4种调用https服务的方式
以前在网厅的时候,请求计费的账单开始使用的是httpclient,后来因为性能问题,换成了使用socket 发送http请求的方式,由于计费服务器端使用了redirect ,因此还需要从响应报文中得到Location 中的url,再次发送一次http请求才能完成整个业务逻辑!
Https 资源在访问的时候会让你输入用户名和密码
1.使用linux 的curl命令
[root@xhuvm03 ~]# curl -k --basic --user "tcloudadmin:tcloud123" --data "" --header 'Content-Type: application/xml' https://123.124.189.***/api/account.list
<Users>
<User>
<isAdmin>1</isAdmin>
<id>f1ebe39d-d0b6-4292-b3cd-774bf945bf63</id>
<name>tcloudadmin</name>
<groupId>be2e0f3a-7684-4b8e-b04d-6ee75aa3d099</groupId>
</User>
<User>
<isAdmin>1</isAdmin>
<id>653d60c5-dc7b-488a-a861-1c67873057fd</id>
<name>gaoyang</name>
<groupId>be2e0f3a-7684-4b8e-b04d-6ee75aa3d099</groupId>
</User>
<User>
<isAdmin>1</isAdmin>
<id>2d393438-9c8f-4704-8dfd-9f00fb7d7d18</id>
<name>teststorage</name>
<groupId>be2e0f3a-7684-4b8e-b04d-6ee75aa3d099</groupId>
</User>
</Users>
[root@xhuvm03 ~]#
-k/--insecure Allow connections to SSL sites without certs (H)
--basic Use HTTP Basic Authentication (H)
-u/--user <user[:password]> Set server user and password
-d/--data <data> HTTP POST data (H)
-H/--header <line> Custom header to pass to server (H)
方式2: 使用socket发送http请求字符串到https 服务上
curl -k --basic --user "tcloudadmin:tcloud123" --data "" --header 'Content-Type: application/xml' https://123.124.189.***/api/account.list -v
使用-v 选项可以 看到http请求的过程和内容,可以作为我们拼 Http 请求字符串的依据
[root@xlhu-linux ~]# curl -k --basic --user "tcloudadmin:tcloud123" --data "" --header 'Content-Type: application/xml' https://123.124.189.196/api/account.list -v
* About to connect() to 123.124.189.xxx port 443
* Trying 123.124.189.xxx... connected
* Connected to 123.124.189.xxx (123.124.189.xxx) port 443
* successfully set certificate verify locations:
* CAfile: /etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt
CApath: none
* SSLv2, Client hello (1):
SSLv3, TLS handshake, Server hello (2):
SSLv3, TLS handshake, CERT (11):
SSLv3, TLS handshake, Server key exchange (12):
SSLv3, TLS handshake, Server finished (14):
SSLv3, TLS handshake, Client key exchange (16):
SSLv3, TLS change cipher, Client hello (1):
SSLv3, TLS handshake, Finished (20):
SSLv3, TLS change cipher, Client hello (1):
SSLv3, TLS handshake, Finished (20):
SSL connection using DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA
* Server certificate:
* subject: /C=TW/ST=Taipei City/L=Taipei/O=Trend Micro/OU=CloudLego/CN=CloudLego
* start date: 2010-02-03 02:13:59 GMT
* expire date: 2020-02-01 02:13:59 GMT
* common name: CloudLego (does not match '123.124.189.xxx')
* issuer: /C=TW/ST=Taipei City/L=Taipei/O=Trend Micro/OU=CloudLego/CN=CloudLego
* SSL certificate verify result: self signed certificate (18), continuing anyway.
