API Demos 2.2 研读笔记(7)——ListActivity
今天仔细研究了一下API Demo中的QuickContactsDemo示例,感觉对ListActivity有了进一步的认识。下面结合官方文档和自己的研究对ListActivity做个总结。
Screen Layout
ListActivity的默认布局由一个位于屏幕中心的全屏列表构成。如果你不想使用默认的布局,可以在onCreate()方法中通过setContentView()方法设定你自己的布局。
如果指定你自己定制的布局,你的布局中必须包含一个id为"@id/android:list"的ListView。 若你还指定了一个id为"@id/android:empty"的view,当ListView中没有数据要显示时,这个view就会被显示,同时ListView会被隐藏。
参考示例:
1. 布局文件,res/layout/main.xml。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="8dp" android:paddingRight="8dp"> <!-- 除了ListView和id为@id/android:empty的view之外,我们还可以任意添加view --> <TextView android:id="@+id/android:title" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="The following is a list:" /> <!-- id为@id/android:list的ListView为客户化的list布局,如果没有,则系统会调用默认的布局 --> <ListView android:id="@id/android:list" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="#00FF00" android:layout_weight="1" android:drawSelectorOnTop="false" /> <!-- 当ListView中没有数据时,id为@id/android:empty的view就会显示出来 --> <TextView android:id="@id/android:empty" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:textColor="#FF0000" android:text="No data" android:gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal" /> </LinearLayout>
2. Activity对应的Java文件,ListActivityDemo.java。
package com.xeedroid;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import android.app.ListActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
public class ListActivityDemo extends ListActivity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
List<String> items = fillList();
ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, items);
setListAdapter(adapter);
}
private List<String> fillList() {
List<String> items = new ArrayList<String>();
items.add("星期一");
items.add("星期二");
items.add("星期三");
items.add("星期四");
items.add("星期五");
items.add("星期六");
items.add("星期日");
//items.clear();
return items;
}
}
3. 运行效果如下:

4. 放开java代码中的"items.clear();"的注释。使得ListView绑定的数据源没有数据。运行效果如下:
Row Layout
Android允许为列表中一个单独的行指定布局。只要在ListAdapter对象中指定一个布局资源就可以了。
一个ListAdapter构造函数有一个参数来指定每一行的布局资源。此外,它还有另外两个参数来指定哪一个数据域与行布局资源中的对象相关联。这两个参数一般是平行数组。
Android在R.layout类中提供了一些标准的布局资源。例如simple_list_item_1, simple_list_item_2, 和two_line_list_item。
参考示例一(使用SimpleCursorAdapter):
1. 使用默认的布局。
2. Activity对应的Java代码如下。
package com.xeedroid;
import android.app.ListActivity;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.provider.ContactsContract.Contacts;
import android.widget.ListAdapter;
import android.widget.SimpleCursorAdapter;
public class ListActivityDemo extends ListActivity {
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Cursor mCursor = this.getContentResolver().query(Contacts.CONTENT_URI,
null, null, null, null);
startManagingCursor(mCursor);
ListAdapter adapter = new SimpleCursorAdapter(this,
android.R.layout.two_line_list_item, mCursor, new String[] {
Contacts.DISPLAY_NAME, Contacts.TIMES_CONTACTED }, new int[] {
android.R.id.text1, android.R.id.text2 });
setListAdapter(adapter);
}
}
客户化的行布局使用了系统的android.R.layout.two_line_list_item。
3. 运行效果如下:
参考示例二(使用ResourceCursorAdapter):
1. 使用系统默认screen layout。
2. Activity对应的Java代码QuickContactsDemo.java(带注释)如下:
package com.example.android.apis.app;
import com.example.android.apis.R;
import android.app.ListActivity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.CharArrayBuffer;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.provider.ContactsContract.Contacts;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.QuickContactBadge;
import android.widget.ResourceCursorAdapter;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class QuickContactsDemo extends ListActivity {
static final String[] CONTACTS_SUMMARY_PROJECTION = new String[] {
Contacts._ID, // 0
Contacts.DISPLAY_NAME, // 1
Contacts.STARRED, // 2
Contacts.TIMES_CONTACTED, // 3
Contacts.CONTACT_PRESENCE, // 4
Contacts.PHOTO_ID, // 5
Contacts.LOOKUP_KEY, // 6
Contacts.HAS_PHONE_NUMBER, // 7
};
static final int SUMMARY_ID_COLUMN_INDEX = 0;
