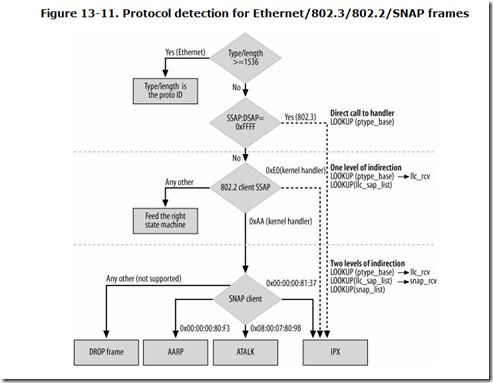
协议处理函数
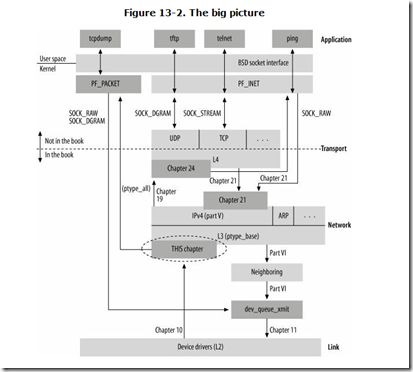
网络协议栈处理整体结构
就每种网络协议而言,无论其所在的分层如何,都有一个初始化函数。其中包括L3协议、链路层协议等等。就静态包含在内核中的协议而言,初始化函数会在引导期间执行;就编译成模块的协议而言,当模块加载时,初始化函数就会执行。此函数会分配内部数据结构,通知其他子系统有关该协议的存在,在/proc中注册文件等等。有一项关键任务是在内核注册一个处理函数,以处理该协议的流量。
协议处理函数的组织
1: struct packet_type {
2: __be16 type; /* This is really htons(ether_type). */
3: struct net_device *dev; /* NULL is wildcarded here */为NULL时指代所有的设备
4: int (*func) (struct sk_buff *,
5: struct net_device *,
6: struct packet_type *,
7: struct net_device *);
8: struct sk_buff *(*gso_segment)(struct sk_buff *skb,
9: netdev_features_t features);
10: int (*gso_send_check)(struct sk_buff *skb);
11: struct sk_buff **(*gro_receive)(struct sk_buff **head,
12: struct sk_buff *skb);
13: int (*gro_complete)(struct sk_buff *skb);
14: void *af_packet_priv;由PF_PACKET套接字使用,指向于packet_type结构建立相关联的sock数据结构。
15: struct list_head list;冲突消除链表
16: };
1: void dev_add_pack(struct packet_type *pt)
2: {
3: struct list_head *head = ptype_head(pt);
4:
5: spin_lock(&ptype_lock);
6: list_add_rcu(&pt->list, head);
7: spin_unlock(&ptype_lock);
8: }
9: EXPORT_SYMBOL(dev_add_pack);
1: void __dev_remove_pack(struct packet_type *pt)
2: {
3: struct list_head *head = ptype_head(pt);
4: struct packet_type *pt1;
5:
6: spin_lock(&ptype_lock);
7:
8: list_for_each_entry(pt1, head, list) {
9: if (pt == pt1) {
10: list_del_rcu(&pt->list);
11: goto out;
12: }
13: }
14:
15: printk(KERN_WARNING "dev_remove_pack: %p not found.\n", pt);
16: out:
17: spin_unlock(&ptype_lock);
18: }
19: EXPORT_SYMBOL(__dev_remove_pack);
协议值确定
1: /**
2: * eth_type_trans - determine the packet's protocol ID.
3: * @skb: received socket data
4: * @dev: receiving network device
5: *
6: * The rule here is that we
7: * assume 802.3 if the type field is short enough to be a length.
8: * This is normal practice and works for any 'now in use' protocol.
9: */
10: __be16 eth_type_trans(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev)
11: {
12: struct ethhdr *eth;
13:
14: skb->dev = dev;
15: skb_reset_mac_header(skb);
16: skb_pull_inline(skb, ETH_HLEN);
17: eth = eth_hdr(skb);
18:
19: if (unlikely(is_multicast_ether_addr(eth->h_dest))) {
20: if (!compare_ether_addr_64bits(eth->h_dest, dev->broadcast))
21: skb->pkt_type = PACKET_BROADCAST;
22: else
23: skb->pkt_type = PACKET_MULTICAST;
24: }
25:
26: /*
27: * This ALLMULTI check should be redundant by 1.4
28: * so don't forget to remove it.
29: *
30: * Seems, you forgot to remove it. All silly devices
31: * seems to set IFF_PROMISC.
32: */
33:
34: else if (1 /*dev->flags&IFF_PROMISC */ ) {
35: if (unlikely(compare_ether_addr_64bits(eth->h_dest, dev->dev_addr)))
36: skb->pkt_type = PACKET_OTHERHOST;
37: }
38:
39: /*
40: * Some variants of DSA tagging don't have an ethertype field
41: * at all, so we check here whether one of those tagging
42: * variants has been configured on the receiving interface,
43: * and if so, set skb->protocol without looking at the packet.
44: */
45: if (netdev_uses_dsa_tags(dev))
46: return htons(ETH_P_DSA);
47: if (netdev_uses_trailer_tags(dev))
48: return htons(ETH_P_TRAILER);
49:
50: if (ntohs(eth->h_proto) >= 1536)
51: return eth->h_proto;
52:
53: /*
54: * This is a magic hack to spot IPX packets. Older Novell breaks
55: * the protocol design and runs IPX over 802.3 without an 802.2 LLC
56: * layer. We look for FFFF which isn't a used 802.2 SSAP/DSAP. This
57: * won't work for fault tolerant netware but does for the rest.
58: */
59: if (skb->len >= 2 && *(unsigned short *)(skb->data) == 0xFFFF)
60: return htons(ETH_P_802_3);
61:
62: /*
63: * Real 802.2 LLC
64: */
65: return htons(ETH_P_802_2);
66: }
67: EXPORT_SYMBOL(eth_type_trans);