第一章 Oracle Architectural基础结构
第1讲00
oracle体系结构包含两个部分:
1、instance
2、database
重要概念
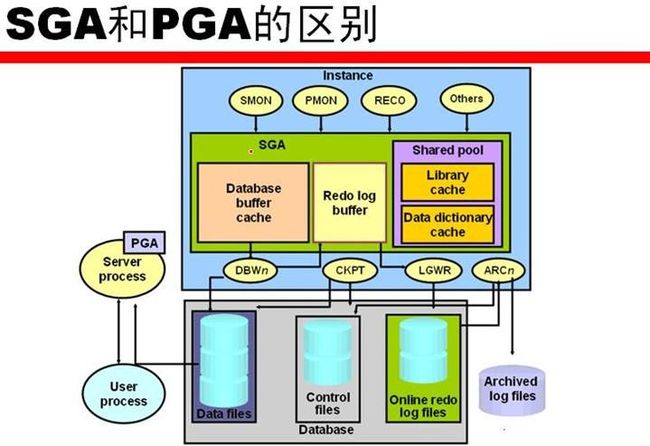
Oracle Server:数据库管理系统(管理信息),包含两个部分(oracle instance和oracle database)
Oracle Instance:访问oracle database(物理数据文件)的一种手段。一个instance只能对应一个database。由后台内存块和后台进程组成。
Connection & Session:Connection是oracle客户端进程与服务器进程建立的tcp连接,连接一开始就创建一个会话session
Oracle Database:由物理文件组成,包含三种类型的文件(data files、control files、redo log files)
Oracle内存结构:SGA(system global area)在一个instance启动时分配而且是instance的基本组成部分。
(ipcs和show sga查看,在linux下其实就是共享内存)
PGA(programglobal area)当server process(客户端连接服务器)启动时分配
第2讲01
SGA:包括shared pool(共享池)、database buffer cache、redo log buffer和可选的large pool和java pool。
9i以后可以动态调整sga大小(SGA_MAX_SIZE)单位是granule size(sga小于128M单位是4M,超过128M单位是16M)
查看SGA大小sql语句:selectcomponent, granule_size from v$sga_dynamci_components;
了解详细参数含义可以查看联机文档
Shared Pool
Used to store:
--Most recently executed sql statements
--Most recently used data definitions
It consists of two key performance-related memory structures:
--Library Cache
--Data Dictionary Cache
Sized by the parameter
SHARED_POOL_SIZE
sql> alter system set SHARED_POOL_SIZE=64M;
Library Cache:
--Stores information about the most recently used SQL and PL/SQL statements(解析过的sql语 句,它的大小决定解析sql语句的快慢)
--Enables the sharing of commonly used statements
--Is managed by a least recently used (LRU) algorithm
(使用最近最少使用LRU算法来管理)
--Consists of two structure:
-Shared SQL area
-Shared PL/SQL area
--Size determined by the Shared Pool sizing
(大小取决于共享池大小)
Data Dictionary Cache:(数据字典缓冲)
--A collection of the most recently used definitions in the database
(包含在数据库中一组最近使用的定义)
--Includes information about database files, tables, indexes, columns, users, privileges, and other database objects
(包含了关于数据库文件、表、索引、列、用户、权限和其他数据库对象)
--During the parse phase, the server process looks at the data dictionary for information to resolve object names and validate access
(在解析阶段,服务器进程查看数据字典信息来解决对象名称和验证访问)
--Caching data dictionary information into memory improves response time on queries and DML
(在查询和DML时,缓存到内存的数据字典信息可以改善响应时间)
--Size determined by the Shared Pool sizing
Database Buffer Cache(真正用来存储数据的缓冲区)
--Store copies of data blocks that have been retrieved from the data files
(存储从物理数据文件中获得的数据块副本)
--Enables great performance gains when you obtain and update data
--Managed through and LRU algorithm
--DB_BLOCK_SIZE determines primary block size
(数据库块的大小决定了主要的块大小)
--Consists of independent sub caches:
-DB_CACHE_SIZE
-DB_KEEP_CACHE_SIZE
-DB_RECYCLE_CACHE_SIZE
--Can be dynamically resized
-sql>alter system set DB_CACHE_SIZE=96M;
--DB_CACHE_ADVICE set to gather statistics for predicting different cache size behavior
(数据库性能调优时是否统计收集在不同cache size大小时的数据库行为)
--Statistics displayed by V$DB_CACHE_ADVICE
(统计结果存在V$DB_CACHE_ADVICE这张表中)
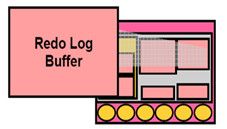
--Records all changes made to the database data blocks
(记录所有数据库中数据块的成功改变)
--Primary purpose is recovery
(主要目的是恢复)
--Changes recorded within are called redo entries
(改变记录内部称为重做条目)
--Redo entries contain information to reconstruct or redo changes
(重做条目包含的信息用来来重建或重做更改)
--Size defined by LOG_BUFFER
可选项Large Pool和Java Pool
PGA:Memory reserved for each user process connecting to an Oracle database.
