- c++ 的iostream 和 c++的stdio的区别和联系
黄卷青灯77
c++算法开发语言iostreamstdio
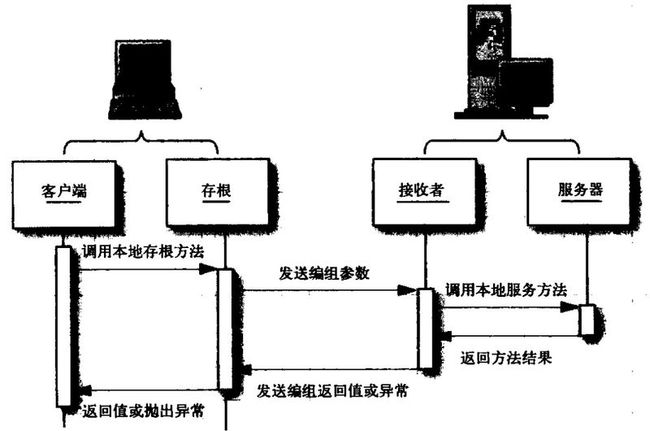
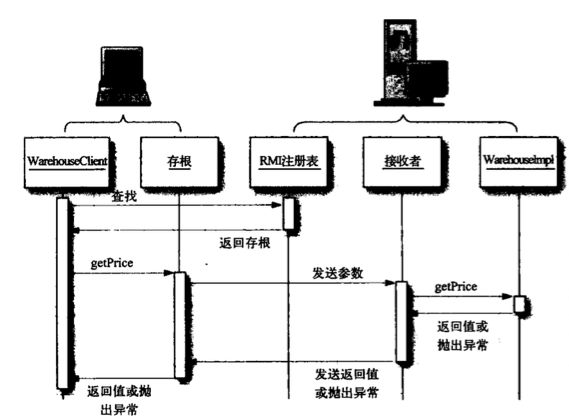
在C++中,iostream和C语言的stdio.h都是用于处理输入输出的库,但它们在设计、用法和功能上有许多不同。以下是两者的区别和联系:区别1.编程风格iostream(C++风格):C++标准库中的输入输出流类库,支持面向对象的输入输出操作。典型用法是cin(输入)和cout(输出),使用>操作符来处理数据。更加类型安全,支持用户自定义类型的输入输出。#includeintmain(){in
- 扫地机类清洁产品之直流无刷电机控制
悟空胆好小
清洁服务机器人单片机人工智能
扫地机类清洁产品之直流无刷电机控制1.1前言扫地机产品有很多的电机控制,滚刷电机1个,边刷电机1-2个,清水泵电机,风机一个,部分中高端产品支持抹布功能,也就是存在抹布盘电机,还有追觅科沃斯石头等边刷抬升电机,滚刷抬升电机等的,这些电机有直流有刷电机,直接无刷电机,步进电机,电磁阀,挪动泵等不同类型。电机的原理,驱动控制方式也不行。接下来一段时间的几个文章会作个专题分析分享。直流有刷电机会自动持续
- 高级编程--XML+socket练习题
masa010
java开发语言
1.北京华北2114.8万人上海华东2,500万人广州华南1292.68万人成都华西1417万人(1)使用dom4j将信息存入xml中(2)读取信息,并打印控制台(3)添加一个city节点与子节点(4)使用socketTCP协议编写服务端与客户端,客户端输入城市ID,服务器响应相应城市信息(5)使用socketTCP协议编写服务端与客户端,客户端要求用户输入city对象,服务端接收并使用dom4j
- 2018-07-23-催眠日作业-#不一样的31天#-66小鹿
小鹿_33
预言日:人总是在逃避命运的路上,与之不期而遇。心理学上有个著名的名词,叫做自证预言;经济学上也有一个很著名的定律叫做,墨菲定律;在灵修派上,还有一个很著名的法则,叫做吸引力法则。这3个领域的词,虽然看起来不太一样,但是他们都在告诉人们一个现象:你越担心什么,就越有可能会发生什么。同样的道理,你越想得到什么,就应该要积极地去创造什么。无论是自证预言,墨菲定律还是吸引力法则,对人都有正反2个维度的影响
- 《大清方方案》| 第二话
谁佐清欢
和珅究竟说了些什么?竟能令堂堂九五之尊龙颜失色!此处暂且按下不表;单说这位乾隆皇帝,果真不愧是康熙从小带过的,一旦决定了要做的事,便杀伐决断毫不含糊。他当即亲自拟旨,着令和珅为钦差大臣,全权负责处理方方事件,并钦赐尚方宝剑,遇急则三品以下官员可先斩后奏。和珅身负皇上重托,岂敢有半点怠慢,当夜即率领相关人等,马不停蹄杀奔江汉。这一路上,和珅的几位幕僚一直在商讨方方事件的处置方案。有位年轻幕僚建议快刀
- 【一起学Rust | 设计模式】习惯语法——使用借用类型作为参数、格式化拼接字符串、构造函数
广龙宇
一起学Rust#Rust设计模式rust设计模式开发语言
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档文章目录前言一、使用借用类型作为参数二、格式化拼接字符串三、使用构造函数总结前言Rust不是传统的面向对象编程语言,它的所有特性,使其独一无二。因此,学习特定于Rust的设计模式是必要的。本系列文章为作者学习《Rust设计模式》的学习笔记以及自己的见解。因此,本系列文章的结构也与此书的结构相同(后续可能会调成结构),基本上分为三个部分
