumeTopActivityLocked()
startHomeActivityLocked();//如果是第一个则启动HomeActivity。
startActivityLocked(。。。)CATEGORY_HOME android 启动流程
In this topic you will learn some information about Android process management. First let’s take a look at the launched processes during Android booting.
USER PID PPID VSIZE RSS WCHAN PC NAME
root 1 0 264 176 c00acc6c 0000c36c S /init
root 28 1 724 308 c0051354 afe0c4cc S /system/bin/sh
system 30 1 796 248 c026516c afe0b74c S /system/bin/servicemanager
root 31 1 1824 316 ffffffff afe0b50c S /system/bin/mountd
root 32 1 652 248 c02976e0 afe0c0bc S /system/bin/debuggerd
radio 33 1 5344 664 ffffffff afe0bdbc S /system/bin/rild
root 34 1 71028 18828 c00ad308 afe0b874 S zygote
media 37 1 16812 3456 ffffffff afe0b74c S /system/bin/mediaserver
root 39 1 788 288 c02f9ae4 afe0b50c S /system/bin/installd
system 86 34 187756 21836 ffffffff afe0b74c S system_server
radio 118 34 103476 13896 ffffffff afe0c824 S com.android.phone
app_4 124 34 117848 19248 ffffffff afe0c824 S android.process.acore
app_5 139 34 98672 11516 ffffffff afe0c824 S com.android.mms
app_3 151 34 92096 10976 ffffffff afe0c824 S com.android.alarmclock
app_6 161 34 94436 12616 ffffffff afe0c824 S com.android.calendar
app_9 173 34 93248 11728 ffffffff afe0c824 S android.process.media
app_15 182 34 91848 9764 ffffffff afe0c824 S com.android.voicedialer
app_16 190 34 94524 10812 ffffffff afe0c824 S android.process.im
They can be divided into three kinds.
Root Process
init is the first process after kernel booting. The major task it performs:
l Parser and execute init.rc and init.%hardware%.rc
l Automatically generate device node under /dev
l Start log and property service
l Monitor for device, property set and child process exit events
Native Application Process
According to init.rc, init will fork the following native application process.
console: star a shell.
servicemanager: start binder IPC service manager.
mountd: mount all fs defined in /system/etc/mountd.conf if started, receive commands through local socket to mount any fs.
debuggerd: start debug system.
rild: start radio interface layer daemon.
zygote: start Android Java VM Runtime and start system server. It’s the most important process.
mediaserver: start AudioFlinger, MediaPlayerService and CameraService.
installd: start install package daemon.
JAVA Application Process
Every JAVA application process is forked from zygote process. system_server is a special JAVA process, which is directly forked from zygote.. Other JAVA process is created from ActivityManagerService(run in system_server process) like this.
int pid = Process.start("android.app.ActivityThread",
mSimpleProcessManagement ? app.processName : null, uid, uid,
gids, ((app.info.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_DEBUGGABLE) != 0), null);
While Process.java use UNIX domain socket to communicate with zygote. So the overall picture is shown as following.
android 启动流程

System Server
It’s the first JAVA application launched by zygote. It starts the core Android services, e.g. ActivityManager, WindowManager, PackageManager etc. It’s the Android core engine.
Persistent Application
During booting, ActivityManagerService.systemReady will start all persistent applications.
List apps = ActivityThread.getPackageManager().
getPersistentApplications(PackageManager.GET_SHARED_LIBRARY_FILES);
if (apps != null) {
int N = apps.size();
int i;
for (i=0; i<N; i++) {
ApplicationInfo info
= (ApplicationInfo)apps.get(i);
if (info != null &&
!info.packageName.equals("android")) {
addAppLocked(info);
}
}
Currently only Phone application is registered as a persistent app in AndroidManifest.xml like this.
<application android:name="PhoneApp"
android:persistent="true"
android:label="@string/dialerIconLabel"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher_phone">
So during booting, only phone application is automatically launched. It’s the “com.android.phone” process.
The First Activity
The first activity is launched by senting Intent.CATEGORY_HOME intent from ActivityManagerService.
Intent intent = new Intent(
mTopAction,
mTopData != null ? Uri.parse(mTopData) : null);
intent.setComponent(mTopComponent);
if (mFactoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME);
}
ActivityInfo aInfo =
intent.resolveActivityInfo(mContext.getPackageManager(),
PackageManager.GET_SHARED_LIBRARY_FILES);
if (aInfo != null) {
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(
aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, aInfo.name));
// Don't do this if the home app is currently being
// instrumented.
ProcessRecord app = getProcessRecordLocked(aInfo.processName,
aInfo.applicationInfo.uid);
if (app == null || app.instrumentationClass == null) {
intent.setFlags(intent.getFlags() | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
startActivityLocked(null, intent, null, null, 0, aInfo,
null, null, 0, 0, 0, false);
}
It’s the “android.process.acore” process. (The process name is defined in AndroidManifest.xml)
Auto-launched Application After Booting
When activity idle is detected in ActivityManagerService, it will broadcast ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED intent at the first time.
if (mFactoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
// Tell anyone interested that we are done booting!
synchronized (this) {
broadcastIntentLocked(null, null,
new Intent(Intent.ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED, null),
null, null, 0, null, null,
android.Manifest.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED,
false, false, MY_PID, Process.SYSTEM_UID);
}
Currently, MMS, AlarmClock, Calendar, MediaProvider, VoiceDialer and IM have registered as a receiver for ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED intent in their AndroidManifest.xml. So they will be automatically launched. (This explains the remained JAVA process.)
Email also registers as a receiver for ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED intent in its AndroidManifest.xml, but it defines android:enable=”false”. So it won’t be launched.
<receiver android:name=".service.BootReceiver"
android:enabled="false"
>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.DEVICE_STORAGE_LOW" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.DEVICE_STORAGE_OK" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
DownloadProvider also registers as a receiver for ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED intent in its AndroidManifest.xml, but it defines android:exported=”false”. So it won’t be launched.
<receiver android:name=".DownloadReceiver" android:exported="false">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED" />
<action android:name="android.net.conn.CONNECTIVITY_CHANGE" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
Behind the JAVA process
system_server is a special case. It calls ActivityThread.java’s systemMain static function, which creates an instance of ActivityThread. ActivityThread then creates an instance of ApplicationThread, Application and ApplicationContext.
Every other JAVA process works in a different way. It’s controlled by system_server while forked by zygote. When any JAVA process other than system_server is forked from zygote, it automatically calls ActivityThread.java’s main static function(See Process.java and the following code snippet).
try {
ZygoteInit.invokeStaticMain(cloader, className, mainArgs);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logAndPrintError (newStderr, "Error starting. ", ex);
}
The ActivityThread.java’s main function creates an instance of ActivityThread. ActivityThread then creates an instance of ApplicationThread. The ApplicationThread will work as an IBinder object to interact with ActivityManagerService in system_server. The new process does nothting at this time other than waiting IPC call from system_server. The Application and ApplicationContext object won’t be created at this time. Actually it’s deferred to when the process really works, eg. start an activity, receive intent or start a service.
For example, when start an activity, ActivityManagerService know which process the to-be-launched activity should run in, so it will RPC call ApplicationThread’s scheduleLaunchActivity to launch a new activity in that process. ApplicationThread then post a message to let ActivityThread know it needs to start an activity. ActivityThread then creates Application and ApplicationContext object. After that, it calls Instrumentation, then Instrumentation finally calls JAVA dalvik VM to really create an activity JAVA object.