C和指针---第十七章:经典抽象数据类型
17.1 内存分配
所有的ADT都必须确定一件事情---如何获取内存来存储值.有三种可选的方案:静态数组,动态分配的数组和动态分配的链式结构.
17.2 堆栈
17.2.1 接口
/* **一个堆栈模块的接口 */ #define STACK_TYPE int /* 堆栈所存储的值的类型 */ /* ** push ** 把一个新值压入到堆栈中.它的参数是需要被压入的值 */ void push( STACK_TYPE value ); /* ** pop ** 从堆栈弹出一个值,并将其丢弃 */ void pop( void ); /* ** top ** 返回堆栈顶部元素的值,但不对堆栈进行修改 */ STACK_TYPE top( void ); /* ** is_empty ** 如果堆栈为空,返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE */ int is_empty( void ); /* ** is_full ** 如果堆栈已满,返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE */ int is_full( void );一: 数组堆栈
备注:所有不属于外部接口的内容都被声明为static,这可以防止用户使用预定义接口之外的任何方式访问堆栈中的值.
/*
** 用一个静态数组实现的堆栈.数组的长度只能通过修改#define定义
** 并对模块重新进行编译来实现
*/
#include "stack.h"
#include <assert.h>
#define STACK_SIZE 100 /*堆栈中最大值的限制*/
static STACK_TYPE stack[ STACK_SIZE ];
static int top_element = -1;
void push( STACK_TYPE value )
{
assert( !is_full() );
top_element += 1;
stack[ top_element ] = value;
}
void pop( void )
{
assert( !is_empty() );
top_element -= 1;
}
STACK_TYPE top( void )
{
assert( !is_empty() );
return stack[ top_element ];
}
int is_empty( void )
{
return -1 == top_element;
}
int is_full( void )
{
return STACK_SIZE - 1 == top_element;
} 二:动态数组堆栈
我们先声明两个额外的函数:
/* ** create_stack ** 创建堆栈.参数指定堆栈可以保存多少个元素 */ void create_stack( size_t size ); /* ** destroy_stack ** 销毁堆栈,它释放堆栈所使用的内存 */ void destroy_stack( void );接口实现:
/*
** 一个用动态分配数组实现的堆栈
** 堆栈的长度在创建堆栈的函数被调用时给出,该函数必须在任何其他操作堆栈的函数被调用之前调用
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include "stack.h"
static STACK_TYPE *stack;
static size_t stack_size;
static int top_element = -1;
void create_stack( size_t size )
{
assert( 0 == stack_size );
stack_size = size;
stack = malloc( stack_size * sizeof( STACK_TYPE ) );
assert( NULL != stack );
}
void destroy_stack( void )
{
assert( stack_size > 0 );
stack_size = 0;
free( stack );
stack = NULL;
}
void push( STACK_TYPE value )
{
assert( !is_full() );
top_element += 1;
stack[ top_element ] = value;
}
void pop( void )
{
assert( !is_empty() );
top_element -= 1;
}
STACK_TYPE top( void )
{
assert( !is_empty() );
return stack[ top_element ];
}
int is_empty( void )
{
assert( stack_size > 0 );
return -1 == top_element;
}
int is_full( void )
{
assert( stack_size > 0 );
return top_element == stack_size - 1;
} 三:链式堆栈
由于只有堆栈的顶部元素才可以被访问,所以使用单链表就可以很好的实现链式堆栈.把一个新元素压入到堆栈是通过在链表的起始位置添加一个元素实现的.从堆栈中弹出一个元素是通过从链表中移除第一个元素实现的.位于链表头部的元素总是很容易被访问.