- 《庄子.达生9》
钱江潮369
【原文】孔子观于吕梁,县水三十仞,流沫四十里,鼋鼍鱼鳖之所不能游也。见一丈夫游之,以为有苦而欲死也,使弟子并流而拯之。数百步而出,被发行歌而游于塘下。孔子从而问焉,曰:“吾以子为鬼,察子则人也。请问,‘蹈水有道乎’”曰:“亡,吾无道。吾始乎故,长乎性,成乎命。与齐俱入,与汩偕出,从水之道而不为私焉。此吾所以蹈之也。”孔子曰:“何谓始乎故,长乎性,成乎命?”曰:“吾生于陵而安于陵,故也;长于水而安于
- 关于提高复杂业务逻辑代码可读性的思考
编程经验分享
开发经验java数据库开发语言
目录前言需求场景常规写法拆分方法领域对象总结前言实际工作中大部分时间都是在写业务逻辑,一般都是三层架构,表示层(Controller)接收客户端请求,并对入参做检验,业务逻辑层(Service)负责处理业务逻辑,一般开发都是在这一层中写具体的业务逻辑。数据访问层(Dao)是直接和数据库交互的,用于查数据给业务逻辑层,或者是将业务逻辑层处理后的数据写入数据库。简单的增删改查接口不用多说,基本上写好一
- 高端密码学院笔记285
柚子_b4b4
高端幸福密码学院(高级班)幸福使者:李华第(598)期《幸福》之回归内在深层生命原动力基础篇——揭秘“激励”成长的喜悦心理案例分析主讲:刘莉一,知识扩充:成功=艰苦劳动+正确方法+少说空话。贪图省力的船夫,目标永远下游。智者的梦再美,也不如愚人实干的脚印。幸福早课堂2020.10.16星期五一笔记:1,重视和珍惜的前提是知道它的价值非常重要,当你珍惜了,你就真正定下来,真正的学到身上。2,大家需要
- 2020-04-12每天三百字之连接与替代
冷眼看潮
不知道是不是好为人师,有时候还真想和别人分享一下我对某些现象的看法或者解释。人类社会不断发展进步的过程,就是不断连接与替代的过程。人类发现了火并应用火以后,告别了茹毛饮血的野兽般的原始生活(火烧、烹饪替代了生食)人类用石器代替了完全手工,工具的使用使人类进步一大步。类似这样的替代还有很多,随着科技的发展,有更多的原始的事物被替代,代之以更高效、更先进的技术。在近现代,汽车替代了马车,高速公路和铁路
- 数组去重
好奇的猫猫猫
整理自js中基础数据结构数组去重问题思考?如何去除数组中重复的项例如数组:[1,3,4,3,5]我们在做去重的时候,一开始想到的肯定是,逐个比较,外面一层循环,内层后一个与前一个一比较,如果是久不将当前这一项放进新的数组,挨个比较完之后返回一个新的去过重复的数组不好的实践方式上述方法效率极低,代码量还多,思考?有没有更好的方法这时候不禁一想当然有了!!!hashtable啊,通过对象的hash办法
- 东南林氏之九牧林候选父系
祖缘树TheYtree
渊源介绍东晋初年晋安林始祖林禄公入闽,传十世隋右丞林茂,由晋安迁居莆田北螺村。又五世而至林万宠,唐开元间任高平太守,生三子:韬、披、昌。韬公之孙攒,唐德宗立双阙以旌表其孝,时号"阙下林家"。昌公字茂吉,乃万宠公第三子,官兵部司马,配宋氏,生一子名萍。萍于唐贞元间明经及第,官沣洲司马(后追赠中宪大夫)。唐太和年间归隐后,迁居仙游游洋,世称“游洋林”;其后裔居游洋后迁移漳州漳浦路下,由路下林第四房平和
- GitHub上克隆项目
bigbig猩猩
github
从GitHub上克隆项目是一个简单且直接的过程,它允许你将远程仓库中的项目复制到你的本地计算机上,以便进行进一步的开发、测试或学习。以下是一个详细的步骤指南,帮助你从GitHub上克隆项目。一、准备工作1.安装Git在克隆GitHub项目之前,你需要在你的计算机上安装Git工具。Git是一个开源的分布式版本控制系统,用于跟踪和管理代码变更。你可以从Git的官方网站(https://git-scm.
