利用RK4更新四元數並轉換成歐拉角及 OpenGL 的 Viewer
開發平台 :
硬體規格
Odroid-U2
作業系統
Ubuntu 13.10
Codename: saucy
下面都是一些基本的程式可示需求修改, 之後我會把算法跟GUI整再一起開發.
四元數更新 :
Windows : dev-c++ 專案 : quat ( 需安裝 dev-c++ )
Linux : GNU GCC
quat.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#define M_PI 3.14159265358979323846
//#define M_PI 3.14
#define D2R(x) ((x) * M_PI/180)
#define R2D(x) ((x) * 180/M_PI)
#define NUM 4
void RK4(float X[NUM], float U[NUM], float dT);
void StateEq(float X[NUM], float U[NUM], float Xdot[NUM]);
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
// gcc quat.c -o quat -lm -std=c99
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
float x[3] = {0};
float q[4] = {1,0,0,0};
float w[4] = {0,0,0,0};
//float r[4] = {0,0,0,0};
float m11, m12, m13, m23, m33;
float dt = 0.000001;
float norm;
printf("x0=%10f, x1=%10f, x2=%10f \n", R2D(x[0]), R2D(x[1]), R2D(x[2]));
// X
printf("---X\n");
w[1] = D2R(100), w[2] = 0, w[3] = 0;
for(int i=0; i < 10; i++) {
//r[0] = -w[1]*q[1] - w[2]*q[2] - w[3]*q[3];
//r[1] = +w[1]*q[0] - w[2]*q[3] + w[3]*q[2];
//r[2] = +w[1]*q[3] + w[2]*q[0] - w[3]*q[1];
//r[3] = -w[1]*q[2] + w[2]*q[1] + w[3]*q[0];
//q[0] = q[0] + (dt/2)* r[0];
//q[1] = q[1] + (dt/2)* r[1];
//q[2] = q[2] + (dt/2)* r[2];
//q[3] = q[3] + (dt/2)* r[3];
RK4(q,w,dt);
#if 1 // 不做的話會出現NAN
norm = sqrtf(q[0]*q[0] + q[1]*q[1] + q[2]*q[2] + q[3]*q[3]);
q[0] = q[0] / norm;
q[1] = q[1] / norm;
q[2] = q[2] / norm;
q[3] = q[3] / norm;
#endif
m11 = q[0]*q[0] + q[1]*q[1] - q[2]*q[2] - q[3]*q[3];
m12 = 2.0 * (q[1]*q[2] + q[0]*q[3]);
m13 = 2.0 * (q[1]*q[3] - q[0]*q[2]);
m23 = 2.0 * (q[2]*q[3] + q[0]*q[1]);
m33 = q[0]*q[0] - q[1]*q[1] - q[2]*q[2] + q[3]*q[3];
x[0] = atanf(m23/m33);
x[1] = -asinf(m13);
x[2] = atanf(m12/m11);
printf("x0=%10f, x1=%10f, x2=%10f \n", R2D(x[0]), R2D(x[1]), R2D(x[2]));
}
// Y
printf("---Y\n");
w[1] = 0, w[2] = D2R(100), w[3] = 0;
for(int i=0; i < 10; i++) {
//r[0] = -w[1]*q[1] - w[2]*q[2] - w[3]*q[3];
//r[1] = +w[1]*q[0] - w[2]*q[3] + w[3]*q[2];
//r[2] = +w[1]*q[3] + w[2]*q[0] - w[3]*q[1];
//r[3] = -w[1]*q[2] + w[2]*q[1] + w[3]*q[0];
//q[0] = q[0] + (dt/2)* r[0];
//q[1] = q[1] + (dt/2)* r[1];
//q[2] = q[2] + (dt/2)* r[2];
//q[3] = q[3] + (dt/2)* r[3];
RK4(q,w,dt);
#if 1 // 不做的話會出現NAN
norm = sqrtf(q[0]*q[0] + q[1]*q[1] + q[2]*q[2] + q[3]*q[3]);
