相关性能测试和使用例子,可以参见另一篇文章: cglib相关性能测试对比
背景
前段时间在工作中,包括一些代码阅读过程中,spring aop经常性的会看到cglib中的相关内容,包括BeanCopier,BulkBean,Enancher等内容,以前虽大致知道一些内容,原理是通过bytecode,但没具体深入代码研究,只知其所用不知其所以然,所以就特地花了半天多的工作时间研究了CGLIB的相关源码,同时结合看了下 spring Aop中对CGLIB的使用。
本文主要通过对cglib有原理的分析,反编译查看源码,例子等方式做一个介绍。
cglib基本信息
- cglib的官方网站: http://cglib.sourceforge.net/
- cglib目前的最新版本应该是2.2,公司普遍使用的版本也是这个
- 官网的samples : http://cglib.sourceforge.net/xref/samples/
cglib代码包结构
- core (核心代码)
- EmitUtils
- ReflectUtils
- KeyFactory
- ClassEmitter/CodeEmitter
- NamingPolicy/DefaultNamingPolicy
- GeneratorStrategy/DefaultGeneratorStrategy
- DebuggingClassWriter
- ClassGenerator/AbstractClassGenerator
- beans (bean操作类)
- BeanCopier
- BulkBean
- BeanMap
- ImmutableBean
- BeanGenerator
- reflect
- proxy
- Enhancer
- CallbackGenerator
- Callback
- MethodInterceptor , Dispatcher, LazyLoader , ProxyRefDispatcher , NoOp , FixedValue , InvocationHandler(提供和jdk proxy的功能)
- CallbackFilter
- util
- StringSwitcher
- ParallelSorter
- transform
core核心代码部分
EmitUtils
重要的工具类,主要封装了一些操作bytecode的基本函数,比如生成一个null_constructor,添加类属性add_property等
ReflectUtils
处理jdk reflect的工具类,比如获取一个类所有的Method,获取构造函数信息等。
ClassEmitter/CodeEmitter
对asm的classAdapter和MethodAdapter的实现,贯穿于cglib代码的处理
KeyFactory
类库中重要的唯一标识生成器,用于cglib做cache时做map key,比较底层的基础类。
例子:
interface BulkBeanKey { public Object newInstance(String target, String[] getters, String[] setters, String[] types);
}
(BulkBeanKey)KeyFactory.create(BulkBeanKey.class).newInstance(targetClassName, getters, setters, typeClassNames);
说明:
- 每个Key接口,都必须提供newInstance方法,但具体的参数可以随意定义,通过newInstance返回的为一个唯一标示,只有当传入的所有参数的equals都返回true时,生成的key才是相同的,这就相当于多key的概念。
NamingPolicy
默认的实现类:DefaultNamingPolicy, 具体cglib动态生成类的命名控制。
一般的命名规则:
- 被代理class name + "$$" + 使用cglib处理的class name + "ByCGLIB" + "$$" + key的hashcode
- 示例:FastSource$$FastClassByCGLIB$$e1a36bab.class
GeneratorStrategy
默认的实现类: DefaultGeneratorStrategy
控制ClassGenerator生成class的byte数据,中间可插入自己的处理。注意这里依赖了:DebuggingClassWriter进行class generator的处理
DebuggingClassWriter
cglib封装asm的处理类,用于生成class的byte流,通过GeneratorStrategy回调ClassGenerator.generateClass(DebuggingClassWriter),将自定义的class byte处理回调给具体的cglib上层操作类,比如由具体的BeanCopier去控制bytecode的生成。
ClassGenerator
其中一个抽象实现:AbstractClassGenerator。cglib代码中核心的Class bytecode操作主体,包含了一些cache,调用NamingPolicy,GeneratorStrategy进行处理,可以说是一个最核心的调度者。
对应的类图:
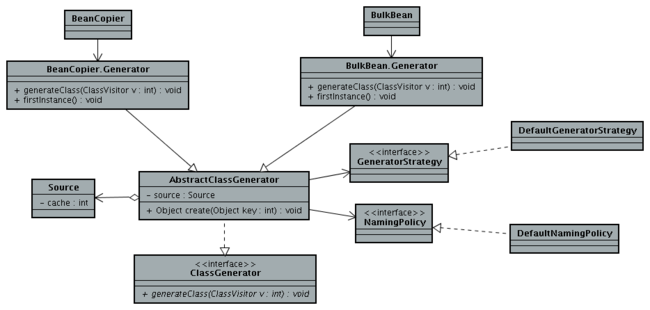
- 外部的BeanCopier都包含了一Generator,继承自AbstractClassGenerator,实现了generateClass(ClassVisitor v),Object firstInstance(Class type)方法。
- AbstractClassGenerator自身会根据Source进行cache,所以针对已经生成过的class,这里KeyFactory对应的值要相等,则会直接返回cache中的结果。所以BeanCopier每次create慢只是每次都需要new两个对象,一个是KeyFactory.newInstance,另一个是firstInstance方法调用生成一个对象。
反编译tips
大家都知道cglib是进行bytecode操作,会动态生成class,最快最直接的学习就是结合他生成的class,对照代码进行学习,效果会好很多。
- system.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "指定输出目录");
system.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "指定输出目录");
可参见 cores/DebuggingClassWriter代码。说明:这样cglib会将动态生成的每个class都输出到文件中,然后我们可以通过decomp进行反编译查看源码。
beans (相关操作类)
BeanCopier
简单的示例代码就不做介绍,相信大家都指导怎么用,这里主要介绍下Convert的使用。