- 大伟说成语之唉声叹气
求索大伟
*大伟说成语*【唉声叹气】叹气:因心里不痛快或不如意而吐出长气,发出声音。因为痛苦、憋闷或感伤而发出叹息的声音。【大伟说】情绪外露,非人类所特有,动物亦有情绪,悲哀和欢乐所表示的情绪亦是不一样的,会嗷嗷大叫也会低吟痛哭。不同的是,人类的情绪更复杂,更多样,更丰富。唉声叹气,可以说是最基础的情绪,因为无奈而举足无措,不知该如何如何化解,只有独自一人慢慢承受,长吁短叹不知如何是好,其实是无能无力的表现
- Python快速入门 —— 第三节:类与对象
孤华暗香
Python快速入门python开发语言
第三节:类与对象目标:了解面向对象编程的基础概念,并学会如何定义类和创建对象。内容:类与对象:定义类:class关键字。类的构造函数:__init__()。类的属性和方法。对象的创建与使用。示例:classStudent:def__init__(self,name,age,major):self.name&#
- libyuv之linux编译
jaronho
Linuxlinux运维服务器
文章目录一、下载源码二、编译源码三、注意事项1、银河麒麟系统(aarch64)(1)解决armv8-a+dotprod+i8mm指令集支持问题(2)解决armv9-a+sve2指令集支持问题一、下载源码到GitHub网站下载https://github.com/lemenkov/libyuv源码,或者用直接用git克隆到本地,如:gitclonehttps://github.com/lemenko
- 2022-11-17
无奇君
又去了一次社康,这次是急性支气管炎……太难了。半夜就猛咳,天天咳醒,还好他戴海绵耳塞睡吵不到他,要不然对他来说也是种煎熬。一累也会猛咳,希望这次是最后一次吃药,吃完就好。又想把头发剪短了,顺便染个色。可是刚刚去看人家还没开门,不是休息日老板好佛系。理发店是个夫妻店,一年多前刚搬来的时候老板还没对象呢,当时聊天老板就说希望能找个对象一起两个人守着店都比上班强。不久后再去他已经有对象了,而且在店里帮忙
- 怎么做淘客赚钱(2022最新免费淘客盈利的方法)
高省_飞智666600
很多人都不知道什么是淘宝客,今天小编为大家解答一下吧。淘宝客,现在简称淘客,是时下比较流行的一个词语,特质为淘宝店推广商品获取提成的人,这些人没有自己的产品,只是在淘宝里面选择适合自己的产品,在自己比较熟悉的领域推广,把产品卖出去之后,会从淘宝店家那里获得百分之五到百分之五十左右的佣金。淘宝客付出的是什么呢?时间。你需要花时间去选适合自己推广的产品,需要花时间去选自己的推广方法,如果你打算自己做个
- Python爬虫解析工具之xpath使用详解
eqa11
python爬虫开发语言
文章目录Python爬虫解析工具之xpath使用详解一、引言二、环境准备1、插件安装2、依赖库安装三、xpath语法详解1、路径表达式2、通配符3、谓语4、常用函数四、xpath在Python代码中的使用1、文档树的创建2、使用xpath表达式3、获取元素内容和属性五、总结Python爬虫解析工具之xpath使用详解一、引言在Python爬虫开发中,数据提取是一个至关重要的环节。xpath作为一门
- 01-Git初识
Meereen
Gitgit
01-Git初识概念:一个免费开源,分布式的代码版本控制系统,帮助开发团队维护代码作用:记录代码内容。切换代码版本,多人开发时高效合并代码内容如何学:个人本机使用:Git基础命令和概念多人共享使用:团队开发同一个项目的代码版本管理Git配置用户信息配置:用户名和邮箱,应用在每次提交代码版本时表明自己的身份命令:查看git版本号git-v配置用户名gitconfig--globaluser.name
- 锁之缘
尘缘诗词原创作品
是谁追寻梦的足迹,是谁在偷偷的哭泣,日月隔离在黑白天地情感在心中蔓延的痕迹天与地的距离有多远流失的星晨落入哪片空间不要让泪水模糊双眼心牢中一样充满温暖谁说爱情没有永远白娘子又为何爱许仙蝴蝶墓地展翅翩翩轻歌慢舞袖卷人间传奇千古留爱万年…………月落星飞徘徊是选择不去问自已为合舍不得寂寞本就是痛苦的不在追寻梦中的痕迹才不会失去真实的自已
- ARM驱动学习之基础小知识
JT灬新一
ARM嵌入式arm开发学习
ARM驱动学习之基础小知识•sch原理图工程师工作内容–方案–元器件选型–采购(能不能买到,价格)–原理图(涉及到稳定性)•layout画板工程师–layout(封装、布局,布线,log)(涉及到稳定性)–焊接的一部分工作(调试阶段板子的焊接)•驱动工程师–驱动,原理图,layout三部分的交集容易发生矛盾•PCB研发流程介绍–方案,原理图(网表)–layout工程师(gerber文件)–PCB板