Allocated when a process is create.
Deallocated when the process is terminated.
Used by only one process.
第3讲02
User Process:客户端连接oracle后的客户端进程
Server Process:有客户端连接时与该客户端进程连接的服务器进程
Background Process:名字格式ora_xxxx_sid,分两种
必须的DBWn、PMON、CKPT、LGWR、SMON
可选的ARCn、LMDn、QMNn、CJQ0、LMON、RECO、Dnnn、LMS、Snnn、LCKn、 Pnnn
后面字母为小写n的表示可能有多个该进程,从0开始
![]() 三者之间的关系类似为:oracle整体相当于一个工厂,background process相当于这个工厂的生产线上的工人,server process相当于销售科的人,user process相当于客户,客户想要下订单要找销售科的人然后销售科的人再找生产部门生产
三者之间的关系类似为:oracle整体相当于一个工厂,background process相当于这个工厂的生产线上的工人,server process相当于销售科的人,user process相当于客户,客户想要下订单要找销售科的人然后销售科的人再找生产部门生产
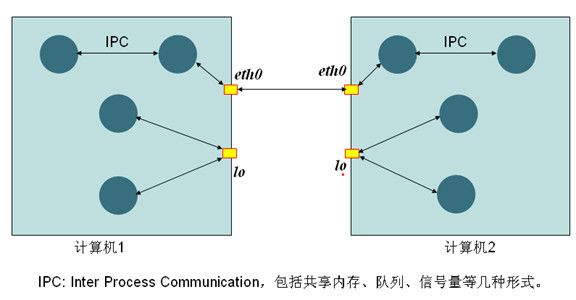
远程连接oracle与本地连接oracle(TCP/IP & IPC):
![]()
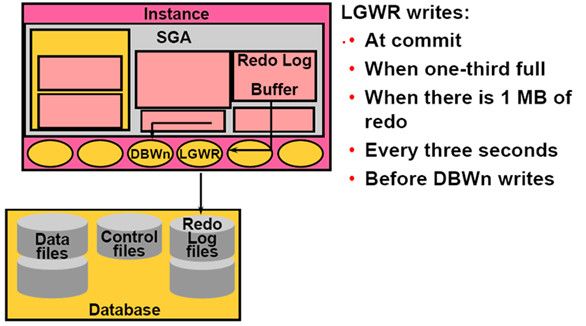
Database Writer(DBWn):
Log Writer(LGWR):
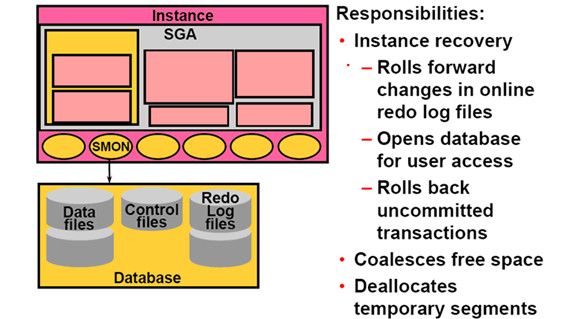
System Monitor(SMON):(监视整个系统)
Process Monitor(PMON):(监控进程)
Checkpoint(CKPT):
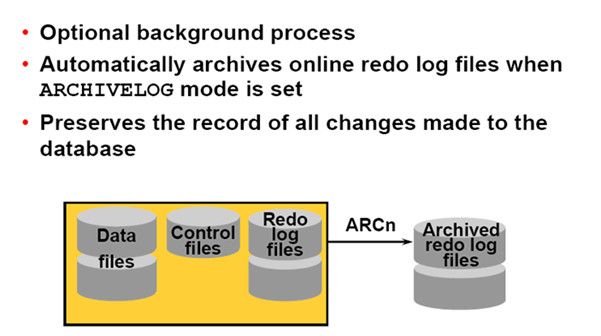
Archiver(ARCn):(归档)
Oracle逻辑结构:
Oracle处理SQL语句的过程:
-
连接一个实例,用到的进程(User process和Server process)
-
安全检查
-
根据SQL语句的类型(查询、DML、Commit)决定使用那些oracle服务器组件
-
解析SQL语句为原子操作再执行
第4讲03一些概念的区别与联系