#include "stack.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#define FALSE 0
typedef struct STACK_NODE {
STACK_TYPE value;
struct STACK_NODE *next;
} StackNode;
static StackNode *stack;
void create_stack( size_t size )
{
}
void destroy_stack( void )
{
while ( !is_empty() ){
pop();
}
}
void push( STACK_TYPE value )
{
StackNode *new_node;
new_node = malloc( sizeof( StackNode ) );
assert( NULL != new_node );
new_node->value = value;
new_node->next = stack; //这里是关键,将新建节点插入到头部
stack = new_node;
}
void pop( void )
{
StackNode *first_node;
assert( !is_empty() );
first_node = stack;
stack = first_node->next;
free( first_node );
}
STACK_TYPE top( void )
{
assert( !is_empty() );
return stack->value;
}
int is_empty( void )
{
return NULL == stack; //备注:这里静态创建stack,所以本身会被初始化为NULL.如果非静态,请手动初始化为NULL
}
int is_full( void )
{
return FALSE;
}
17.3 队列
接口:
/* ** 一个队列模块的接口 */ #include <stdlib.h> #define QUEUE_TYPE int /* ** create_queue ** 创建一个队列,参数指定队列可以存储的元素的最大数量 */ void create_queue( size_t size ); /* ** 销毁一个队列. */ void destroy_queue( void ); /* ** insert ** 向队列添加一个新元素,参数就是需要添加的元素 */ void insert( QUEUE_TYPE value ); /* ** delete ** 从队列中移除一个元素并将其丢弃 */ void delete( void ); /* ** first ** 返回队列中第一个元素的值,但不修改队列本身 */ QUEUE_TYPE first( void ); /* ** is_empty ** 如果队列为空,返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE */ int is_empty( void ); /* ** is_full ** 如果队列已满,返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE */ int is_full( void );实现:
/*
** 一个用静态数组实现的队列.数组的长度只能通过修改#define定义并重新编译模块来调整
*/
#include "queue.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#define QUEUE_SIZE 100
#define ARRAY_SIZE ( QUEUE_SIZE + 1 )
static QUEUE_TYPE queue[ ARRAY_SIZE ];
static size_t front = 1; //第一个元素空出来,用于判断队列满还是空
static size_t rear = 0;
void insert( QUEUE_TYPE value )
{
assert( !is_full() );
rear = ( rear + 1 ) % ARRAY_SIZE;
queue[ rear ] = value;
}
void delete( void )
{
assert( !is_empty() );
front = ( front + 1 ) % ARRAY_SIZE;
}
QUEUE_TYPE first( void )
{
assert( !is_empty() );
return queue[ front ];
}
int is_empty( void )
{
return ( rear + 1 ) % ARRAY_SIZE == front;
}
int is_full( void )
{
return ( rear + 2 ) % ARRAY_SIZE == front;
}
17.4 数---二叉搜索树
17.4.5 二叉搜索树的接口
#define TREE_TYPE int /* ** insert ** 向树添加一个新值.参数是需要被添加的值,它必须原先并不存在于树中 */ void insert( TREE_TYPE value ); /* ** find ** 查找一个特定的值,这个值作为第一个参数传递给函数 */ TREE_TYPE *find( TREE_TYPE value ); /* ** pre_order_traverse ** 执行树的前序遍历.它的参数是一个回调函数指针,它所指向的函数将在树中处理每个 ** 节点被调用,节点的值作为参数传递给这个函数 */ void pre_order_traverse( void ( *callback )( TREE_TYPE value ) );实现:
/*
** 一个使用静态数组实现的二叉搜索树.数组的长度只能通过修改#define定义
** 并对模块进行重新编译来实现
*/
#include "tree.h"
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define TREE_SIZE 100
#define ARRAY_SIZE ( TREE_SIZE + 1 )
/*
** 用于存储树的所有节点的数组
*/
static TREE_TYPE tree[ ARRAY_SIZE ];
/*
** 计算一个节点左孩子的下标
*/
static int left_child( int current )
{
return current * 2;
}
/*
** 计算一个节点右孩子的下标
*/
static int right_child( int current )
{
return current * 2 + 1;
}
void insert( TREE_TYPE value )
{
int current;
/*
** 确保值为非零,因为零用于提示一个未使用的节点
*/
assert( 0 != value );
/*
** 从根节点开始
*/
current = 1;
/*
** 从适合的子树开始,知道到达一个叶节点
*/
while ( 0 != tree[ current ] ){
if ( value < tree[ current ] ){
current = left_child( current );
}
else{
assert( value != tree[ current ] ); //直接终止程序非常不好,可以用return来代替
current = right_child( current );
}
assert( current < ARRAY_SIZE );
}
tree[ current ] = value;
}
TREE_TYPE *find( TREE_TYPE value )
{
int current;
/*
** 从根节点开始.知道找到那个值,进入合适的子树
*/
current = 1;
while ( current < ARRAY_SIZE && tree[ current ] != value ){
if ( value < tree[ current ] ){
current = left_child( current );
}
else{
current = right_child( current );
}
}
if ( current < ARRAY_SIZE ){
return tree + current;
}
return 0;