- ARM驱动学习之5 LEDS驱动
JT灬新一
嵌入式C底层arm开发学习单片机
ARM驱动学习之5LEDS驱动知识点:•linuxGPIO申请函数和赋值函数–gpio_request–gpio_set_value•三星平台配置GPIO函数–s3c_gpio_cfgpin•GPIO配置输出模式的宏变量–S3C_GPIO_OUTPUT注意点:DRIVER_NAME和DEVICE_NAME匹配。实现步骤:1.加入需要的头文件://Linux平台的gpio头文件#include//三
- ARM驱动学习之4小结
JT灬新一
嵌入式C++arm开发学习linux
ARM驱动学习之4小结#include#include#include#include#include#defineDEVICE_NAME"hello_ctl123"MODULE_LICENSE("DualBSD/GPL");MODULE_AUTHOR("TOPEET");staticlonghello_ioctl(structfile*file,unsignedintcmd,unsignedlo
- C++ | Leetcode C++题解之第409题最长回文串
Ddddddd_158
经验分享C++Leetcode题解
题目:题解:classSolution{public:intlongestPalindrome(strings){unordered_mapcount;intans=0;for(charc:s)++count[c];for(autop:count){intv=p.second;ans+=v/2*2;if(v%2==1andans%2==0)++ans;}returnans;}};
- 2020-12-24
我和我的天使们
阅读《老子的心事》391—403“将欲取之,必固与之”:想要得到什么,首先就要送出什么。我常常对孩子们说,你希望别人怎样对你你就怎样对待别人。想要得到别人的尊重,首先要尊重别人。我希望她们可以不迟到,因为不迟到是对别人的尊重,我就自己就先做到不迟到。哪怕是约朋友逛街,我尽量准时赴约。我严格要求孩子们,也同样严格要求自己,我跟孩子们一起把好的品格变成习惯。“是谓微明”:这就是微妙的智慧。看起来很少很
- 18、架构-可观测性之聚合度量
大树~~
架构javapython后端架构
聚合度量聚合度量是指对系统运行时产生的各种指标数据进行收集、聚合和分析,以了解系统的健康状况和性能表现。聚合度量是可观测性的关键组成部分,通过对度量数据的分析,可以及时发现系统中的异常和瓶颈。以下是对聚合度量各个方面的详细解析,并结合具体的数据案例和技术支撑。指标收集收集系统运行时产生的各种指标数据是聚合度量的基础。常见的指标包括CPU使用率、内存使用率、请求处理时间、请求数、错误率等。以下是指标
- 学习“论语”-第59天
春峰轩
12.14子张问政。子曰:“居之无倦,行之以忠。”子张问为政之道。孔子说:“在位尽职不懈怠,执行政令要忠诚。”12.15子曰:“博学于文,约之以礼,亦可以弗畔矣夫!”孔子说:“君子广泛地学习文献,并且用礼节约束自己,也就不会离经叛道了。”12.16子曰:“君子成人之美,不成人之恶。小人反是。”孔子说:“君子成全别人的好事,而不助长别人的坏处。小人则与此相反行事。”知识点:“成人之美,不成人之恶”贯
- 2021-11-15
宙火
我给宋小姐写了首诗,是我在课上因思恋宋小姐而写的。“自古多情是唐宋,从来双飞归巢燕。邻家小女相聘婷,常使春意荡漾我。不知单思可为爱,惟愿一心付之汝。”我拿给宋小姐看了,她说我写得很棒。我很开心,但又不是那么开心。宋小姐是回复我了,但也只是说我写得很棒,对我诗句中蕴藏的真切感情,不知道是真的没发现,还是装作没发现。但我不深究,只是这样,我就很开心了。我答应宋小姐,一天给她写一首诗。
- 《我的青葱岁月之缘来是你》 第二章 迎新晚会
思源思缘思怨
“怎么你也来了这里?”我愉快的问到,想着这是上天给的缘分吗?我还没去找他竟然就相遇了。那个让我开心的老乡。“你好,我也是舞蹈社的新人啊!”他说,笑起来回答我,眼睛弯弯的。“这么巧,我叫吴倩,你叫啥?”“我叫韩欢,你也是B市人吧,c中毕业的?”“我不是,我是f中的,不然肯定会认识你的”“是吗?以后多多关照了”他还冲我眨了眨眼睛。内心一阵悸动,这是……回到寝室,我兴奋的告诉我的室友这个事情,我再次觉得