static final int SUMMARY_NAME_COLUMN_INDEX = 1;
static final int SUMMARY_STARRED_COLUMN_INDEX = 2;
static final int SUMMARY_TIMES_CONTACTED_COLUMN_INDEX = 3;
static final int SUMMARY_PRESENCE_STATUS_COLUMN_INDEX = 4;
static final int SUMMARY_PHOTO_ID_COLUMN_INDEX = 5;
static final int SUMMARY_LOOKUP_KEY = 6;
static final int SUMMARY_HAS_PHONE_COLUMN_INDEX = 7;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 查找符合条件的所有contact
String select = "((" + Contacts.DISPLAY_NAME + " NOTNULL) AND ("
+ Contacts.HAS_PHONE_NUMBER + "=1) AND ("
+ Contacts.DISPLAY_NAME + " != '' ))";
Cursor c =
getContentResolver().query(Contacts.CONTENT_URI, CONTACTS_SUMMARY_PROJECTION, select,
null, Contacts.DISPLAY_NAME + " COLLATE LOCALIZED ASC");
// 将cursor交给Activity管理
startManagingCursor(c);
// 创建adapter,将客户化的UI和要显示的数据与adapter绑定
ContactListItemAdapter adapter = new ContactListItemAdapter(this, R.layout.quick_contacts, c);
// 将adapter和当前list activity绑定
setListAdapter(adapter);
}
/*
* ResourceCursorAdapter主要是将数据按照ListActivity的要求传递给它。它的祖宗类实现了List Adapter接口。
* 在对ListActivity界面进行渲染过程中,对于Cursor中每一条记录都会依次调用newView和bindView方法来生成UI。
*/
private final class ContactListItemAdapter extends ResourceCursorAdapter {
public ContactListItemAdapter(Context context, int layout, Cursor c) {
super(context, layout, c);
}
// 将newView生成的view和当前cursor指定的数据绑定
@Override
public void bindView(View view, Context context, Cursor cursor) {
final ContactListItemCache cache = (ContactListItemCache) view.getTag();
TextView nameView = cache.nameView;
QuickContactBadge photoView = cache.photoView;
// Set the name
cursor.copyStringToBuffer(SUMMARY_NAME_COLUMN_INDEX, cache.nameBuffer);
int size = cache.nameBuffer.sizeCopied;
cache.nameView.setText(cache.nameBuffer.data, 0, size);
final long contactId = cursor.getLong(SUMMARY_ID_COLUMN_INDEX);
final String lookupKey = cursor.getString(SUMMARY_LOOKUP_KEY);
cache.photoView.assignContactUri(Contacts.getLookupUri(contactId, lookupKey));
}
// 按照ContactListItemAdapter(Context context, int layout, Cursor c)中的layout生成view
@Override
public View newView(Context context, Cursor cursor, ViewGroup parent) {
View view = super.newView(context, cursor, parent);
ContactListItemCache cache = new ContactListItemCache();
cache.nameView = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.name);
cache.photoView = (QuickContactBadge) view.findViewById(R.id.badge);
// Tag用于传递任意对象,将当前方法生成的view中的子view以参数的形式暴露,供bindView()调用
view.setTag(cache);
return view;
}
}
/*
* 自定义的数据结构,用于存储newView()所生成的view中的元素(各个子view)
*/
final static class ContactListItemCache {
public TextView nameView;
public QuickContactBadge photoView;
public CharArrayBuffer nameBuffer = new CharArrayBuffer(128);
}
}
3. 行布局对应的资源文件,res/layout/quick_contacts.xml。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:paddingLeft="0dip"
android:paddingRight="9dip"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
android:minHeight="48dip">
<QuickContactBadge
android:id="@+id/badge"
android:layout_marginLeft="2dip"
android:layout_marginRight="14dip"
android:layout_marginTop="4dip"
android:layout_marginBottom="3dip"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/ic_contact_picture"
style="?android:attr/quickContactBadgeStyleWindowSmall" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/name"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:paddingLeft="2dip"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/badge"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</RelativeLayout>
ListActivity会根据row对应的layout文件和数据逐渐渲染生成整个UI。
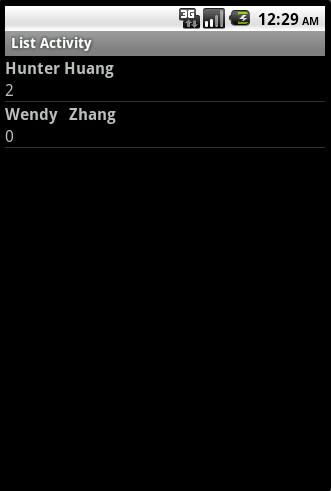
4. 运行效果如下:
Binding to Data
我们通过实现了ListAdapter的类的对象向ListView传递数据。
主要被使用的类有:SimpleAdapter,ArrayAdapter,SimpleCursorAdapter,ResourceCursorAdapter(用其子类)。
SimpleCursorAdapter,ResourceCursorAdapter(抽象类)都是CursorAdapter的子类。在CursorAdapter中有两个方法:newView()和bindView()方法,newView方法用来创建一个RowLayout,bindView方法用来向这个新的RowLayout绑定数据。需要使用ResourceCursorAdapter是因为有些数据不能用SimpleCursorAdapter来进行绑定。