Java学习笔记(37)——Java集合09之Vector
一、概述
Vector简介
Vector 是矢量队列,它是JDK1.0版本添加的类。继承于AbstractList,实现了List, RandomAccess, Cloneable这些接口。
Vector 继承了AbstractList,实现了List;所以,它是一个队列,支持相关的添加、删除、修改、遍历等功能。
Vector 实现了RandmoAccess接口,即提供了随机访问功能。RandmoAccess是java中用来被List实现,为List提供快速访问功能的。在Vector中,我们即可以通过元素的序号快速获取元素对象;这就是快速随机访问。
Vector 实现了Cloneable接口,即实现clone()函数。它能被克隆。
和ArrayList不同,Vector中的操作是线程安全的。
Vector的构造函数
Vector共有4个构造函数 // 默认构造函数 Vector() // capacity是Vector的默认容量大小。当由于增加数据导致容量增加时,每次容量会增加一倍。 Vector(int capacity) // capacity是Vector的默认容量大小,capacityIncrement是每次Vector容量增加时的增量值。 Vector(int capacity, int capacityIncrement) // 创建一个包含collection的Vector Vector(Collection<? extends E> collection)
Vector的API
synchronized boolean add(E object) void add(int location, E object) synchronized boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> collection) synchronized boolean addAll(int location, Collection<? extends E> collection) synchronized void addElement(E object) synchronized int capacity() void clear() synchronized Object clone() boolean contains(Object object) synchronized boolean containsAll(Collection<?> collection) synchronized void copyInto(Object[] elements) synchronized E elementAt(int location) Enumeration<E> elements() synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity) synchronized boolean equals(Object object) synchronized E firstElement() E get(int location) synchronized int hashCode() synchronized int indexOf(Object object, int location) int indexOf(Object object) synchronized void insertElementAt(E object, int location) synchronized boolean isEmpty() synchronized E lastElement() synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object object, int location) synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object object) synchronized E remove(int location) boolean remove(Object object) synchronized boolean removeAll(Collection<?> collection) synchronized void removeAllElements() synchronized boolean removeElement(Object object) synchronized void removeElementAt(int location) synchronized boolean retainAll(Collection<?> collection) synchronized E set(int location, E object) synchronized void setElementAt(E object, int location) synchronized void setSize(int length) synchronized int size() synchronized List<E> subList(int start, int end) synchronized <T> T[] toArray(T[] contents) synchronized Object[] toArray() synchronized String toString() synchronized void trimToSize()
二、Vector数据结构
Vector的继承关系
java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractCollection<E>
↳ java.util.AbstractList<E>
↳ java.util.Vector<E>
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
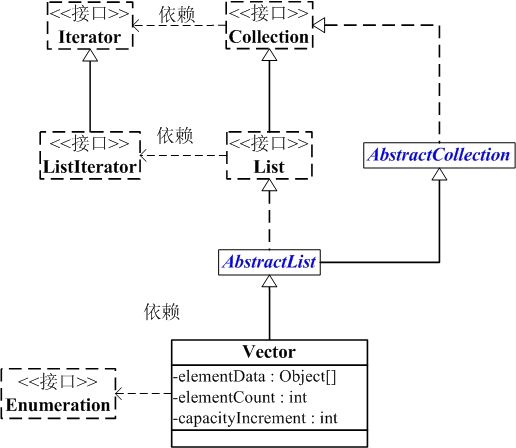
Vector与Collection关系如下图:
Vector的数据结构和ArrayList差不多,它包含了3个成员变量:elementData , elementCount, capacityIncrement。
(01) elementData 是"Object[]类型的数组",它保存了添加到Vector中的元素。elementData是个动态数组,如果初始化Vector时,没指定动态数组的>大小,则使用默认大小10。随着Vector中元素的增加,Vector的容量也会动态增长,capacityIncrement是与容量增长相关的增长系数,具体的增长方式,请参考源码分析中的ensureCapacity()函数。
(02) elementCount 是动态数组的实际大小。
(03) capacityIncrement 是动态数组的增长系数。如果在创建Vector时,指定了capacityIncrement的大小;则,每次当Vector中动态数组容量增加时>,增加的大小都是capacityIncrement。
三、Vector遍历方式
Vector支持4种遍历方式。建议使用下面的第二种去遍历Vector,因为效率问题。
(01) 第一种,通过迭代器遍历。即通过Iterator去遍历。
Integer value = null;
int size = vec.size();
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
value = (Integer)vec.get(i);
}
(02) 第二种,随机访问,通过索引值去遍历。
由于Vector实现了RandomAccess接口,它支持通过索引值去随机访问元素。
Integer value = null;
int size = vec.size();
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
value = (Integer)vec.get(i);
}
(03) 第三种,另一种for循环。如下:
Integer value = null;for (Integer integ:vec) {
value = integ;
}
(04) 第四种,Enumeration遍历。如下:
Integer value = null;
Enumeration enu = vec.elements();
while (enu.hasMoreElements()) {
value = (Integer)enu.nextElement();
}
测试这些遍历方式效率的代码如下:
import java.util.*;
/*
* @desc Vector遍历方式和效率的测试程序。
*
* @author skywang
*/
public class VectorRandomAccessTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector vec= new Vector();
for (int i=0; i<100000; i++)
vec.add(i);
iteratorThroughRandomAccess(vec) ;
iteratorThroughIterator(vec) ;
iteratorThroughFor2(vec) ;
iteratorThroughEnumeration(vec) ;
}
private static void isRandomAccessSupported(List list) {
if (list instanceof RandomAccess) {
System.out.println("RandomAccess implemented!");
} else {
System.out.println("RandomAccess not implemented!");
}
}
public static void iteratorThroughRandomAccess(List list) {
long startTime;
long endTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i=0; i<list.size(); i++) {
list.get(i);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughRandomAccess:" + interval+" ms");
}
public static void iteratorThroughIterator(List list) {
long startTime;
long endTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Iterator iter = list.iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) {
iter.next();
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughIterator:" + interval+" ms");
}
public static void iteratorThroughFor2(List list) {
long startTime;
long endTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Object obj:list)
;
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughFor2:" + interval+" ms");
}
public static void iteratorThroughEnumeration(Vector vec) {
long startTime;
long endTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Enumeration enu = vec.elements(); enu.hasMoreElements(); ) {
enu.nextElement();
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughEnumeration:" + interval+" ms");
}
}
运行结果:
iteratorThroughRandomAccess:6 ms iteratorThroughIterator:9 ms iteratorThroughFor2:8 ms iteratorThroughEnumeration:7 ms
总结:遍历Vector,使用索引的随机访问方式最快,使用迭代器最慢。