- ASM系列四 利用Method 组件动态注入方法逻辑
lijingyao8206
字节码技术jvmAOP动态代理ASM
这篇继续结合例子来深入了解下Method组件动态变更方法字节码的实现。通过前面一篇,知道ClassVisitor 的visitMethod()方法可以返回一个MethodVisitor的实例。那么我们也基本可以知道,同ClassVisitor改变类成员一样,MethodVIsistor如果需要改变方法成员,注入逻辑,也可以
- java编程思想 --内部类
百合不是茶
java内部类匿名内部类
内部类;了解外部类 并能与之通信 内部类写出来的代码更加整洁与优雅
1,内部类的创建 内部类是创建在类中的
package com.wj.InsideClass;
/*
* 内部类的创建
*/
public class CreateInsideClass {
public CreateInsideClass(
- web.xml报错
crabdave
web.xml
web.xml报错
The content of element type "web-app" must match "(icon?,display-
name?,description?,distributable?,context-param*,filter*,filter-mapping*,listener*,servlet*,s
- 泛型类的自定义
麦田的设计者
javaandroid泛型
为什么要定义泛型类,当类中要操作的引用数据类型不确定的时候。
采用泛型类,完成扩展。
例如有一个学生类
Student{
Student(){
System.out.println("I'm a student.....");
}
}
有一个老师类
- CSS清除浮动的4中方法
IT独行者
JavaScriptUIcss
清除浮动这个问题,做前端的应该再熟悉不过了,咱是个新人,所以还是记个笔记,做个积累,努力学习向大神靠近。CSS清除浮动的方法网上一搜,大概有N多种,用过几种,说下个人感受。
1、结尾处加空div标签 clear:both 1 2 3 4
.div
1
{
background
:
#000080
;
border
:
1px
s
- Cygwin使用windows的jdk 配置方法
_wy_
jdkwindowscygwin
1.[vim /etc/profile]
JAVA_HOME="/cgydrive/d/Java/jdk1.6.0_43" (windows下jdk路径为D:\Java\jdk1.6.0_43)
PATH="$JAVA_HOME/bin:${PATH}"
CLAS
- linux下安装maven
无量
mavenlinux安装
Linux下安装maven(转) 1.首先到Maven官网
下载安装文件,目前最新版本为3.0.3,下载文件为
apache-maven-3.0.3-bin.tar.gz,下载可以使用wget命令;
2.进入下载文件夹,找到下载的文件,运行如下命令解压
tar -xvf apache-maven-2.2.1-bin.tar.gz
解压后的文件夹
- tomcat的https 配置,syslog-ng配置
aichenglong
tomcathttp跳转到httpssyslong-ng配置syslog配置
1) tomcat配置https,以及http自动跳转到https的配置
1)TOMCAT_HOME目录下生成密钥(keytool是jdk中的命令)
keytool -genkey -alias tomcat -keyalg RSA -keypass changeit -storepass changeit
- 关于领号活动总结
alafqq
活动
关于某彩票活动的总结
具体需求,每个用户进活动页面,领取一个号码,1000中的一个;
活动要求
1,随机性,一定要有随机性;
2,最少中奖概率,如果注数为3200注,则最多中4注
3,效率问题,(不能每个人来都产生一个随机数,这样效率不高);
4,支持断电(仍然从下一个开始),重启服务;(存数据库有点大材小用,因此不能存放在数据库)
解决方案
1,事先产生随机数1000个,并打
- java数据结构 冒泡排序的遍历与排序
百合不是茶
java
java的冒泡排序是一种简单的排序规则
冒泡排序的原理:
比较两个相邻的数,首先将最大的排在第一个,第二次比较第二个 ,此后一样;
针对所有的元素重复以上的步骤,除了最后一个
