NUnit详细使用方法
前一段时间,有人问我在.NET里如何进行TDD开发.这个问题促使我想对NUnit做一个详细的介绍.因为我们大家都知道NUnit是在.NET进行TDD的利器.
如果你已经知道很多关于NUnit的应用,请指出我的不对之处和提出一些建议,使本文更加完善.如果你对NUnit还不是很了解的话,我建议你还是阅读一下.
1. TDD的简介
2.NUnit的介绍
2.1 NUnit的介绍
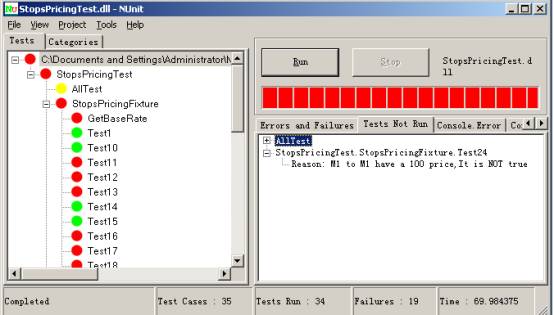
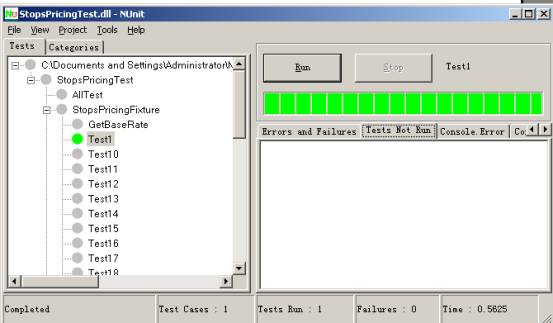
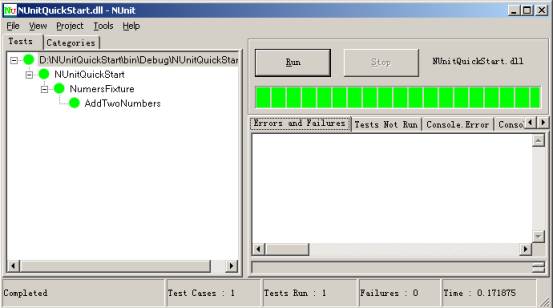
- 绿色 描述目前所执行的测试都通过
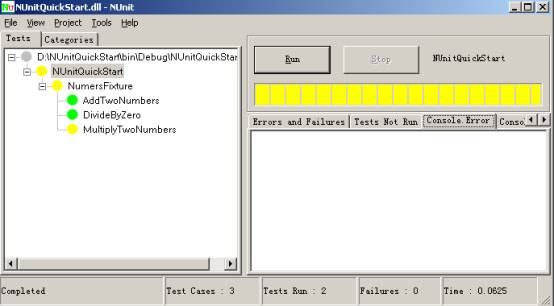
- 黄色 意味某些测试忽略,但是这里没有失败
- 红色 表示有失败
- 状态.说明了现在运行测试的状态。当所有测试完成时,状态变为Completed.运行测试中,状态是Running: <test-name> (<test-name>是正在运行的测试名称)。
- Test Cases说明加载的程序集中测试案例的总个数。这也是测试树里叶子节点的个数。
- Tests Run 已经完成的测试个数。
- Failures 到目前为止,所有测试中失败的个数.
- Time 显示运行测试时间(以秒计)
- New Project允许你创建一个新工程。工程是一个测试程序集的集合。这种机制让你组织多个测试程序集,并把他们作为一个组对待。
- Open 加载一个新的测试程序集,或一个以前保存的NUnit工程文件。
- Close关闭现在加载的测试程序集或现在加载的NUnit工程。
- Save 保存现在的Nunit工程到一个文件。如果正工作单个程序集,本菜单项允许你创建一个新的NUnit工程,并把它保存在文件里。
- Save As允许你将现有NUnit工程作为一个文件保存。
- Reload 强制重载现有测试程序集或NUnit工程。NUnit-Gui自动监测现加载的测试程序集的变化。
- Recent Files 说明5个最近在NUnit中加载的测试程序集或NUnit工程(这个列表在Windows注册表,由每个用户维护,因此如果你共享你的PC,你仅看到你的测试)。最近程序集的数量可以使用Options菜单项修改,可以访问Tool主菜单。
- Exit退出。
- View菜单有以下内容:
- Expand一层层扩展现在树中所选节点
- Collapse 折叠现在树中选择的节点
- Expand All递归扩展树中所选节点后的所有节点
- Collapse All递归折叠树中所选节点后的所有节点
- Expand Fixtures扩展树中所有代表测试fixture的节点。
- Collapse Fixtures 折叠树中所有代表测试fixture的节点。
- Properties 显示树中现所选节点的属性。
- Tools 菜单由这些项:
- Save Results as XML作为一XML文件保存运行测试的结果。
- Options让你定制NUnit的行为。
- Errors and Failures 窗口显示失败的测试。在我们的例子里,这个窗口是空。
- Tests Not Run 窗口显示没有得到执行的测试。
- Console.Error 窗口显示运行测试产生的错误消息。这些此消息是应用程序代码使用Console.Error输出流可以输出的。
- Console.Out窗口显示运行测试打印到Console.Error输出流的文本消息。
2.2 一些常用属性
- TestFixture
- Test
TestFixtureAttribute
- 必须是Public,否则NUnit看不到它的存在.