}
/*
** do_pre_order_traverse
** 执行一层前序遍历,这个帮助函数用于保存我们当前正在处理的节点的信息.
** 它并不是用户接口的一部分
*/
static void do_pre_order_traverse( int current, void ( *callback )( TREE_TYPE value ) )
{
if ( current < ARRAY_SIZE && tree[ current ] != 0 ){
callback( tree[ currentr ] );
do_pre_order_traverse( left_child( current ), callback );
do_pre_order_traverse( right_child( current ), callback );
}
}
void pre_order_traverse( void ( *callback )( TREE_TYPE value ) )
{
do_pre_order_traverse( 1, callback );
} 二叉树的链式实现:
/*
** 一个使用动态分配的链式结构实现的二叉搜索树.
*/
#include "tree.h"
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/*
** TreeNode结构包含了值和两个指向某个树节点的指针
*/
typedef struct TREE_NODE {
TREE_TYPE value;
struct TREE_NODE *left;
struct TREE_NODE *right;
} TreeNode;
/*
** 指向树根节点的指针
*/
static TreeNode *tree;
void insert( TREE_TYPE value )
{
TreeNode *current;
TreeNode **link; //注意:这里用到指向节点指针的指针,这样才能做到修改
link = &tree;
while ( ( current = *link ) != NULL ){
if ( value < current->value ){
link = ¤t->left;
}
else{
assert( value != current->value );
link = ¤t->right;
}
}
/*
** 分配一个新节点,使适当节点的link字段指向它.
** 备注:任何一个节点总可以插入到叶节点的位置
*/
current = malloc( sizeof( TreeNode ) );
assert( NULL != current );
current->value = value;
current->left = NULL;
current->right = NULL;
*link = current;
}
TREE_TYPE *find( TREE_TYPE value )
{
TreeNode *current;
current = tree;
while ( current != NULL && current->value != value ){
if ( value < current->value ){
current = current->left;
}
else{
current = current->right;
}
}
if ( NULL != current ){
return ¤t->value;
}
return NULL;
}
/*
** do_pre_order_traverse
** 执行一层前序遍历.这个帮助函数用于保存我们当前正在处理的节点信息.
** 这个函数并不是用户接口的一部分
*/
static void do_pre_order_traverse( TreeNode *current, void ( *callback )( TREE_TYPE value ) )
{
if ( NULL != current ){
callback( current->value );
do_pre_order_traverse( current->left, callback );
do_pre_order_traverse( current->right, callback );
}
}
void pre_order_traverse( void ( *callback )( TREE_TYPE value ) )
{
do_pre_order_traverse( tree, callback );
}
17.5 实现的改进
改进的方案就是用到面向对象的思想.但是不推荐用C的宏来完成面向对象--如果可以,请用C++.
(学习C后,才慢慢了解了一点C++,希望学完C后能学习下Java,更懂得C++.然后,当一名合格的C/C++程序员)
问题:
1.
void resize_stack( size_t newSize )
{
assert( 0 == stack_size );
stack_size = newSize;
stack = realloc( stack, stack_size );
}
这里有中粗暴的方法是:直接销毁原来的堆栈,然后新malloc一个堆栈.但是这样的话,原来的数据均销毁了.所以,用realloc分配新的一块内存.
2.