q[0] = q[0] / norm;
q[1] = q[1] / norm;
q[2] = q[2] / norm;
q[3] = q[3] / norm;
#endif
m11 = q[0]*q[0] + q[1]*q[1] - q[2]*q[2] - q[3]*q[3];
m12 = 2.0 * (q[1]*q[2] + q[0]*q[3]);
m13 = 2.0 * (q[1]*q[3] - q[0]*q[2]);
m23 = 2.0 * (q[2]*q[3] + q[0]*q[1]);
m33 = q[0]*q[0] - q[1]*q[1] - q[2]*q[2] + q[3]*q[3];
x[0] = atanf(m23/m33);
x[1] = -asinf(m13);
x[2] = atanf(m12/m11);
printf("x0=%10f, x1=%10f, x2=%10f \n", R2D(x[0]), R2D(x[1]), R2D(x[2]));
}
// Z
printf("---Z\n");
w[1] = 0, w[2] = 0, w[3] = D2R(100);
for(int i=0; i < 10; i++) {
//r[0] = -w[1]*q[1] - w[2]*q[2] - w[3]*q[3];
//r[1] = +w[1]*q[0] - w[2]*q[3] + w[3]*q[2];
//r[2] = +w[1]*q[3] + w[2]*q[0] - w[3]*q[1];
//r[3] = -w[1]*q[2] + w[2]*q[1] + w[3]*q[0];
//q[0] = q[0] + (dt/2)* r[0];
//q[1] = q[1] + (dt/2)* r[1];
//q[2] = q[2] + (dt/2)* r[2];
//q[3] = q[3] + (dt/2)* r[3];
RK4(q,w,dt);
#if 1 // 不做的話會出現NAN
norm = sqrtf(q[0]*q[0] + q[1]*q[1] + q[2]*q[2] + q[3]*q[3]);
q[0] = q[0] / norm;
q[1] = q[1] / norm;
q[2] = q[2] / norm;
q[3] = q[3] / norm;
#endif
m11 = q[0]*q[0] + q[1]*q[1] - q[2]*q[2] - q[3]*q[3];
m12 = 2.0 * (q[1]*q[2] + q[0]*q[3]);
m13 = 2.0 * (q[1]*q[3] - q[0]*q[2]);
m23 = 2.0 * (q[2]*q[3] + q[0]*q[1]);
m33 = q[0]*q[0] - q[1]*q[1] - q[2]*q[2] + q[3]*q[3];
x[0] = atanf(m23/m33);
x[1] = -asinf(m13);
x[2] = atanf(m12/m11);
printf("x0=%10f, x1=%10f, x2=%10f \n", R2D(x[0]), R2D(x[1]), R2D(x[2]));
}
return 0;
}
// ************* RungeKutta **********************
// Does a 4th order Runge Kutta numerical integration step
// Output, Xnew, is written over X
// NOTE the algorithm assumes time invariant state equations and
// constant inputs over integration step
// ************************************************
void RK4(float X[NUM], float U[NUM], float dT)
{
float dT2 = dT / 2, K1[NUM], K2[NUM], K3[NUM], K4[NUM], Xlast[NUM];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < NUM; i++)
Xlast[i] = X[i]; // make a working copy
StateEq(X, U, K1); // k1 = f(x,u)
for (i = 0; i < NUM; i++)
X[i] = Xlast[i] + dT2 * K1[i];
StateEq(X, U, K2); // k2 = f(x+0.5*dT*k1,u)
for (i = 0; i < NUM; i++)
X[i] = Xlast[i] + dT2 * K2[i];
StateEq(X, U, K3); // k3 = f(x+0.5*dT*k2,u)
for (i = 0; i < NUM; i++)
X[i] = Xlast[i] + dT * K3[i];
StateEq(X, U, K4); // k4 = f(x+dT*k3,u)