- 许多网友都做过BeanCopier,BeanUtils的测试,基本BeanCopier的性能是BeanUtils的10倍以上。,出了反射这一性能差异外,BeanUtils默认是开启Converter功能,允许同名,不同类型的属性进行拷贝,比如Date对象到String属性。
- 有兴趣的同学可以去比较下PropertyUtils,默认不开启Converter功能,发现性能是BeanUtils的2倍多。
初始化例子:BeanCopier copier = BeanCopier.create(Source.class, Target.class, true);
第三个参数useConverter,是否开启Convert,默认BeanCopier只会做同名,同类型属性的copier,否则就会报错。
- public class BeanCopierTest {
-
- public static void main(String args[]) {
- System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "/tmp/1");
- BeanCopier copier = BeanCopier.create(Source.class, Target.class, true);
- Source from = new Source();
- from.setValue(1);
-
- Target to = new Target();
- Converter converter = new BigIntConverter();
- copier.copy(from, to, converter); //使用converter类
-
- System.out.println(to.getValue());
- }
- }
-
- class BigIntConverter implements net.sf.cglib.core.Converter {
-
- @Override
- public Object convert(Object value, Class target, Object context) {
- System.out.println(value.getClass() + " " + value); // from类中的value对象
- System.out.println(target); // to类中的定义的参数对象
- System.out.println(context.getClass() + " " + context); // String对象,具体的方法名
- if (target.isAssignableFrom(BigInteger.class)) {
- return new BigInteger(value.toString());
- } else {
- return value;
- }
- }
-
- }
- ----
- 反编译后看的代码:
- public class Target$$BeanCopierByCGLIB$$e1c34377 extends BeanCopier
- {
- public void copy(Object obj, Object obj1, Converter converter)
- {
- Target target = (Target)obj1;
- Source source = (Source)obj;
- // 注意是直接调用,没有通过reflect
- target.setValue((BigInteger)converter.convert(new Integer(source.getValue()), CGLIB$load_class$java$2Emath$2EBigInteger, "setValue"));
- }
- }
public class BeanCopierTest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "/tmp/1");
BeanCopier copier = BeanCopier.create(Source.class, Target.class, true);
Source from = new Source();
from.setValue(1);
Target to = new Target();
Converter converter = new BigIntConverter();
copier.copy(from, to, converter); //使用converter类
System.out.println(to.getValue());
}
}
class BigIntConverter implements net.sf.cglib.core.Converter {
@Override
public Object convert(Object value, Class target, Object context) {
System.out.println(value.getClass() + " " + value); // from类中的value对象
System.out.println(target); // to类中的定义的参数对象
System.out.println(context.getClass() + " " + context); // String对象,具体的方法名
if (target.isAssignableFrom(BigInteger.class)) {
return new BigInteger(value.toString());
} else {
return value;
}
}
}
----
反编译后看的代码:
public class Target$$BeanCopierByCGLIB$$e1c34377 extends BeanCopier
{
public void copy(Object obj, Object obj1, Converter converter)
{
Target target = (Target)obj1;
Source source = (Source)obj;
// 注意是直接调用,没有通过reflect
target.setValue((BigInteger)converter.convert(new Integer(source.getValue()), CGLIB$load_class$java$2Emath$2EBigInteger, "setValue"));
}
}
使用注意
- 避免每次进行BeanCopier.create创建对象,一般建议是通过static BeanCopier copier = BeanCopier.create()
- 合理使用converter。
- 应用场景:两个对象之间同名同属性的数据拷贝, 不能单独针对其中的几个属性单独拷贝