例题;将int array[]
- JS检查输入框输入的是否是数字的一种校验方法
bijian1013
js
如下是JS检查输入框输入的是否是数字的一种校验方法:
<form method=post target="_blank">
数字:<input type="text" name=num onkeypress="checkNum(this.form)"><br>
</form>
- Test注解的两个属性:expected和timeout
bijian1013
javaJUnitexpectedtimeout
JUnit4:Test文档中的解释:
The Test annotation supports two optional parameters.
The first, expected, declares that a test method should throw an exception.
If it doesn't throw an exception or if it
- [Gson二]继承关系的POJO的反序列化
bit1129
POJO
父类
package inheritance.test2;
import java.util.Map;
public class Model {
private String field1;
private String field2;
private Map<String, String> infoMap
- 【Spark八十四】Spark零碎知识点记录
bit1129
spark
1. ShuffleMapTask的shuffle数据在什么地方记录到MapOutputTracker中的
ShuffleMapTask的runTask方法负责写数据到shuffle map文件中。当任务执行完成成功,DAGScheduler会收到通知,在DAGScheduler的handleTaskCompletion方法中完成记录到MapOutputTracker中
- WAS各种脚本作用大全
ronin47
WAS 脚本
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/websphere/library/samples/SampleScripts.html
无意中,在WAS官网上发现的各种脚本作用,感觉很有作用,先与各位分享一下
获取下载
这些示例 jacl 和 Jython 脚本可用于在 WebSphere Application Server 的不同版本中自
- java-12.求 1+2+3+..n不能使用乘除法、 for 、 while 、 if 、 else 、 switch 、 case 等关键字以及条件判断语句
bylijinnan
switch
借鉴网上的思路,用java实现:
public class NoIfWhile {
/**
* @param args
*
* find x=1+2+3+....n
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n=10;
int re=find(n);
System.o
- Netty源码学习-ObjectEncoder和ObjectDecoder
bylijinnan
javanetty
Netty中传递对象的思路很直观:
Netty中数据的传递是基于ChannelBuffer(也就是byte[]);
那把对象序列化为字节流,就可以在Netty中传递对象了
相应的从ChannelBuffer恢复对象,就是反序列化的过程
Netty已经封装好ObjectEncoder和ObjectDecoder
先看ObjectEncoder
ObjectEncoder是往外发送
- spring 定时任务中cronExpression表达式含义
chicony
cronExpression
一个cron表达式有6个必选的元素和一个可选的元素,各个元素之间是以空格分隔的,从左至右,这些元素的含义如下表所示:
代表含义 是否必须 允许的取值范围 &nb
- Nutz配置Jndi
ctrain
JNDI
1、使用JNDI获取指定资源:
var ioc = {
dao : {
type :"org.nutz.dao.impl.NutDao",
args : [ {jndi :"jdbc/dataSource"} ]
}
}
以上方法,仅需要在容器中配置好数据源,注入到NutDao即可.