#include "queue.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
static QUEUE_TYPE *queue;
static size_t front = 1; //第一个元素空出来,用于判断队列满还是空
static size_t rear = 0;
static size_t queue_size;
static size_t array_size;
void create_queue( size_t size )
{
assert( 0 == queue_size );
queue_size = size;
array_size = queue_size + 1;
queue = malloc( queue_size * sizeof( QUEUE_TYPE ) );
assert( NULL != queue );
}
void insert( QUEUE_TYPE value )
{
assert( !is_full() );
rear = ( rear + 1 ) % array_size;
queue[ rear ] = value;
}
void delete( void )
{
assert( !is_empty() );
front = ( front + 1 ) % array_size;
}
QUEUE_TYPE first( void )
{
assert( !is_empty() );
return queue[ front ];
}
int is_empty( void )
{
return ( rear + 1 ) % array_size == front;
}
int is_full( void )
{
return ( rear + 2 ) % array_size == front;
}
3.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define QUEUE_TYPE int
typedef struct QUEUE{
QUEUE_TYPE value;
struct QUEUE *preNode;
struct QUEUE *nextNode;
} QueueNode;
static QueueNode *queue;
void push( QUEUE_TYPE value )
{
QueueNode *newnode;
newnode = malloc( sizeof( QueueNode ) );
newnode->nextNode = queue;
newnode->value = value;
if ( queue ){
queue->preNode = newnode;
while ( queue->nextNode ){
queue = queue->nextNode;
}
newnode->preNode = queue; //不为空的时候,头节点的prenode指向最后一个节点
}
else{
newnode->preNode = newnode; //为空的时候,头节点指向自身
}
queue = newnode;
}
void pop()
{
QueueNode *newnode;
if ( queue->preNode == queue ){ //当只有一个值的时候,特殊处理
free( queue );
queue = NULL;
return;
}
if ( queue ){
newnode = queue->preNode;
queue->preNode = newnode->preNode;
newnode->preNode->nextNode = NULL;
free( newnode );
}
}
void delete( void )
{
while ( NULL != queue ){
pop();
}
}
QUEUE_TYPE top( void )
{
if ( queue ){
return queue->preNode->value;
}
return -1;
}
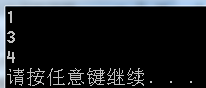
int main(void)
{
push( 1 );
push( 2 );
push( 3 );
push( 4 );
push( 5 );
printf("%d\n", top() ); //5-->4-->3-->2-->1-->NULL 输出1
pop(); //5-->4-->3-->2-->NULL
pop(); //5-->4-->3-->NULL
push( 10 ); //10-->5-->4-->3-->NULL
printf("%d\n", top() ); //输出3
pop(); //10-->5-->4-->NULL
push( 111 ); //111-->10-->5-->4-->NULL
printf("%d\n", top() ); //输出4
return 0;
} 程序输出:
备注:并为进行严格的检查,比如空队列进行top时候,只是显示-1一样.
4.用数组,实际上很难实现的,或者说实现起来很麻烦.可以用链表实现:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef struct STACK_NODE {
int *stack;
int size;
int top_elements;
} StackNode;
static StackNode stackArray[10];
void create_stack( int index, int size )
{
assert( 0 == stackArray[ index ].size );
stackArray[ index ].size = size;
stackArray[ index ].stack = malloc( size * sizeof( int ) );
assert( NULL != stackArray[ index ].stack );
stackArray[ index ].top_elements = -1;
}
void delete_stack( int index )
{
assert( index >= 0 && index < 10 );
assert( stackArray[ index ].size > 0 );
stackArray[ index ].size = 0;
free( stackArray[ index ].stack );
stackArray[ index ].stack = NULL;
}
int is_full( int index )
{
assert( index >= 0 && index < 10 );
assert( stackArray[ index ].size > 0);
return stackArray[ index ].top_elements == stackArray[ index ].size - 1;
}
int is_empty( int index )
{
assert( index >= 0 && index < 10 );
assert( stackArray[ index ].size > 0);
return -1 == stackArray[ index ].top_elements;
}
void push( int index, int value )
{
assert( index >= 0 && index < 10 );
assert( !is_full( index ) );
stackArray[ index ].top_elements++;
stackArray[ index ].stack[ stackArray[ index ].top_elements ] = value;
}
void pop( int index )
{
assert( index >= 0 && index < 10 );
assert( !is_empty( index ) );
stackArray[ index ].top_elements--;
}