BulkBean
相比于BeanCopier,BulkBean将整个Copy的动作拆分为getPropertyValues,setPropertyValues的两个方法,允许自定义处理的属性。
- public class BulkBeanTest {
-
- public static void main(String args[]) {
- System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "/home/ljh/cglib");
- String[] getter = new String[] { "getValue" };
- String[] setter = new String[] { "setValue" };
- Class[] clazzs = new Class[] { int.class };
-
- BulkBean bean = BulkBean.create(BulkSource.class, getter, setter, clazzs);
- BulkSource obj = new BulkSource();
- obj.setValue(1);
-
- Object[] objs = bean.getPropertyValues(obj);
- for (Object tmp : objs) {
- System.out.println(tmp);
- }
- }
- }
- class BulkSource {
- private int value;
- .....
- }
-
- // 反编译后的代码:
- public void getPropertyValues(Object obj, Object aobj[])
- {
- BulkSource bulksource = (BulkSource)obj;
- aobj[0] = new Integer(bulksource.getValue());
- }
public class BulkBeanTest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "/home/ljh/cglib");
String[] getter = new String[] { "getValue" };
String[] setter = new String[] { "setValue" };
Class[] clazzs = new Class[] { int.class };
BulkBean bean = BulkBean.create(BulkSource.class, getter, setter, clazzs);
BulkSource obj = new BulkSource();
obj.setValue(1);
Object[] objs = bean.getPropertyValues(obj);
for (Object tmp : objs) {
System.out.println(tmp);
}
}
}
class BulkSource {
private int value;
.....
}
// 反编译后的代码:
public void getPropertyValues(Object obj, Object aobj[])
{
BulkSource bulksource = (BulkSource)obj;
aobj[0] = new Integer(bulksource.getValue());
}
使用注意
- 避免每次进行BulkBean.create创建对象,一般建议是通过static BulkBean.create copier = BulkBean.create
- 应用场景:针对特定属性的get,set操作,一般适用通过xml配置注入和注出的属性,运行时才确定处理的Source,Target类,只需关注属性名即可。
BeanMap
相比于BeanCopier,BulkBean,都是针对两个Pojo Bean进行处理,那如果对象一个是Pojo Bean和Map对象之间,那就得看看BeanMap,将一个java bean允许通过map的api进行调用。
几个支持的操作接口:
- Object get(Object key)
- Object put(Object key, Object value)
- void putAll(Map t)
- Set entrySet()
- Collection values()
- boolean containsKey(Object key)
- ....
- public class BeanMapTest {
-
- public static void main(String args[]) {
- // 初始化
- BeanMap map = BeanMap.create(new Pojo());
- // 构造
- Pojo pojo = new Pojo();
- pojo.setIntValue(1);
- pojo.setBigInteger(new BigInteger("2"));
- // 赋值
- map.setBean(pojo);
- // 验证
- System.out.println(map.get("intValue"));
- System.out.println(map.keySet());
- System.out.println(map.values());
- }
- }
-
- class Pojo {
-
- private int intValue;
- private BigInteger bigInteger;
- ....
- }
-
- //反编译代码查看:
- //首先保存了所有的属性到一个set中
- private static FixedKeySet keys = new FixedKeySet(new String[] {
- "bigInteger", "intValue"
- });
- public Object get(Object obj, Object obj1)
- {
- (Pojo)obj;
- String s = (String)obj1;
- s;
- s.hashCode();
- JVM INSTR lookupswitch 2: default 72
- // -139068386: 40
- // 556050114: 52;
- goto _L1 _L2 _L3
- _L2:
- "bigInteger";
- //属性判断是否相等
- equals();
- JVM INSTR ifeq 73;
- goto _L4 _L5
- _L5:
- break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_73;
- _L4:
- getBigInteger();
- return;
- _L3:
-
- ....