// Xnew = X + dT*(k1+2*k2+2*k3+k4)/6
for (i = 0; i < NUM; i++)
X[i] = Xlast[i] + dT * (K1[i] + 2 * K2[i] + 2 * K3[i] + K4[i]) / 6;
}
// *** StateEq ********
//
// State Variables = [Quaternion]
// Deterministic Inputs = [AngularVel]
// Disturbance Noise = [GyroNoise AccelNoise GyroRandomWalkNoise NO-AccelRandomWalkNoise]
//
// Notes:
// AngularVel in body frame
// Xdot is output of StateEq()
// ************************************************
void StateEq(float X[NUM], float U[NUM], float Xdot[NUM])
{
float wx, wy, wz, q0, q1, q2, q3;
wx = U[1];
wy = U[2];
wz = U[3];
q0 = X[0];
q1 = X[1];
q2 = X[2];
q3 = X[3];
// qdot = Q*w
Xdot[0] = (-q1 * wx - q2 * wy - q3 * wz) / 2;
Xdot[1] = ( q0 * wx - q3 * wy + q2 * wz) / 2;
Xdot[2] = ( q3 * wx + q0 * wy - q1 * wz) / 2;
Xdot[3] = (-q2 * wx + q1 * wy + q0 * wz) / 2;
}
Makefile
# # 'make depend' uses makedepend to automatically generate dependencies # (dependencies are added to end of Makefile) # 'make' build executable file 'quat' # 'make clean' removes all .o and executable files # # define the C compiler to use CC = gcc # define any compile-time flags CFLAGS = -Wall -g -std=c99 # define any directories containing header files other than /usr/include # INCLUDES = -Iinclude # define library paths in addition to /usr/lib # if I wanted to include libraries not in /usr/lib I'd specify # their path using -Lpath, something like: LFLAGS = -Llib # define any libraries to link into executable: # if I want to link in libraries (libx.so or libx.a) I use the -llibname # option, something like (this will link in libmylib.so and libm.so: LIBS = -lm # define the C source files SRCS = quat.c # define the C object files # # This uses Suffix Replacement within a macro: # $(name:string1=string2) # For each word in 'name' replace 'string1' with 'string2' # Below we are replacing the suffix .c of all words in the macro SRCS # with the .o suffix # OBJS = $(SRCS:.c=.o) # define the executable file TARGET = quat # # The following part of the makefile is generic; it can be used to # build any executable just by changing the definitions above and by # deleting dependencies appended to the file from 'make depend' # .PHONY: depend clean all: $(TARGET) @echo Simple compiler named $(TARGET) has been compiled $(TARGET): $(OBJS) $(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(INCLUDES) -o $(TARGET) $(OBJS) $(LFLAGS) $(LIBS) # this is a suffix replacement rule for building .o's from .c's # it uses automatic variables $<: the name of the prerequisite of # the rule(a .c file) and $@: the name of the target of the rule (a .o file) # (see the gnu make manual section about automatic variables) .c.o: $(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(INCLUDES) -c $< -o $@ clean: $(RM) *.o *~ $(TARGET) depend: $(SRCS) makedepend $(INCLUDES) $^ # DO NOT DELETE THIS LINE -- make depend needs it
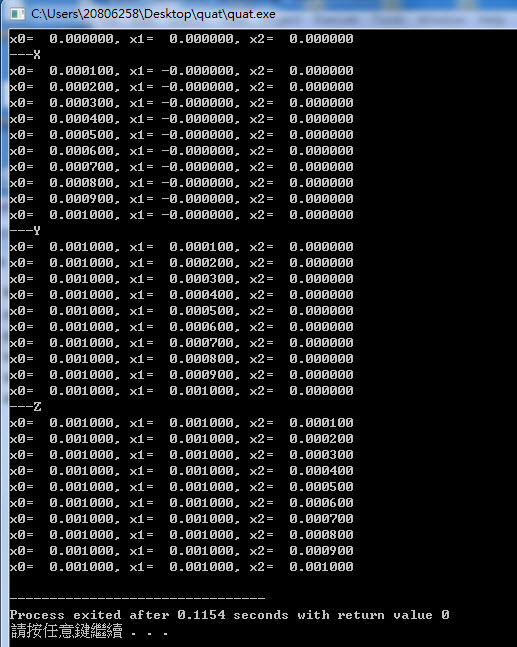
執行結果
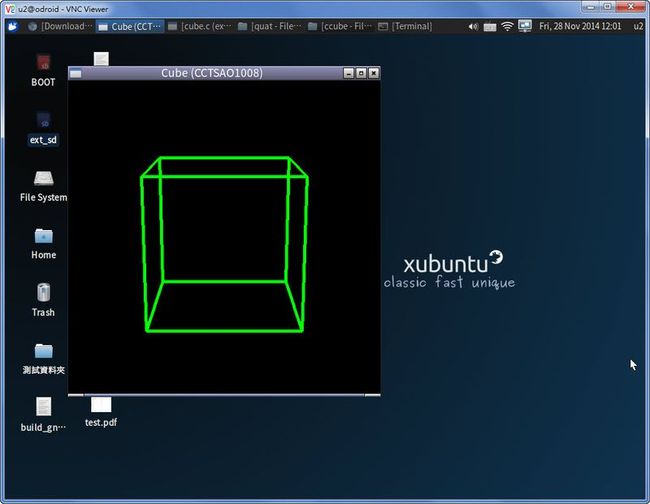
圖形介面 3D-Cube :
cube.c
/**** Traditional first 3D program: spinning cube
Written by Hugh Fisher ****/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <GL/glut.h>
#include "utility.h"
#include "glUtils.h"
#define Near 0.5
#define Far 20.0
#define ESC 27
#define cmdRed 1
#define cmdGreen 2
#define cmdBlue 3
#define cmdExit 99
static int WinWidth, WinHeight;
static RGBA CubeColor;
static int AppMenu;
static GLfloat Spin;
static GLfloat ViewPoint[3];
/**** Cube in points-polygons (polyhedron) form ****/
static GLfloat Verts[8][3] = {
{ -0.5, 0.5, -0.5 }, /* 0 left top rear */
{ 0.5, 0.5, -0.5 }, /* 1 right top rear */
{ 0.5, -0.5, -0.5 }, /* 2 right bottom rear */
{ -0.5, -0.5, -0.5 }, /* 3 left bottom rear */
{ -0.5, 0.5, 0.5 }, /* 4 left top front */
{ 0.5, 0.5, 0.5 }, /* 5 right top front */
{ 0.5, -0.5, 0.5 }, /* 6 right bottom front */
{ -0.5, -0.5, 0.5 } /* 7 left bottom front */
};
static GLuint Faces[] = {
4, 5, 6, 7, /* front */
5, 1, 2, 6, /* right */
0, 4, 7, 3, /* left */
4, 0, 1, 5, /* top */
7, 6, 2, 3, /* bottom */
1, 0, 3, 2 /* rear */
};
static void drawCube()
{
int i;
glPointSize(5.0f);
glLineWidth(5.0f);
/* Draw cube in traditional OpenGL style */
glBegin(GL_QUADS);
for (i = 0; i < 6 * 4; i++)
glVertex3fv(Verts[Faces[i]]);
glEnd();
}
#if 0
static void arrayCube()
{
/* Modern version using vertex arrays. Exactly the same effect
as above, but only 2 OpenGL calls instead of 26. */
/* Vertices are 3 floating point values each (XYZ), tightly
packed in array. Array size is not specified nor checked!
