linux kernel中的免锁算法
在《LINUX设备驱动程序》(第三版)有几页对免锁算法的实现进行了分析。对于作者的分析有两点我想在这里作更加细致的说明。一是作者对循环缓冲的分析,当缓冲区满时分析错了;二是作者没有对里面的实现技巧作详细的介绍。针对以上两点,本文就用2.6.11(2.6.10和2.6.11是一样的)的kfifo.h和kfifo.c代码实现的免锁算法进行较为详细的分析。
对于临界区的访问一般的做法是在访问前加锁,退出访问时解锁,在加锁的过程中可能会有漫长的等待时间,也因此可能会影响到效率。如果在安全的情况下能够进行免锁访问无疑是可以提高效率,使人振奋。当然做任何事情都受一定的环境、条件的影响和制约,免锁算法的实现也不例外。那么在什么情况下可以实现和使用免锁算法呢,其实代码的作者Stelian在kfifo.c的注释代码行115--117已明确告诉了我们,如果只有一个读者和一个写者并发访问临界区的话就可以免锁。
以下是kfifo.h中声明的循环缓冲数据结构:
| 29 struct kfifo {
30 unsigned char *buffer; /* the buffer holding the data */
31 unsigned int size; /* the size of the allocated buffer */
32 unsigned int in; /* data is added at offset (in % size) */
33 unsigned int out; /* data is extracted from off. (out % size) */
34 spinlock_t *lock; /* protects concurrent modifications */
35 };
缓冲区buffer是以字节为单位的循环缓冲区
size是缓冲区的大小
in是写入数据时以 (in % size) 运算取得在buffer中的写下标
out是读取数据时以 (out % size) 运算取得在buffer中的读下标 |
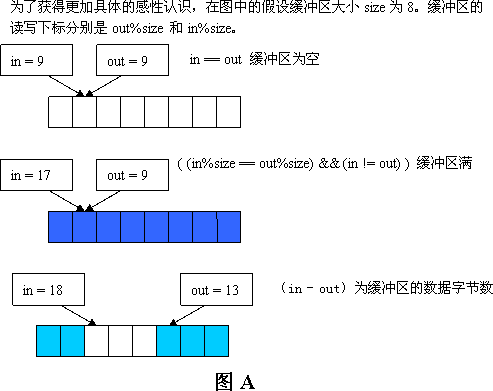
缓冲区buffer, size, in, out以一定的逻辑关系在代码中组织起来, 下面结合图A分析一下它们的特征和逻辑关系:
1. 缓冲区的特性是当缓冲区满时,不允许向缓冲区写数据,即缓冲区中的数据不会被覆盖,缓冲区的数据为空时不会读取无用的数据。
2. 在语义上in总是大于等于out,因此总会有( out + len ) <= in ,而len的取值范围是0 <= len <= size-1。注意这里是这语义上是in和out总是这样的关系,其实在实际运算时如果不会超出无符号整形的表示范围,in和out的关系无论是语义上还是逻辑上都是这种关系。
3. 当 (in == out) 时,缓冲区中的数据为空。当( (in != out) && ((in % size) == (out % size)) ) 时,也即它们的读写下标相等,而in和out不等时,表示缓冲区满。这种缓冲区满的情况是数据占满了所有的缓冲空间,并非《LINUX设备驱动程序》(第三版)描述的那样有一个字节浪费的情况。
4. 在kfifo.c代码的72--79行确保了size的值是2的n次方。
5. 循环缓冲区的数据字节数为(in - out),我们用BUF_DATA_BYTES来表示。相应地(size - (in - out))则表示循环缓冲区还有多少字节的空闲空间,我们就用BUF_FREE_SPACE来表示。
6. (size - (in % size))表示从写下标开始到循环缓冲结束有多少字节数,我们用WRETE_INDEX_TO_BUF_END_BYTES表示。相应地(size - (out % size))表示从读下标开始到循环缓冲结束有多少字节数,我们用READ_INDEX_TO_BUF_END_BYTES。
kfifo.c代码行数不多,而我们要在这里要分析的代码则更少,主要是对缓冲区的读写接口get/put分析:
|
...............// 点代表省略的代码
72 /*
73 * round up to the next power of 2, since our 'let the indices
74 * wrap' tachnique works only in this case.