int top( int index )
{
assert( index >= 0 && index < 10 );
assert( !is_empty( index ) );
return stackArray[ index ].stack[ stackArray[ index ].top_elements ];
}
void printStack( int index )
{
while ( !is_empty( index ) ){
printf("%d ", top( index ) );
pop( index );
}
printf("\n");
}
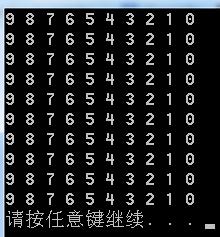
int main(void)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ){
create_stack( i, 10 );
}
for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ){
for ( j = 0; j < 10; j++ ){
push( i, j );
}
}
for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ){
printStack( i );
}
return 0;
} 程序输出:
5.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct TREE{
struct TREE *leftChild;
struct TREE *rightChild;
int value;
} TreeNode;
void insertNode( TreeNode **tree, int value )
{
TreeNode *current;
while ( NULL != *tree ){
if ( value < ( *tree )->value ){
tree = &( *tree )->leftChild; //这里注意:要用tree而不是*tree.否则无法进行修改
}
else if ( value == ( *tree )->value ){
return;
}
else{
tree = &( *tree )->rightChild;
}
}
current = malloc( sizeof( TreeNode ) );
current->leftChild = NULL;
current->rightChild = NULL;
current->value = value;
*tree = current;
}
void deleteNode( TreeNode **tree, int value )
{
while ( NULL != *tree ){
if ( value == ( *tree )->value ){
break;
}
else if ( value < ( *tree )->value ){
tree = &( *tree )->leftChild;
}
else{
tree = &( *tree )->rightChild;
}
}
if ( NULL == *tree ){ //为空时删除完毕
return;
}
if ( NULL == ( *tree )->leftChild && NULL == ( *tree )->rightChild ){ //为叶节点
free( *tree );
*tree = NULL;
}
else if ( NULL == ( *tree )->leftChild && NULL != ( *tree )->rightChild ){ //包含左节点
TreeNode *tempNode;
tempNode = ( *tree );
*tree = (*tree)->rightChild;
free( tempNode );
}
else if ( NULL != ( *tree )->leftChild && NULL == ( *tree )->rightChild ){ //包含右节点
TreeNode *tempNode;
tempNode = ( *tree );
*tree = ( *tree )->leftChild;
free( tempNode );
}
else{
TreeNode *tempNode = ( *tree )->leftChild;
TreeNode *preNode = NULL;
if ( NULL == tempNode->rightChild ){ //当子节点无右节点的时候,特殊处理
( *tree )->value = tempNode->value;
( *tree )->leftChild = tempNode->leftChild;
return;
}
while ( tempNode->rightChild ){ //否则,将子树中的最大值(即最最右节点copy到删除节点上面)
preNode = tempNode;
tempNode = tempNode->rightChild;
}
(*tree)->value = tempNode->value;
free( tempNode );
tempNode = NULL;
preNode->rightChild = NULL;
}
}
int countNode( TreeNode *tree )
{
static countNum = 0;
if ( NULL != tree ){
countNum++;
countNode( tree->leftChild );
countNode( tree->rightChild );
}
return countNum;
}
void pre_print( TreeNode *tree )
{
if ( NULL != tree ){
printf("%d ", tree->value );
pre_print( tree->leftChild );
pre_print( tree->rightChild );
}
}
void mid_print( TreeNode *tree )
{
if ( NULL != tree ){
mid_print( tree->leftChild );
printf("%d ", tree->value );
mid_print( tree->rightChild );
}
}
void last_print( TreeNode *tree )
{
if ( NULL != tree ){
last_print( tree->leftChild );
last_print( tree->rightChild );
printf("%d ", tree->value );
}
}
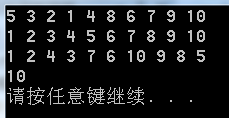
int main( void )
{
TreeNode *node = NULL;
insertNode( &node, 5 );
insertNode( &node, 3 );
insertNode( &node, 8 );
insertNode( &node, 2 );
insertNode( &node, 4 );
insertNode( &node, 1 );
insertNode( &node, 6 );
insertNode( &node, 9 );
insertNode( &node, 7 );
insertNode( &node, 10 );
pre_print( node );
printf("\n");
mid_print( node );
printf("\n");
last_print( node );
printf("\n");
printf("%d\n", countNode( node ) );
return 0;
}
程序输出:
6.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define QUEUE_TYPE TreeNode*
typedef struct TREE{