(Except by your program crashing if you get it wrong.) */
glVertexPointer(3, GL_FLOAT, 0, Verts);
/* Draw quads, using N vertices in total, in the order given
by an array of ints, from the vertex array specified earlier. */
glDrawElements(GL_QUADS, 6 * 4, GL_UNSIGNED_INT, Faces);
}
#endif
/**** Window events ****/
static void setProjection()
{
GLfloat aspect;
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
aspect = (float)WinWidth / (float)WinHeight;
gluPerspective(30.0, aspect, Near, Far); // 60.0
/* Back to normal */
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
}
static void setViewPoint()
{
glLoadIdentity();
gluLookAt(ViewPoint[0], ViewPoint[1], ViewPoint[2],
0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
}
static void drawWorld()
{
glPushMatrix();
glRotatef(Spin, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0);
//glRotatef(Spin, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
//glRotatef(Spin, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
glScalef(0.5, 0.5, 0.5);
glColor3fv(CubeColor);
drawCube();
/* arrayCube() */
glPopMatrix();
}
static void display()
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
setProjection();
setViewPoint();
drawWorld();
/* Check everything OK and update screen */
CheckGL();
glutSwapBuffers();
}
static void resize(int width, int height)
{
/* Save for event handlers */
WinWidth = width;
WinHeight = height;
/* Reset view in window. */
glViewport(0, 0, WinWidth, WinHeight);
}
/**** User events ****/
static void menuChoice(int item)
{
switch (item) {
case cmdRed:
SetColor(CubeColor, 1, 0, 0);
break;
case cmdGreen:
SetColor(CubeColor, 0, 1, 0);
break;
case cmdBlue:
SetColor(CubeColor, 0, 0, 1);
break;
case cmdExit:
exit(0);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
/* In most GUI systems we would write just one event handler
for all kinds of keystrokes. In GLUT, we need one for the
standard ASCII keys and one for special cursor or function
style keys that vary from system to system. Because the
GLUT special key code range overlaps with ASCII lowercase,
it isn't safe to use the same function for both. */
static void asciiKey(unsigned char key, int x, int y)
{
if (key == ESC)
menuChoice(cmdExit);
}
static void specialKey(int key, int x, int y)
{
/* Nothing yet */
}
/**** Startup ****/
static void initGraphics(void)
{
/* Black background */
glClearColor(0, 0, 0, 0);
/* Wireframe mode */
glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_LINE);
/* Needed for vertex arrays */
glEnableClientState(GL_VERTEX_ARRAY);
/* Popup menu attached to right mouse button */
AppMenu = glutCreateMenu(menuChoice);
glutSetMenu(AppMenu);
glutAddMenuEntry("R", cmdRed);
glutAddMenuEntry("G", cmdGreen);
glutAddMenuEntry("B", cmdBlue);
glutAddMenuEntry("----", 0);
glutAddMenuEntry("Exit", cmdExit);
glutAttachMenu(GLUT_RIGHT_BUTTON);
/* Start values */
Spin = 0.0;
ViewPoint[0] = 0.0;
ViewPoint[1] = 0.5;
ViewPoint[2] = 2.0;
menuChoice(cmdGreen);
}
/**** Main control ****/
static void spinDisplay(void)
{
Spin += 1;
if (Spin >= 360.0)
Spin -= 360.0;
glutPostRedisplay();
}
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_DEPTH | GLUT_RGB);
glutInitWindowSize(500, 500);
glutInitWindowPosition(100, 75);
glutCreateWindow("Cube (CCTSAO1008)");
initGraphics();
glutDisplayFunc(display);
glutReshapeFunc(resize);
glutKeyboardFunc(asciiKey);
glutSpecialFunc(specialKey);
glutIdleFunc(spinDisplay);
glutMainLoop();
/* Should never get here, but keeps compiler happy */
return 0;
}
Makefile
## Linux CC = gcc CFLAGS = -I../util -DGL_GLEXT_PROTOTYPES -Wall LDFLAGS = # Older systems might need -lXi -lXmu GLIBS = -lglut -lGLU -lGL -lX11 -lm OBJS = \ ../util/utility.o \ ../util/glUtils.o \ TARGET = cube $(TARGET): $(TARGET).c $(OBJS) /bin/rm -f $@ $(CC) $(CFLAGS) -o $@ $(TARGET).c $(OBJS) $(LDFLAGS) $(GLIBS) clean: /bin/rm -f *.o $(TARGET) cube.o: cube.c
參考資料 :
1. OpenGL SuperBible http://www.openglsuperbible.com
2. 四元數更新 https://qcopter.googlecode.com/files/推導_四元數.pdf