-
- }
public class BeanMapTest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// 初始化
BeanMap map = BeanMap.create(new Pojo());
// 构造
Pojo pojo = new Pojo();
pojo.setIntValue(1);
pojo.setBigInteger(new BigInteger("2"));
// 赋值
map.setBean(pojo);
// 验证
System.out.println(map.get("intValue"));
System.out.println(map.keySet());
System.out.println(map.values());
}
}
class Pojo {
private int intValue;
private BigInteger bigInteger;
....
}
//反编译代码查看:
//首先保存了所有的属性到一个set中
private static FixedKeySet keys = new FixedKeySet(new String[] {
"bigInteger", "intValue"
});
public Object get(Object obj, Object obj1)
{
(Pojo)obj;
String s = (String)obj1;
s;
s.hashCode();
JVM INSTR lookupswitch 2: default 72
// -139068386: 40
// 556050114: 52;
goto _L1 _L2 _L3
_L2:
"bigInteger";
//属性判断是否相等
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 73;
goto _L4 _L5
_L5:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_73;
_L4:
getBigInteger();
return;
_L3:
....
}
使用注意
- 避免每次进行BeanMap map = BeanMap.create();创建对象,不同于BeanCopier对象,BeanMap主要针对对象实例进行处理,所以一般建议是map.setBean(pojo);进行动态替换持有的对象实例。
- 应用场景:针对put,putAll操作会直接修改pojo对象里的属性,所以可以通过beanMap.putAll(map)进行map<->pojo属性的拷贝。
BeanGenerator
暂时没有想到合适的使用场景,不过BeanGenerator使用概念是很简单的,就是将一个Map<String,Class>properties的属性定义,动态生成一个pojo bean类。
- BeanGenerator generator = new BeanGenerator();
- generator.addProperty("intValue", int.class);
- generator.addProperty("integer", Integer.class);
- generator.addProperty("properties", Properties.class);
-
- Class clazz = (Class) generator.createClass();
- Object obj = generator.create();
-
- PropertyDescriptor[] getters = ReflectUtils.getBeanGetters(obj.getClass());
- for (PropertyDescriptor getter : getters) {
- Method write = getter.getWriteMethod();
- System.out.println(write.getName());
- }
BeanGenerator generator = new BeanGenerator();
generator.addProperty("intValue", int.class);
generator.addProperty("integer", Integer.class);
generator.addProperty("properties", Properties.class);
Class clazz = (Class) generator.createClass();
Object obj = generator.create();
PropertyDescriptor[] getters = ReflectUtils.getBeanGetters(obj.getClass());
for (PropertyDescriptor getter : getters) {
Method write = getter.getWriteMethod();
System.out.println(write.getName());
}
ImmutableBean
bean Immutable模式的一种动态class实现,Immutable模式主要应用于服务设计上,返回的pojo bean对象,不运行进行write方法调用。
说明
个人是不太建议使用cglib动态class的方式来实现bean Immutable的模式,Immutable模式应该是一种服务接口上的显示声明,而不是如此隐晦,而且pojo bean尽量做到是轻量级,简答的set/get方法,如果要做充血的领域模型那就另当别论了。 |
reflect (class,method处理)
FastClass
顾明思义,FastClass就是对Class对象进行特定的处理,比如通过数组保存method引用,因此FastClass引出了一个index下标的新概念,比如getIndex(String name, Class[] parameterTypes)就是以前的获取method的方法。
通过数组存储method,constructor等class信息,从而将原先的反射调用,转化为class.index的直接调用,从而体现所谓的FastClass。
- public class FastClassTest {
- public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
- System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "/home/ljh/cglib");
-
- FastClass clazz = FastClass.create(FastSource.class);
- // fast class反射调用
- FastSource obj = (FastSource) clazz.newInstance();
- clazz.invoke("setValue", new Class[] { int.class }, obj, new Object[] { 1 });
- clazz.invoke("setOther", new Class[] { int.class }, obj, new Object[] { 2 });