* Server auth using Basic with user 'tcloudadmin'
> POST /api/account.list HTTP/1.1
> Authorization: Basic dGNsb3VkYWRtaW46dGNsb3VkMTIz
> User-Agent: curl/7.15.5 (i686-redhat-linux-gnu) libcurl/7.15.5 OpenSSL/0.9.8b zlib/1.2.3 libidn/0.6.5
> Host: 123.124.189.xxx
> Accept: */*
> Content-Type: application/xml
> Content-Length: 0
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Date: Sun, 16 Jan 2011 11:40:25 GMT
< Server: Apache/2.2.15 (Fedora)
< Vary: Authorization
< Content-Type: text/xml; charset=utf-8
< Connection: close
< Transfer-Encoding: chunked
<Users>
<User>
<isAdmin>1</isAdmin>
<id>f1ebe39d-d0b6-4292-b3cd-774bf945bf63</id>
<name>tcloudadmin</name>
<groupId>be2e0f3a-7684-4b8e-b04d-6ee75aa3d099</groupId>
</User>
<User>
<isAdmin>1</isAdmin>
<id>653d60c5-dc7b-488a-a861-1c67873057fd</id>
<name>gaoyang</name>
<groupId>be2e0f3a-7684-4b8e-b04d-6ee75aa3d099</groupId>
</User>
<User>
<isAdmin>0</isAdmin>
<id>2a228769-3b2d-4d26-b2c8-697c86f78b65</id>
<name>test1234</name>
<groupId>ce2666d0-6c95-47f3-a908-cadf333a214e</groupId>
</User>
<User>
<isAdmin>1</isAdmin>
<id>543ae799-df16-438d-9071-6618f5c09ba3</id>
<name>test123</name>
<groupId>be2e0f3a-7684-4b8e-b04d-6ee75aa3d099</groupId>
</User>
<User>
<isAdmin>0</isAdmin>
<id>3bbc0f32-4490-49fd-8944-751ae28c1073</id>
<name>elaster-demo</name>
<groupId>fb86fe86-210a-4242-b157-fce26ba41545</groupId>
</User>
<User>
<isAdmin>0</isAdmin>
<id>bd2636fa-b92e-47e8-b658-e540e9307839</id>
<name>test11</name>
<groupId>a2b2179a-8f96-420a-be59-1cc5d12394e3</groupId>
</User>
<User>
<isAdmin>0</isAdmin>
<id>4867561a-9566-4740-a3ce-4bf78289490c</id>
<name>gavin</name>
<groupId>237b3b70-5d13-4325-a5aa-83a28aabb693</groupId>
</User>
</Users>
* Closing connection #0
* SSLv3, TLS alert, Client hello (1):
[root@xlhu-linux ~]#
这种方式调用要求 掌握Http协议的请求 格式,如果请求协议的格式错误,则不能得到正确的返回结果!
必须要知道的:
a.
报文都由5个成员组成,其中请求报文的结构如下:
1、第1成员:请求行(Request-Line)或状态行(Status-line)
2、第2成员:通用头(General-Header)
3、第2成员:请求头(Request-Header)
4、第4成员:实体头(Entity-Header)
5、第5成员:实体主体(Entiry-Body)
b. 每个请求行都要以 回车换行结尾
c. 协议结束的标志是 2个换行
c. 如果返回的 响应有 location 字段,也就是重定向了 需要我们根据location 字段重新发起请求
下面是 一个socket 拼接 http请求字符串的 例子
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.Socket;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;
public class SocketHttpsClient
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
String url="https://123.124.189.xxx:443/api/vm.list";
SSLSocketFactory ssf = (SSLSocketFactory) SSLSocketFactory.getDefault();
String reqMsg=getFirestRequestMsg(url);
Socket socket=null;
try {
System.out.println("请求消息:"+reqMsg);
socket = ssf.createSocket("123.124.189.xxx", 443);
PrintWriter tOut = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream())));
tOut.write(reqMsg);
tOut.println();
tOut.flush();
System.out.println("消息发送成功!等待返回结果。。。");
BufferedReader tIn = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String tLine = null;
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
while ((tLine = tIn.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(tLine).append("\n");
}
System.out.println("返回内容:"+sb.toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
throw e;
}finally{
if(socket!=null){
socket.close();
}
}
}
private static String getFirestRequestMsg(String url){
StringBuilder reqMsg = new StringBuilder("")
.append("POST ").append("/api/vm.list").append(" HTTP/1.1").append("\r\n")
.append("Authorization: Basic dGNsb3VkYWRtaW46dGNsb3VkMTIz").append("\r\n")
.append("User-Agent: curl/7.15.5 (x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu) libcurl/7.15.5 OpenSSL/0.9.8b zlib/1.2.3 libidn/0.6.5").append("\r\n")
.append("Host: ").append("123.124.189.xxx").append("\r\n")
.append("Accept: */*").append("\r\n")
.append("Content-Type: application/xml").append("\r\n")
.append("Content-Length: 0").append("\r\n")
.append("\r\n")
.append("\r\n");
return reqMsg.toString();
}
}
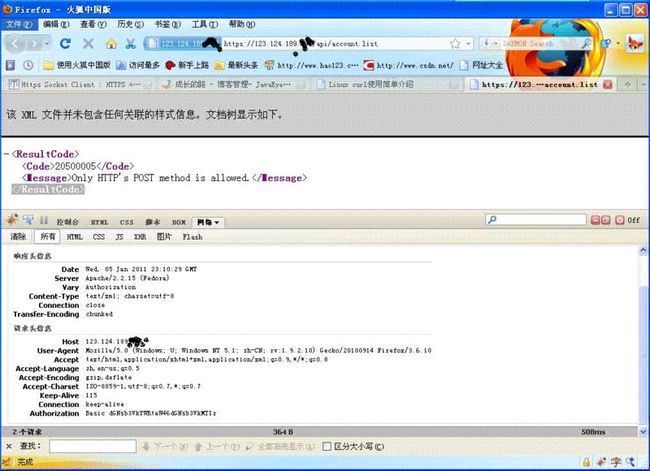