- 解决 /bin/sh^M: bad interpreter: No such file or directory
daizj
shell
在Linux中执行.sh脚本,异常/bin/sh^M: bad interpreter: No such file or directory。
分析:这是不同系统编码格式引起的:在windows系统中编辑的.sh文件可能有不可见字符,所以在Linux系统下执行会报以上异常信息。
解决:
1)在windows下转换:
利用一些编辑器如UltraEdit或EditPlus等工具
- [转]for 循环为何可恨?
dcj3sjt126com
程序员读书
Java的闭包(Closure)特征最近成为了一个热门话题。 一些精英正在起草一份议案,要在Java将来的版本中加入闭包特征。 然而,提议中的闭包语法以及语言上的这种扩充受到了众多Java程序员的猛烈抨击。
不久前,出版过数十本编程书籍的大作家Elliotte Rusty Harold发表了对Java中闭包的价值的质疑。 尤其是他问道“for 循环为何可恨?”[http://ju
- Android实用小技巧
dcj3sjt126com
android
1、去掉所有Activity界面的标题栏
修改AndroidManifest.xml 在application 标签中添加android:theme="@android:style/Theme.NoTitleBar"
2、去掉所有Activity界面的TitleBar 和StatusBar
修改AndroidManifes
- Oracle 复习笔记之序列
eksliang
Oracle 序列sequenceOracle sequence
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2098859
1.序列的作用
序列是用于生成唯一、连续序号的对象
一般用序列来充当数据库表的主键值
2.创建序列语法如下:
create sequence s_emp
start with 1 --开始值
increment by 1 --増长值
maxval
- 有“品”的程序员
gongmeitao
工作
完美程序员的10种品质
完美程序员的每种品质都有一个范围,这个范围取决于具体的问题和背景。没有能解决所有问题的
完美程序员(至少在我们这个星球上),并且对于特定问题,完美程序员应该具有以下品质:
1. 才智非凡- 能够理解问题、能够用清晰可读的代码翻译并表达想法、善于分析并且逻辑思维能力强
(范围:用简单方式解决复杂问题)
- 使用KeleyiSQLHelper类进行分页查询
hvt
sql.netC#asp.nethovertree
本文适用于sql server单主键表或者视图进行分页查询,支持多字段排序。KeleyiSQLHelper类的最新代码请到http://hovertree.codeplex.com/SourceControl/latest下载整个解决方案源代码查看。或者直接在线查看类的代码:http://hovertree.codeplex.com/SourceControl/latest#HoverTree.D
- SVG 教程 (三)圆形,椭圆,直线
天梯梦
svg
SVG <circle> SVG 圆形 - <circle>
<circle> 标签可用来创建一个圆:
下面是SVG代码:
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1">
<circle cx="100" c
- 链表栈
luyulong
java数据结构
public class Node {
private Object object;
private Node next;
public Node() {
this.next = null;
this.object = null;
}
public Object getObject() {
return object;
}
public
- 基础数据结构和算法十:2-3 search tree
sunwinner
Algorithm2-3 search tree
Binary search tree works well for a wide variety of applications, but they have poor worst-case performance. Now we introduce a type of binary search tree where costs are guaranteed to be loga
- spring配置定时任务
stunizhengjia
springtimer
最近因工作的需要,用到了spring的定时任务的功能,觉得spring还是很智能化的,只需要配置一下配置文件就可以了,在此记录一下,以便以后用到:
//------------------------定时任务调用的方法------------------------------
/**
* 存储过程定时器
*/
publi
- ITeye 8月技术图书有奖试读获奖名单公布
ITeye管理员
活动
ITeye携手博文视点举办的8月技术图书有奖试读活动已圆满结束,非常感谢广大用户对本次活动的关注与参与。
8月试读活动回顾:
http://webmaster.iteye.com/blog/2102830
本次技术图书试读活动的优秀奖获奖名单及相应作品如下(优秀文章有很多,但名额有限,没获奖并不代表不优秀):
《跨终端Web》
gleams:http