-
- int value = (Integer) clazz.invoke("getValue", new Class[] {}, obj, new Object[] {});
- int other = (Integer) clazz.invoke("getOther", new Class[] {}, obj, new Object[] {});
- System.out.println(value + " " + other);
- // fastMethod使用
- FastMethod setValue = clazz.getMethod("setValue", new Class[] { int.class });
- System.out.println("setValue index is : " + setValue.getIndex());
-
- FastMethod getValue = clazz.getMethod("getValue", new Class[] {});
- System.out.println("getValue index is : " + getValue.getIndex());
-
- FastMethod setOther = clazz.getMethod("setOther", new Class[] { int.class });
- System.out.println("setOther index is : " + setOther.getIndex());
-
- FastMethod getOther = clazz.getMethod("getOther", new Class[] {});
- System.out.println("getOther index is : " + getOther.getIndex());
- // 其他
- System.out.println("getDeclaredMethods : " + clazz.getJavaClass().getDeclaredMethods().length);
- System.out.println("getConstructors : " + clazz.getJavaClass().getConstructors().length);
- System.out.println("getFields : " + clazz.getJavaClass().getFields().length);
- System.out.println("getMaxIndex : " + clazz.getMaxIndex());
- }
- }
-
- class FastSource {
- private int value;
- private int other;
-
- }
public class FastClassTest {
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "/home/ljh/cglib");
FastClass clazz = FastClass.create(FastSource.class);
// fast class反射调用
FastSource obj = (FastSource) clazz.newInstance();
clazz.invoke("setValue", new Class[] { int.class }, obj, new Object[] { 1 });
clazz.invoke("setOther", new Class[] { int.class }, obj, new Object[] { 2 });
int value = (Integer) clazz.invoke("getValue", new Class[] {}, obj, new Object[] {});
int other = (Integer) clazz.invoke("getOther", new Class[] {}, obj, new Object[] {});
System.out.println(value + " " + other);
// fastMethod使用
FastMethod setValue = clazz.getMethod("setValue", new Class[] { int.class });
System.out.println("setValue index is : " + setValue.getIndex());
FastMethod getValue = clazz.getMethod("getValue", new Class[] {});
System.out.println("getValue index is : " + getValue.getIndex());
FastMethod setOther = clazz.getMethod("setOther", new Class[] { int.class });
System.out.println("setOther index is : " + setOther.getIndex());
FastMethod getOther = clazz.getMethod("getOther", new Class[] {});
System.out.println("getOther index is : " + getOther.getIndex());
// 其他
System.out.println("getDeclaredMethods : " + clazz.getJavaClass().getDeclaredMethods().length);
System.out.println("getConstructors : " + clazz.getJavaClass().getConstructors().length);
System.out.println("getFields : " + clazz.getJavaClass().getFields().length);
System.out.println("getMaxIndex : " + clazz.getMaxIndex());
}
}
class FastSource {
private int value;
private int other;
}
proxy (spring aop相关)
总体类结构图:
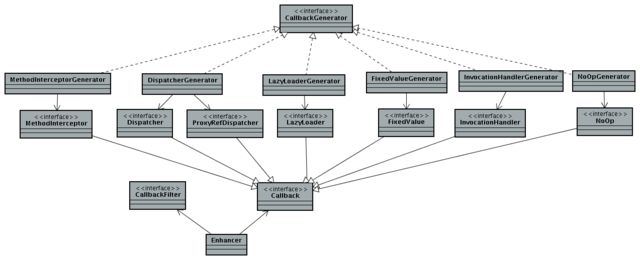
Callback & CallbackGenerator
- MethodInterceptor
- 类似于spring aop的around Advise的功能,大家都知道,不多做介绍。唯一需要注意的就是proxy.invokeSuper和proxy.invoke的区别。invokeSuper是退出当前interceptor的处理,进入下一个callback处理,invoke则会继续回调该方法,如果传递给invoke的obj参数出错容易造成递归调用
- Dispatcher, ProxyRefDispatcher
- LazyLoader
- 相比于Dispatcher,lazyLoader在第一次获取了loadObject后,会进行缓存,后续的请求调用都会直接调用该缓存的属性.