- 它必须有一个缺省的构造函数,否则是NUnit不会构造它.
- 构造函数应该没有任何副作用,因为NUnit在运行时经常会构造这个类多次,如果要是构造函数要什么副作用的话,那不是乱了.
1using System;
2using NUnit.Framework;
3namespace MyTest.Tests
4{
5
6[TestFixture]
7publicclassPriceFixture
8{
9//
10}
11}
12
TestAttribute
public void MethodName()
1using System;
2using NUnit.Framework;
3
4namespace MyTest.Tests
5{
6[TestFixture]
7publicclassSuccessTests
8{
9[Test]publicvoidTest1()
10{/*
*/}
11}
12}
13
14
一般来说,有了上面两个属性,你可以做基本的事情了.
另外,我们再对如何进行比较做一个描述。
在NUnit中,用Assert(断言)进行比较,Assert是一个类,它包括以下方法:AreEqual,AreSame,Equals, Fail,Ignore,IsFalse,IsNotNull,具体请参看NUnit的文档。
3.如何在.NET中应用NUnit
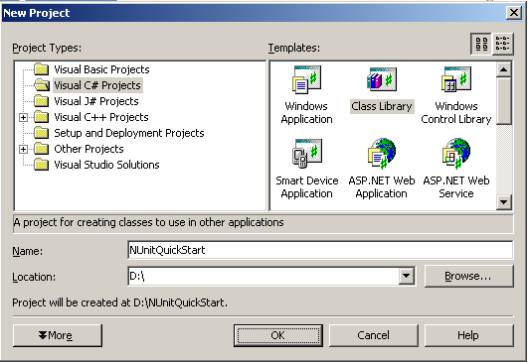
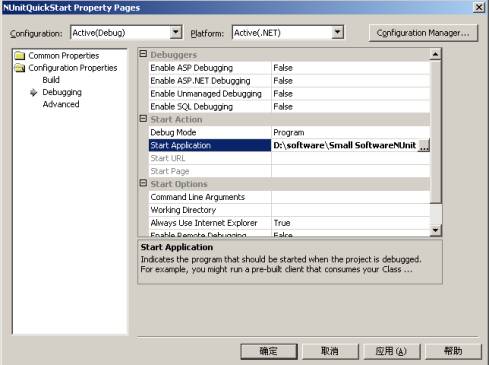
第1步.为测试代码创建一个Visual Studio工程。
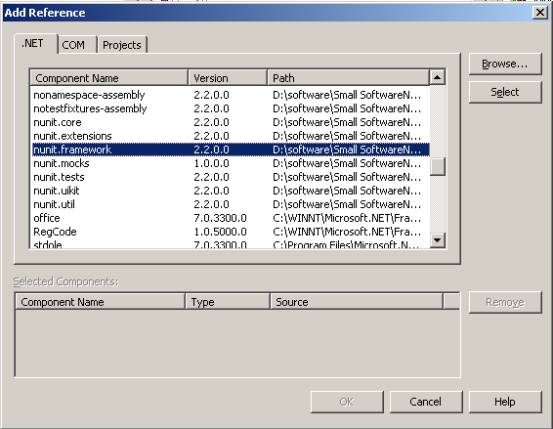
第2步.增加一个NUnit框架引用
第3步.为工程加一个类.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
第4步.建立你的Visual Studio 工程,使用NUnit-Gui测试
第5步.编译运行测试.
