Spring Batch Concepts(2)
Spring Batch Concepts(2)
Spring Batch supportsthe following database engines: DB2, Derby, H2, HSQLDB, MySQL, Oracle,PostgreSQL, SQLServer, and Sybase.
To work properly, thepersistent job repository needs a data source and a transaction manager. A datasource implementation that holds a single JDBC connection and reuses it foreach query is used because it’s convenient and good enough for a single-threadedapplication (like a batch process). If you plan to use the datya source in aconcurrent application, then use a connection pool, like Apache Commons DBCP orc3p0.
What is Spring BatchAdmin?
Spring Batch Admin isan open source project from SpringSource that provides a webbased UI for SpringBatch Applications.
The job is thecentral concept in a batch application: it’s the batch process itself. A jobhas two aspects that we examine in this section: a static aspect used for jobmodeling and a dynamic aspect used for runtime job management. Spring Batchprovides a well-defined model for jobs and includes tools-such as Spring BatchXML-to configure this model. Spring Batch also provides a strong runtimefoundation to execute and dynamically manage jobs. This foundation provides areliable way to control which instance of a job Spring Batch executes and theability to restart a job where it failed.
A spring Batch job isa sequence of steps configured in Spring Batch XML.
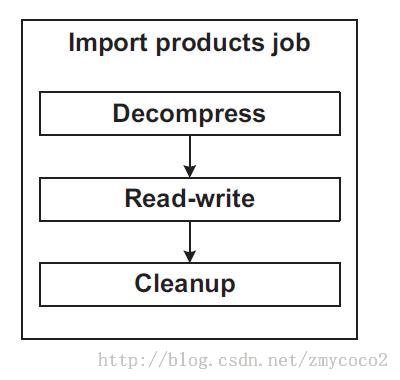
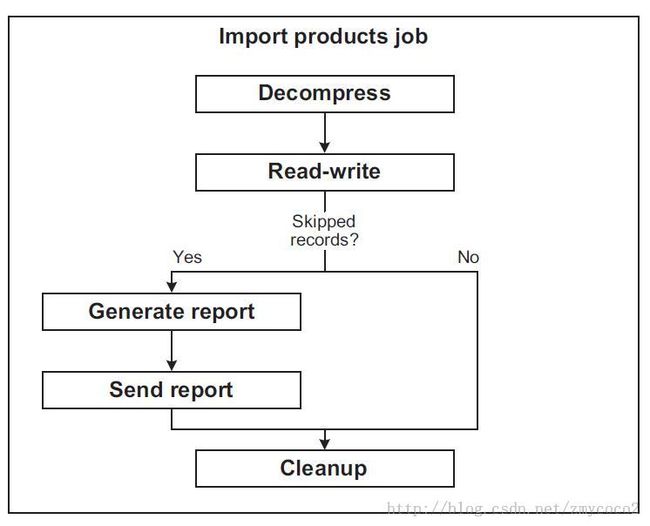
A Spring Batch job isa sequence of steps, such as this import products job, which includes threesteps: decompress, read-write, and cleanup. Job built of thress successivelinear steps, but the sequence of steps doesn’t have to be linear, a moreadvanced version of the import products job generates and send a report to an administratorif the read-write step skipped records.
Job: A batch process,or sequence of steps.
Job Instance: Aspecific run of a job.
Job execution: Theexecution of a job instance (with success or failure).