Spring系列之 二 Spring AOP
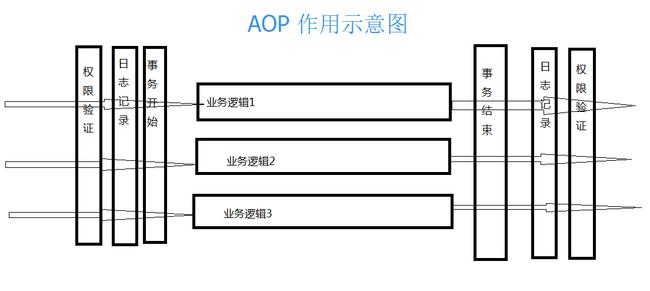
AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming)是一项伟大的开阔者,之前OOP的思想一直很流行,但是OOP也有其缺点:针对很多地方都要执行的无关于业务的代码,很难分离出来,导致很多业务方法中都要加入很多无关业务逻辑的方法,比如监控,,日志,权限,事务等很多地方都要重复写的代码.AOP把这些无关的代码从业务逻辑中分离出来.画了个简单的图来说明AOP的作用.
Spring中的AOP
Spring中AOP是利用了AspectJ的切点表达式语法来定位PointCut(切点:需要加入),然后定义Advance(增强:需要加入的方法)和其方位(before,after,round,afterThrowing .... ),具体实现就是利用反射和动态代理模式生成代理类.Spring可以用JDK自己的动态代理(基于接口),CGLIB(基于继承)来实现动态代理.CGLIB的效率比较高,而且JDK动态代理必须要被代理类继承了接口.
选择使用代理的方式是在 DefaultAopProxyFactory 中的createAopProxy方法判断的
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface()) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
意思是如果实现了接口,没有用 proxy-target-class="true"强制指定使用类继承的方式的话就会使用JDK代理,如果指定了使用类继承或者被代理类没有实现接口就会使用CGlib代理.
1.在Spring中使用AOP的XML配置(aspect风格):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.1.xsd"> <aop:config proxy-target-class="true"> <aop:aspect id="myAspect" ref="logIntercepter"> <aop:pointcut id="loginPointCut" expression="execution(* com.lubby.service.impl.*.*(..))" /> <aop:before pointcut-ref="loginPointCut" method="startLog"/> <aop:after pointcut-ref="loginPointCut" method="endLog"/> <aop:around pointcut-ref="loginPointCut" method="round" /> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>
其实就是先配置一个aop指定使用类继承(cglib)的实现,然后指定需要增强(增加的方法),然后使用aspectJ语法定于切面,然后定义增强的方位.就这么简单.
2.在Spring中使用Anotation:
启用aspectJ注解,指定使用类代理实现动态代理
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true" />
指定增强类,在需要加入的方法上面指定方位以及切面
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogIntercepter {
@Before("execution(* com.lubby.service.impl.*.*(..))")
public void startLog(){
System.out.println("starting time:" + new Date());
}
@After("execution(* com.lubby.service.impl.*.*(..))")
public void endLog(){
System.out.println("ending time:" + new Date());
}
@Around("execution(* com.lubby.service.impl.*.*(..))")
public Object round(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("starting time:" + new Date());
Object object = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("ending time:" + new Date());
return object;
}
}
下一章节再说利用Spring AOP实现事物管理