75 */
// 这里的操作是确保size的值为2的n次方
76 if (size & (size - 1)) {
77 BUG_ON(size > 0x80000000);
78 size = roundup_pow_of_two(size);
79 }
...............
105 /*
106 * __kfifo_put - puts some data into the FIFO, no locking version
107 * @fifo: the fifo to be used.
108 * @buffer: the data to be added.
109 * @len: the length of the data to be added.
110 *
111 * This function copies at most 'len' bytes from the 'buffer' into
112 * the FIFO depending on the free space, and returns the number of
113 * bytes copied.
114 *
115 * Note that with only one concurrent reader and one concurrent
116 * writer, you don't need extra locking to use these functions.
117 */
118 unsigned int __kfifo_put(struct kfifo *fifo,
119 unsigned char *buffer, unsigned int len)
120 {
121 unsigned int l;
122
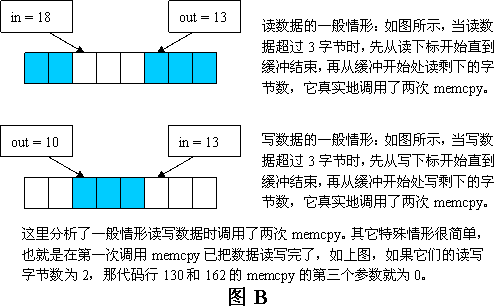
// 读这段程序可结合图B的分析
// min函数的第二个参数实为(fifo->size - (fifo->in - fifo->out)),
// 很显然它就是上面提到的BUF_FREE_SPACE,BUF_FREE_SPACE和本
// 函数__kfifo_put 参数len比较求出的最小值就是本次要写入循环缓冲区
// 的字节个数,也即调用min函数后len为要写入循环缓冲区的真正字节个数
// 注意:这里的fifo->size可能是小于fifo->in,但fifo->size,
// fifo->in, fifo->out三者都是无符号整形,运算中的逻辑不会出错,这
// 个技巧后面再解释。
123 len = min(len, fifo->size - fifo->in + fifo->out);
124
125 /* first put the data starting from fifo->in to buffer end */
/* 首先把数据写到从写下标开始到缓冲buffer结束 */
// (fifo->in & (fifo->size - 1))和(fifo->in % fifo->size)是等价的,
// 这一技巧后面再解释。既然它们是等价的,那么
// fifo->size - (fifo->in & (fifo->size - 1))就是
// WRETE_INDEX_TO_BUF_END_BYTES。函数min目的就很显然了,它求出来的
// 是要写的字节数,而这字节数的范围是:从写下标开始到循环缓冲结束。
126 l = min(len, fifo->size - (fifo->in & (fifo->size - 1)));
127 memcpy(fifo->buffer + (fifo->in & (fifo->size - 1)), buffer, l);
128
129 /* then put the rest (if any) at the beginning of the buffer */
/* 然后如果还有数据没有写入,就把剩下的字节数len - l 从缓冲
* 区buffer的开始处写入剩余数据
*/
130 memcpy(fifo->buffer, buffer + l, len - l);
131
// 注意fifo->in只有加没有减,当它达到它所能表达的最大范围时会遵循
// 无符号整形的规则,这也是使用了无符号整形的技巧,也将在后面解释。
132 fifo->in += len;
133
134 return len;
135 }
136 EXPORT_SYMBOL(__kfifo_put);
137
138 /*
139 * __kfifo_get - gets some data from the FIFO, no locking version
140 * @fifo: the fifo to be used.