3. 使用HttpClient,首先直接访问 https://123.124.189.xxx/api/account.list ,使用firefox 的firebug插件拦截http请求和响应
package cn.com.xinli.test.httpclient;
import java.io.InputStream;
import org.apache.commons.httpclient.HttpClient;
import org.apache.commons.httpclient.NameValuePair;
import org.apache.commons.httpclient.methods.PostMethod;
public class TestHttps {
/**
* 参考
* http://wanglei0119.iteye.com/blog/607046
*/
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
HttpClient httpclient = new HttpClient();
PostMethod postMethod = new PostMethod("https://123.124.189.xxx:443/api/vm.list");
NameValuePair[] data = {};
try {
postMethod.addRequestHeader("Content-Type","application/xml");
postMethod.addRequestHeader("Authorization", "basic dGNsb3VkYWRtaW46dGNsb3VkMTIz");
postMethod.setRequestBody(data);
httpclient.executeMethod(postMethod);
InputStream insr = postMethod.getResponseBodyAsStream();
int respInt = insr.read();
while (respInt != -1) {
System.out.print((char) respInt);
respInt = insr.read();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getLocalizedMessage());
} finally {
postMethod.releaseConnection();
}
}
}
运行这段代码 会报一个错误 unable to find valid certification path to requested target
这个文章有解决方案 :
http://wanglei0119.iteye.com/blog/607046
当使用 正确生成的cert 后 httpclient 可以调用到https的服务了
方式4 :还是使用httpclient ,使用 httpclient的 X509TrustManager 类,这种调用方式不需要客户端制作证书,很方便!
package com.platform.vmo.elasterAgent.elaster;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.security.cert.CertificateException;
import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext;
import javax.net.ssl.TrustManager;
import javax.net.ssl.X509TrustManager;
import org.apache.http.HttpEntity;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
import org.apache.http.conn.scheme.Scheme;
import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;
import org.apache.http.entity.StringEntity;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultHttpClient;
public class HttpClinetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// First create a trust manager that won't care.
X509TrustManager trustManager = new X509TrustManager() {
public void checkClientTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain,
String authType) throws CertificateException {
// Don't do anything.
}
public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain,
String authType) throws CertificateException {
// Don't do anything.
}
public X509Certificate[] getAcceptedIssuers() {
// Don't do anything.
return null;
}
};
// Now put the trust manager into an SSLContext.
SSLContext sslcontext = SSLContext.getInstance("SSL");
sslcontext.init(null, new TrustManager[] { trustManager }, null);
// Use the above SSLContext to create your socket factory
// (I found trying to extend the factory a bit difficult due to a
// call to createSocket with no arguments, a method which doesn't
// exist anywhere I can find, but hey-ho).
SSLSocketFactory sf = new SSLSocketFactory(sslcontext);
sf.setHostnameVerifier(SSLSocketFactory.ALLOW_ALL_HOSTNAME_VERIFIER);
DefaultHttpClient httpclient = new DefaultHttpClient();
httpclient.getConnectionManager().getSchemeRegistry().register(new Scheme("https", sf, 443));
String requset ="https://180.168.35.140/api/vm.list";
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(requset);
String result = "";
// Execute HTTP request
httpPost.setHeader("Authorization", "basic " + "dGNsb3VkYWRtaW46dGNsb3VkMTIz");
httpPost.setHeader("Content-type", "application/xml");
StringEntity reqEntity;
reqEntity = new StringEntity("");
httpPost.setEntity(reqEntity);
HttpResponse response = httpclient.execute(httpPost);
HttpEntity resEntity = response.getEntity();
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(resEntity.getContent());
char[] buff = new char[1024];
int length = 0;
while ((length = reader.read(buff)) != -1) {
result += new String(buff, 0, length);
}
httpclient.getConnectionManager().shutdown();
System.out.println(">>>:"+result);
}
}