-
- //反编译部分代码
- public final int cal(int i, int j)
- {
- this;
- return ((DefaultCalcService)CGLIB$LOAD_PRIVATE_3()).cal(i, j);
- }
-
- private final synchronized Object CGLIB$LOAD_PRIVATE_3()
- {
- CGLIB$LAZY_LOADER_3; //保存的属性
- if(CGLIB$LAZY_LOADER_3 != null) goto _L2; else goto _L1
- _L1:
- JVM INSTR pop ;
- this;
- CGLIB$CALLBACK_3;
- if(CGLIB$CALLBACK_3 != null) goto _L4; else goto _L3
- _L3:
- JVM INSTR pop ;
- CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
- CGLIB$CALLBACK_3;
- _L4:
- loadObject();
- JVM INSTR dup_x1 ;
- CGLIB$LAZY_LOADER_3;
- _L2:
- return;
- }
//反编译部分代码
public final int cal(int i, int j)
{
this;
return ((DefaultCalcService)CGLIB$LOAD_PRIVATE_3()).cal(i, j);
}
private final synchronized Object CGLIB$LOAD_PRIVATE_3()
{
CGLIB$LAZY_LOADER_3; //保存的属性
if(CGLIB$LAZY_LOADER_3 != null) goto _L2; else goto _L1
_L1:
JVM INSTR pop ;
this;
CGLIB$CALLBACK_3;
if(CGLIB$CALLBACK_3 != null) goto _L4; else goto _L3
_L3:
JVM INSTR pop ;
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
CGLIB$CALLBACK_3;
_L4:
loadObject();
JVM INSTR dup_x1 ;
CGLIB$LAZY_LOADER_3;
_L2:
return;
}
- NoOp
- 不做任何处理,结合Filter针对不需要做代理方法直接返回,调用其原始方法
- FixedValue
- InvocationHandler(提供和jdk proxy的功能),不常用
CallbackFilter
主要的作用就是callback调度,主要的一个方法:int accept(Method method);
返回的int在int值,代表对应method需要插入的callback,会静态生成到class的代码中,这样是cglib proxy区别于jdk proxy的方式,一个是静态的代码调用,一个是动态的reflect。
可以查看: Enhancer类中的emitMethods方法,line:883。在构造class method字节吗之前就已经确定需要运行的callback。
Enhancer
- System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "/home/ljh/cglib");
- LogInteceptor logInteceptor = new LogInteceptor();
- CalDispatcher calDispatcher = new CalDispatcher();
- CalcProxyRefDispatcher calcProxyRefDispatcher = new CalcProxyRefDispatcher();
- LazyLoaderCallback lazyLoaderCallback = new LazyLoaderCallback();
-
- Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
- enhancer.setSuperclass(CalcService.class); //接口类
- enhancer.setCallbacks(new Callback[] { logInteceptor, calDispatcher, calcProxyRefDispatcher,lazyLoaderCallback, NoOp.INSTANCE }); // callback数组
- enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new CalcCallbackFilter()); // filter
- CalcService service = (CalcService) enhancer.create();
-
- int result = service.cal(1, 1);
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "/home/ljh/cglib");
LogInteceptor logInteceptor = new LogInteceptor();
CalDispatcher calDispatcher = new CalDispatcher();
CalcProxyRefDispatcher calcProxyRefDispatcher = new CalcProxyRefDispatcher();
LazyLoaderCallback lazyLoaderCallback = new LazyLoaderCallback();
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(CalcService.class); //接口类
enhancer.setCallbacks(new Callback[] { logInteceptor, calDispatcher, calcProxyRefDispatcher,lazyLoaderCallback, NoOp.INSTANCE }); // callback数组
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new CalcCallbackFilter()); // filter
CalcService service = (CalcService) enhancer.create();
int result = service.cal(1, 1);
Util (工具类,感觉有点鸡肋)
- StringSwitcher 提供string和int的map映射查询,给定一个string字符串,返回同个下标数组的int值,感觉很鸡肋,用Map不是可以很快速的实现功能
- ParallelSorter 看了具体的代码,没啥意思,就是提供了一个二分的快速排序和多路归并排序。没有所谓的并行排序,原本以为会涉及多线程处理,可惜没有
transform
暂时没仔细研究,更多的是对asm的封装,等下次看了asm代码后再回来研究下。
-----
相关性能测试和使用说明,可以参见另一篇文章: cglib相关性能测试对比