141 * @buffer: where the data must be copied.
142 * @len: the size of the destination buffer.
143 *
144 * This function copies at most 'len' bytes from the FIFO into the
145 * 'buffer' and returns the number of copied bytes.
146 *
147 * Note that with only one concurrent reader and one concurrent
148 * writer, you don't need extra locking to use these functions.
149 */
150 unsigned int __kfifo_get(struct kfifo *fifo,
151 unsigned char *buffer, unsigned int len)
152 {
153 unsigned int l;
154
// 读这段程序可结合图B的分析
// 调用min函数后len为要读取的真正字节个数
155 len = min(len, fifo->in - fifo->out);
156
157 /* first get the data from fifo->out until the end of the buffer */
/* 首先从读下标开始读取数据直到缓冲结束 */
158 l = min(len, fifo->size - (fifo->out & (fifo->size - 1)));
159 memcpy(buffer, fifo->buffer + (fifo->out & (fifo->size - 1)), l);
160
161 /* then get the rest (if any) from the beginning of the buffer */
/* 如果没有读完所需的字节数据,就从缓冲的开始读取剩下的字节 */
162 memcpy(buffer + l, fifo->buffer, len - l);
163
// fifo->out也是只有加没有减,跟fifo->in类似
164 fifo->out += len;
165
166 return len;
167 }
168 EXPORT_SYMBOL(__kfifo_get); |
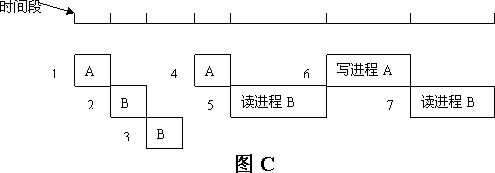
现在我们结合图C分析一个读者和一个写者并发访问循环缓冲区的一个情景,看看免锁的情形具体是怎样的。首先假设size为8,out为0,in为5, A进程要写10字节数据到循环缓冲, B进程要从循环缓冲读15字节的数据。为了方便描述,我们把A进程简称为A, B进程简称为B。下面对两进程A、B的7个时间段作假设性的分析:
1. 当A执行完 时间段1时,它把3字节数据写入了循环缓冲。但是A刚好执行到kfifo.c的第131行,而132行的写下标更新代码还没执行就调度进程B。在这种情形下,数据虽然写入到循环缓冲,但是写下标还没有更新,所以逻辑上缓冲区的字节数还是in-out即5。
2. 假如B在第2个时间段读完了缓冲中所有的数据并更新了读下标,那么第2个时间段结束时,in和out的值都为5,表明缓冲中的数据为空。
3. 在第3个时间段还是调度B,虽然A已把数据写入缓冲,但是还没有更新写下标,in和out的值都为5,缓冲中的数据看上去还是为空,那么B就可以直接调用调度程序而放弃CUP。
4. 第4时间段A把写下标更新,调度程序又调度B进程。
5. 执行完第4时间段,in的值为8,out为5,有3字节的数据在缓冲。第5时间段B把3字节数据读完后调用调度程序放弃CPU。
6. 第6时间段A把所有要写的数据写入了缓冲,第7时间段B读出了它要读的字节数。
在这第3个时间段可看出,读进程本质上已是在等待(写进程等待情况也类似),但它不是加锁解锁的睡眠唤醒等待方式,它可以主动放弃CPU或轮循的方式。无论任何时候当读进程被调度时,读进程又可以随时访问缓冲区这个临界区,而不受锁的限制。由此可见免锁的目的达到了。