struct TREE *leftChild;
struct TREE *rightChild;
int value;
} TreeNode;
typedef struct QUEUE{
QUEUE_TYPE value;
struct QUEUE *preNode;
struct QUEUE *nextNode;
} QueueNode;
static QueueNode *queue;
void insertNode( TreeNode **tree, int value )
{
TreeNode *current;
while ( NULL != *tree ){
if ( value < ( *tree )->value ){
tree = &( *tree )->leftChild; //这里注意:要用tree而不是*tree.否则无法进行修改
}
else if ( value == ( *tree )->value ){
return;
}
else{
tree = &( *tree )->rightChild;
}
}
current = malloc( sizeof( TreeNode ) );
current->leftChild = NULL;
current->rightChild = NULL;
current->value = value;
*tree = current;
}
void deleteNode( TreeNode **tree, int value )
{
while ( NULL != *tree ){
if ( value == ( *tree )->value ){
break;
}
else if ( value < ( *tree )->value ){
tree = &( *tree )->leftChild;
}
else{
tree = &( *tree )->rightChild;
}
}
if ( NULL == *tree ){ //为空时删除完毕
return;
}
if ( NULL == ( *tree )->leftChild && NULL == ( *tree )->rightChild ){ //为叶节点
free( *tree );
*tree = NULL;
}
else if ( NULL == ( *tree )->leftChild && NULL != ( *tree )->rightChild ){ //包含左节点
TreeNode *tempNode;
tempNode = ( *tree );
*tree = (*tree)->rightChild;
free( tempNode );
}
else if ( NULL != ( *tree )->leftChild && NULL == ( *tree )->rightChild ){ //包含右节点
TreeNode *tempNode;
tempNode = ( *tree );
*tree = ( *tree )->leftChild;
free( tempNode );
}
else{
TreeNode *tempNode = ( *tree )->leftChild;
TreeNode *preNode = NULL;
if ( NULL == tempNode->rightChild ){ //当子节点无右节点的时候,特殊处理
( *tree )->value = tempNode->value;
( *tree )->leftChild = tempNode->leftChild;
return;
}
while ( tempNode->rightChild ){ //否则,将子树中的最大值(即最最右节点copy到删除节点上面)
preNode = tempNode;
tempNode = tempNode->rightChild;
}
(*tree)->value = tempNode->value;
free( tempNode );
tempNode = NULL;
preNode->rightChild = NULL;
}
}
int countNode( TreeNode *tree )
{
static countNum = 0;
if ( NULL != tree ){
countNum++;
countNode( tree->leftChild );
countNode( tree->rightChild );
}
return countNum;
}
void pre_print( TreeNode *tree )
{
if ( NULL != tree ){
printf("%d ", tree->value );
pre_print( tree->leftChild );
pre_print( tree->rightChild );
}
}
void mid_print( TreeNode *tree )
{
if ( NULL != tree ){
mid_print( tree->leftChild );
printf("%d ", tree->value );
mid_print( tree->rightChild );
}
}
void last_print( TreeNode *tree )
{
if ( NULL != tree ){
last_print( tree->leftChild );
last_print( tree->rightChild );
printf("%d ", tree->value );
}
}
void value_print( TreeNode *tree )
{
if ( tree ){
printf("%d ", tree->value );
}
}
//----------------------------//
void push( QUEUE_TYPE value )
{
QueueNode *newnode;
newnode = malloc( sizeof( QueueNode ) );
newnode->nextNode = queue;
newnode->value = value;
if ( queue ){
queue->preNode = newnode;
while ( queue->nextNode ){
queue = queue->nextNode;
}
newnode->preNode = queue; //不为空的时候,头节点的prenode指向最后一个节点
}
else{
newnode->preNode = newnode; //为空的时候,头节点指向自身
}
queue = newnode;
}
void pop()
{
QueueNode *newnode;
if ( queue->preNode == queue ){ //当只有一个值的时候,特殊处理
free( queue );
queue = NULL;
return;
}
if ( queue ){
newnode = queue->preNode;
queue->preNode = newnode->preNode;
newnode->preNode->nextNode = NULL;
free( newnode );
}
}
void delete( void )
{
while ( NULL != queue ){
pop();
}
}
QUEUE_TYPE top( void )
{
if ( queue ){
return queue->preNode->value;
}
return NULL;
}
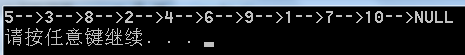
int main( void )
{
TreeNode *node = NULL;
TreeNode *tempNode;
insertNode( &node, 5 );
insertNode( &node, 3 );
insertNode( &node, 8 );
insertNode( &node, 2 );
insertNode( &node, 4 );
insertNode( &node, 1 );
insertNode( &node, 6 );
insertNode( &node, 9 );
