基础总结篇之七:ContentProvider之读写短消息(二)
发送和写入短信
在某些场合,我们需要发送短信,并将短信写入数据源中,这时我们就需要了解一下发送短信机制和写入短信机制。
我们将试图发送一条短信到指定的地址,同时将短信的内容写入到短信数据源中,待短信发送成功后,我们告知用户发送成功,待对方接收到短信后,我们告知用户对方接收成功。
要实现这些功能,我们需要了解以下几个重点内容:
1.使用android.telephony.SmsManager的API发送短信
2.使用ContentProvider机制对“content://sms/sent”这个URI进行写入操作
3.注册“SENT_SMS_ACTION”这个广播地址,待短信发送成功后接收到这条广播
4.注册“DELIVERED_SMS_ACTION”这个广播地址,待对方接收到短信后接收到这条广播
下面我们就用代码实现这些功能,创建一个名为SMSActivity的Activity,如下:
package com.scott.provider;
import java.util.List;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.telephony.SmsManager;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class SMSActivity extends Activity {
private SendReceiver sendReceiver = new SendReceiver();
private DeliverReceiver deliverReceiver = new DeliverReceiver();
private EditText address;
private EditText body;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.sms);
address = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.address);
body = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.body);
//注册发送成功的广播
registerReceiver(sendReceiver, new IntentFilter("SENT_SMS_ACTION"));
//注册接收成功的广播
registerReceiver(deliverReceiver, new IntentFilter("DELIVERED_SMS_ACTION"));
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
unregisterReceiver(sendReceiver);
unregisterReceiver(deliverReceiver);
}
public void sendSMS(View view) {
String address = this.address.getText().toString();
String body = this.body.getText().toString();
//android.telephony.SmsManager, not [android.telephony.gsm.SmsManager]
SmsManager smsManager = SmsManager.getDefault();
//短信发送成功或失败后会产生一条SENT_SMS_ACTION的广播
PendingIntent sendIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(this, 0, new Intent("SENT_SMS_ACTION"), 0);
//接收方成功收到短信后,发送方会产生一条DELIVERED_SMS_ACTION广播
PendingIntent deliveryIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(this, 0, new Intent("DELIVERED_SMS_ACTION"), 0);
if (body.length() > 70) { //如果字数超过70,需拆分成多条短信发送
List<String> msgs = smsManager.divideMessage(body);
for (String msg : msgs) {
smsManager.sendTextMessage(address, null, msg, sendIntent, deliveryIntent);
}
} else {
smsManager.sendTextMessage(address, null, body, sendIntent, deliveryIntent);
}
//写入到短信数据源
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("address",address); //发送地址
values.put("body", body); //消息内容
values.put("date", System.currentTimeMillis()); //创建时间
values.put("read", 0); //0:未读;1:已读
values.put("type", 2); //1:接收;2:发送
getContentResolver().insert(Uri.parse("content://sms/sent"), values); //插入数据
}
private class SendReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
switch (getResultCode()) {
case Activity.RESULT_OK:
Toast.makeText(context, "Sent Successfully.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
default:
Toast.makeText(context, "Failed to Send.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}
/**
* 发送方的短信发送到对方手机上之后,对方手机会返回给运营商一个信号,
* 运营商再把这个信号发给发送方,发送方此时可确认对方接收成功
* 模拟器不支持,真机上需等待片刻
* @author user
*
*/
private class DeliverReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(context, "Delivered Successfully.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}
布局文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="address"/> <EditText android:id="@+id/address" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="body"/> <EditText android:id="@+id/body" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="150dp" android:gravity="top"/> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="sendSMS" android:onClick="sendSMS"/> </LinearLayout>
需要注意的是,这个过程要声明发送短信的权限和写入短信的权限,我们在AndroidManifest.xml的声明如下:
<!-- 发送短消息 --> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.SEND_SMS"/> <!-- 写入短消息 --> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_SMS" />
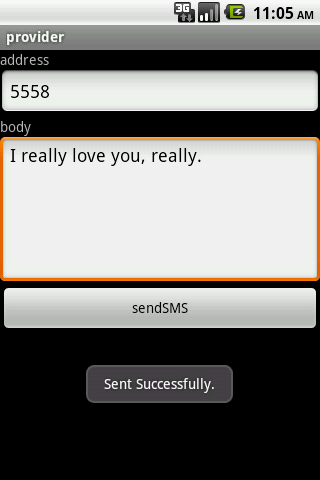
然后,运行该程序,我们让Jack给Lisa发送一条短信,看看结果如何:
看来我们的操作成功了,到底Jack能不能泡到Lisa呢,朋友们,发挥你们的想象力吧。
最后需要注意的一件事,代码里也提到过,就是在模拟器测试时,是不支持“接收成功”这个功能的,所以朋友们想要看到“Delivered Successfully”,还必须在真机上试,并且需要耐心等上片刻。感兴趣的朋友赶紧试一试吧。