免锁的目的达到了,但是kfifo.c又是如何保证数据的正确性呢?保证读数据的正确性和保证写数据的正确性情况类似,在这里就只讨论写数据的情况。写数据时正确性的保证有两点:一是写数据和写下标更新的先后顺序;二是求出正确的可写字节数。
(一)在__kfifo_put接口中总体上是先写数据后更新写下标,这就确保了读进程读到的数据是正确了。如果反过来先更新写下标后写数据的话,而读写进程是并发访问的,那么写进程有可能在更新下标后就进入睡眠等待状态而把CPU交给了读进程,这样读进程极有可能读到不正确的数据。因为写下标的更新表明了原来的更新范围内的空闲空间变成了有数据的空间,也即变成了读进程可以读取数据的空间,而实际上写进程还没有把数据写进去。
(二)在代码的123行,通过和剩余空闲空间的比较,求出了正确的可写字节数,确保写数据时不会覆盖掉缓冲中已存在的数据。
最后把这一免锁算法用到的一些技巧作一些解释说明:
1. 二进制技巧:
如果一个数是2的n次方减1,那么它的低n位都是1,其它位都为0。当一个数要被2的n次方整除,那么它的低n位就必须为0,相反如果这个数的低n位不全为0那么这个数就不能被2的n次方整除。而一个数的低n位就是对2的n次方数据求模运算的余数。
例如一个数要被8(2的3次方)整除,它的二进制低3位就得为0。如在16位机器中16和32的二进制分别是0000 0000 0001 0000和0000 0000 00010 0000,它们的低3 位全为0。而19和33在16位机器中的二进制分别是0000 0000 0001 0011和0000 0000 000100001,它们的低3位都不全为0,低3位是对8进行求模运算的余数。能被2的n次方整除的这个特性还有别外的叫法:以某某(一般都是2的n次方)字节对齐,以某某字节为边界。如以8字节对齐,以页面对齐等等。知道这一特性就可以用'&'操作判断某一变量是否是以某某字节对齐,例如判断变量x是否以8字节对齐 if(x&8), 也即x是否能被8整除或者说x是否是以8字节为边界。
那么又如何解释(fifo->in & (fifo->size - 1))和(fifo->in % fifo->size)是等价的呢?还是假设fifo->size为8,8是2 的3次方。(8-1)就是7,也就是低3位为1其它高位为0的二进制数据。7和一个整数进行&操作就是求一个数的低3位,也就是对整数8进行求模的余数。
2. 无符号整形技巧:
在32位机器中无符号整数的最大值是4294967295,最小值是0。那么就有这样的运算:((0-1) == 4294967295)、((0-2) == 4294967294),相反则((4294967295+1)== 0)、((4294967295+2)== 1)。
根据无符号的以上特性,可以解释kfifo.c的程序代码132和164行fifo->in和fifo->out只有不断地加而没有减小的运算情况。当fifo->in和fifo->out的值超过了无符号整形能表示的最大值时,它们又可以从无符号整形最小值0开始。假如当fifo->in已超过了无符号整形最大值并且数据值现在已为2,而fifo->out值为4294967294,这时((fifo->out + 4) == fifo->in),因此有上面提到的当len的取值范围是0 <= len <= fifo->size-1,语义上总会有(fifo->out + len) <= fifo->in。
在kfifo.c代码中都统一用了无符号整形,没有和其它的有符号一起混用,这种处理效率会比多种类型值混用的运算效率会更高,因为不同类型的数据一起运算时要先进行数据类型的转换。
另外要注意的是无符号整形和有符号整形一起运算时,首先会把有符号整形转换为无符号整形,其运算结果是无符号的整形数据。运算时要特别注意无符号整形的范围,更是要注意0值范围。我曾两次查找过别人在这方面出现的BUG。BUG类似于这样:if((x-y) > 0),x是无符号的整形,当x小于y时这个条件判断就会有问题了。因为是无符号运算,x小于y时,算出来的结果超出了无符号最小值0的范围,所以结果会变成远远大于0的值,致使最终判断有误。一个建议是不要在这种情况下用符号整形的运算。
3. 循环缓冲技巧:
通过in、out技巧性操作实现,见程序的分析。