4.其他的一些核心概念
SetUp/TearDown 属性
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
这样NUnit将在执行每个测试前执行标记SetUp属性的方法.在本例中就是执行InitializeOperands()方法.记住,这里这个方法必须为public,不然就会有以下错误:Invalid Setup or TearDown method signature
ExpectedException
1[Test]
2[ExpectedException( typeof (DivideByZeroException))]
3public void DivideByZero()
4{
5intzero=0;
6intinfinity=a/zero;
7Assert.Fail("Shouldhavegottenanexception");
8}
9
Ignore 属性
1[Test]
2[Ignore( " Multiplicationisignored " )]
3public void MultiplyTwoNumbers()
4{
5intproduct=a*b;
6Assert.AreEqual(2,product);
7}
TestFixtureSetUp/TestFixtureTearDown
1using NUnit.Framework;
2
3[TestFixture]
4public class DatabaseFixture
5{
6[TestFixtureSetUp]
7publicvoidOpenConnection()
8{
9//opentheconnectiontothedatabase
10}
11
12[TestFixtureTearDown]
13publicvoidCloseConnection()
14{
15//closetheconnectiontothedatabase
16}
17
18[SetUp]
19publicvoidCreateDatabaseObjects()
20{
21//inserttherecordsintothedatabasetable
22}
23
24[TearDown]
25publicvoidDeleteDatabaseObjects()
26{
27//removetheinsertedrecordsfromthedatabasetable
28}
29
30[Test]
31publicvoidReadOneObject()
32{
33//loadonerecordusingtheopendatabaseconnection
34}
35
36[Test]
37publicvoidReadManyObjects()
38{
39//loadmanyrecordsusingtheopendatabaseconnection
40}
41}
42
43
Test Suite
1
 namespace
NUnit.Tests
namespace
NUnit.Tests
2
 {
{
3 usingSystem;
usingSystem;
4 usingNUnit.Framework;
usingNUnit.Framework;
5
6
7
8 publicclassAllTests
publicclassAllTests
9 {
{
10 [Suite]
[Suite]
11 publicstaticTestSuiteSuite
publicstaticTestSuiteSuite
12 {
{
13 get
get
14 {
{
15 TestSuitesuite=newTestSuite("AllTests");
TestSuitesuite=newTestSuite("AllTests");
16 suite.Add(newOneTestCase());
suite.Add(newOneTestCase());
17 suite.Add(newAssemblies.AssemblyTests());
suite.Add(newAssemblies.AssemblyTests());
18 suite.Add(newAssertionTest());
suite.Add(newAssertionTest());
19 returnsuite;
returnsuite;
20 }
}
21 }
}
22 }
}
23 }
}
24
 Category属性
Category属性
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
1using System;
2using NUnit.Framework;
3
4namespace NUnitQuickStart
5{
6[TestFixture]
7publicclassNumersFixture
8{
9privateinta;
10privateintb;
11[SetUp]
12publicvoidInitializeOperands()
13{
14a=1;
15b=2;
16}
17
18[Test]
19[Category("Numbers")]
20publicvoidAddTwoNumbers()
21{
22intsum=a+b;
23Assert.AreEqual(sum,3);
24}
25
26[Test]
27[Category("Exception")]
28[ExpectedException(typeof(DivideByZeroException))]
29publicvoidDivideByZero()
30{
31intzero=0;
32intinfinity=a/zero;
33Assert.Fail("Shouldhavegottenanexception");
34}
35[Test]
36[Ignore("Multiplicationisignored")]
37[Category("Numbers")]
38publicvoidMultiplyTwoNumbers()
39{
40intproduct=a*b;
41Assert.AreEqual(2,product);
42}
43
44}
45
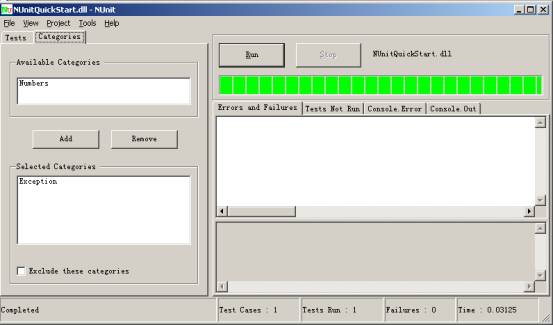
NUnit-GUI界面如图5-2:
图5-2:使用Catagories属性的界面
Explicit属性
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Expected Exception属性
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
5 . 测试生命周期合约
1using System;
2using NUnit.Framework;
3[TestFixture]
4public class LifeCycleContractFixture
5{
6[TestFixtureSetUp]
7publicvoidFixtureSetUp()
8{
9Console.Out.WriteLine("FixtureSetUp");
10}
11
12[TestFixtureTearDown]
13publicvoidFixtureTearDown()
14{
15Console.Out.WriteLine("FixtureTearDown");
16}
17
18[SetUp]
19publicvoidSetUp()
20{
21Console.Out.WriteLine("SetUp");
22}
23
24[TearDown]
25publicvoidTearDown()
26{
27Console.Out.WriteLine("TearDown");
28}
29
30[Test]
31publicvoidTest1()
32{
33Console.Out.WriteLine("Test1");
34}
35
36[Test]
37publicvoidTest2()
38{
39Console.Out.WriteLine("Test2");
40}
41
42}
43
44
FixtureSetUp
SetUp
Test 1
TearDown
SetUp
Test 2
TearDown
FixtureTearDown

6) NUnit中文文档: http://www.36sign.com/nunit
Last Updated:2007年4月12日
posted on 2005-06-20 17:01 Confach 阅读(22232) 评论(76) 编辑 收藏 所属分类: 框架&库 、敏捷软件开发