insertNode( &node, 7 );
insertNode( &node, 10 );
push( node );
while ( queue ){
while ( queue ){
tempNode = top();
printf("%d-->", tempNode->value );
pop();
if ( tempNode->leftChild){
push( tempNode->leftChild );
}
if ( tempNode->rightChild ){
push( tempNode->rightChild );
}
}
}
printf("NULL\n");
return 0;
}
程序输出:
7. 只要看中序是否是升序就可以了.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct TREE{
struct TREE *leftChild;
struct TREE *rightChild;
int value;
} TreeNode;
void insertNode( TreeNode **tree, int value )
{
TreeNode *current;
while ( NULL != *tree ){
if ( value < ( *tree )->value ){
tree = &( *tree )->leftChild; //这里注意:要用tree而不是*tree.否则无法进行修改
}
else if ( value == ( *tree )->value ){
return;
}
else{
tree = &( *tree )->rightChild;
}
}
current = malloc( sizeof( TreeNode ) );
current->leftChild = NULL;
current->rightChild = NULL;
current->value = value;
*tree = current;
}
void deleteNode( TreeNode **tree, int value )
{
while ( NULL != *tree ){
if ( value == ( *tree )->value ){
break;
}
else if ( value < ( *tree )->value ){
tree = &( *tree )->leftChild;
}
else{
tree = &( *tree )->rightChild;
}
}
if ( NULL == *tree ){ //为空时删除完毕
return;
}
if ( NULL == ( *tree )->leftChild && NULL == ( *tree )->rightChild ){ //为叶节点
free( *tree );
*tree = NULL;
}
else if ( NULL == ( *tree )->leftChild && NULL != ( *tree )->rightChild ){ //包含左节点
TreeNode *tempNode;
tempNode = ( *tree );
*tree = (*tree)->rightChild;
free( tempNode );
}
else if ( NULL != ( *tree )->leftChild && NULL == ( *tree )->rightChild ){ //包含右节点
TreeNode *tempNode;
tempNode = ( *tree );
*tree = ( *tree )->leftChild;
free( tempNode );
}
else{
TreeNode *tempNode = ( *tree )->leftChild;
TreeNode *preNode = NULL;
if ( NULL == tempNode->rightChild ){ //当子节点无右节点的时候,特殊处理
( *tree )->value = tempNode->value;
( *tree )->leftChild = tempNode->leftChild;
return;
}
while ( tempNode->rightChild ){ //否则,将子树中的最大值(即最最右节点copy到删除节点上面)
preNode = tempNode;
tempNode = tempNode->rightChild;
}
(*tree)->value = tempNode->value;
free( tempNode );
tempNode = NULL;
preNode->rightChild = NULL;
}
}
int countNode( TreeNode *tree )
{
static countNum = 0;
if ( NULL != tree ){
countNum++;
countNode( tree->leftChild );
countNode( tree->rightChild );
}
return countNum;
}
void pre_print( TreeNode *tree )
{
if ( NULL != tree ){
printf("%d ", tree->value );
pre_print( tree->leftChild );
pre_print( tree->rightChild );
}
}
void mid_print( TreeNode *tree )
{
if ( NULL != tree ){
mid_print( tree->leftChild );
printf("%d ", tree->value );
mid_print( tree->rightChild );
}
}
void last_print( TreeNode *tree )
{
if ( NULL != tree ){
last_print( tree->leftChild );
last_print( tree->rightChild );
printf("%d ", tree->value );
}
}
void isTree( TreeNode *tree, int arr[] )
{
static int i = 0;
if ( NULL != tree ){
isTree( tree->leftChild, arr );
arr[ i++ ] = tree->value;
isTree( tree->rightChild, arr );
}
}
int main( void )
{
TreeNode *node = NULL;
int arr[10];
int i = 0;
insertNode( &node, 5 );
insertNode( &node, 3 );
insertNode( &node, 8 );
insertNode( &node, 2 );
insertNode( &node, 4 );
insertNode( &node, 1 );
insertNode( &node, 6 );
insertNode( &node, 9 );
insertNode( &node, 7 );
insertNode( &node, 10 );
for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ){
arr[ i ] = 0;
}
isTree( node, arr );
for ( i = 0; i < 9; i++ ){
if ( arr[ i ] > arr[ i + 1 ]){
break;
}
}
if ( 9 == i ){
printf("yes, it is right!\n");
}
return 0;
} 程序输出:
9.
void destroy_tree( TreeNode **tree )
{
while ( *tree ){
deleteNode( tree, ( *tree )->value );
}
}
备注:进行添加和删除的时候,请把指针传递进去.
10.第七题已实现此功能,但不是终止程序,只是return了回去.