centos下安装和使用mysql测试工具super-smack
如果想看super-smack的发展历史的话,请看:http://mysqldatabaseadministration.blogspot.com/2006/10/mysql-benchmarking-4-compiling-super.html
环境介绍:
centos5.4
[root@26 super-smack-1.3]# uname -a
Linux 26 2.6.18-164.el5 #1 SMP Thu Sep 3 03:28:30 EDT 2009 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
1.前提步骤
1 yum -y install mysql-devel
2 yum -y install flex
3 yum -y install byacc
4 yum -y install bison
2.安装super-smack
[object Object]
解决办法:
修改文件super-smack-1.3/src/query.cc
第193行:
< int len = 0, num_recs = 0;
修改成:
> long len = 0; int num_recs = 0;
第199,200行
< int str_len = (*i).first.length();
< if((unsigned)p + str_len + 3 *sizeof(int) < (unsigned)p_end )
修改成:
> long str_len = (*i).first.length();
> if((long)p + str_len + 3 *sizeof(int) < (long)p_end )
第219行
< len = (unsigned)p - (unsigned)buf;
修改成:
> len = (long)p - (long)buf;
附改造后的文件:
query.rar
3.下面就来看看如何使用吧
测试命令
super-smack -d mysql select-key.smack n m
其中super-smack近似于一个解释执行器,解释执行select-key.smack中的内容,n为该次测试的并发线程数,m为每个线程执行数据库操作的次数
smack文件,近似于一个c源文件,详细包含以下几个内容
1.client,定义始于毗连用到的参量,包孕host,user,passwd,port,socket。包孕两种client,admin client和普通client,admin需要具有办理职权范围,需要始于表以及load数据等操作
2.表定义,自定义测试表的表结构,需要指定由哪个client始于表,以及表的记载数,以及填充数据文件的位置,如果数据文件不存在,需要天生数据文件,可以自定义数据天生剧本
3.dictionary,定义了一批可选的字段,源码实现患上比较简略,只供给了几种next要领,读取下一行数据,如果改行数据用逗点分隔,只取第一个逗点前的字段,其他符号分隔则取整行数据。所以如果一个查询里有几个字段需要从外部获取数据,就应该始于几个dictionary
4.查询,可以自定义查询的语句,查询类型(主要用于分类计数的作用),查询语句也可以为更新操作,如update。如果是查询语句,has_result_set选项应该定义为y,否则会出现Commands out of sync错误,感觉这里是super-smack的一个bug
5.main,测试运行的入口,一般改动不大,主要是一些client名称的改动
测试历程中始于的毗连数包含:
1.表数据分析毗连(select count(*) from test_table),判断表是不是已经装载了数据
2.线程数,每个线程执行的查询都只打开一个毗连,与执行的次数以及每个线程执行的几多条语句无关
我们到安装路径看下,
[root@sunss-26 ~]# ll /usr/local/super-smack/bin/
gen-data super-smack
有连个命令,从名字我们就可以看出gen-data是用来生成测试数据的,我们使用帮助命令看下:
[root@sunss-26 ~]# gen-data --help
gen-data version 1.1
MySQL AB, by Sasha Pachev
Prints lines random data to stdout in given format
Usage: gen-data [options]
-?, --help - this message
-V, --version - show version
-n, --num-rows=num - number of rows
-f, --format=fmt_str - format string
Format can contain any character + % followed by
a format specifier. Valid format specifiers:
s - string
d - integer
Additionally, you can prefix a format speficier with:
n - generate exactly n characters
m-n - generate between m and n characters
命令及参数都简单易懂:
-n选项:指定生成数据行的行数
-f选项:指定格式字符串
例如:
gen-data -n 90000 -f %12-12s%n,%25-25s,%n,%d>words.data
[root@sunss-26 ~]# super-smack --help
super-smack version 1.1
MySQL AB, by Sasha Pachev and Jeremy Cole
Runs multi-threaded benchmarks on database engines.
The following engines are supported:
Id Handle Name Version Author
-- ------ ---- ------- ------
1 mysql MySQL 1.0 Sasha Pachev
Usage: super-smack [options] [smack_source]
Valid options are: -h, --help Display this message
-V, --version Show version
-d, --db-type=handle Select database type
-D, --datadir=path Path to super-smack datadir
[root@sunss-26 ~]#
现在命令所在路径是:/usr/local/super-smack/bin/super-smack,如果不想输入路径的话,添加一个连接:
ln -s /usr/local/super-smack/bin/super-smack /usr/bin/super-smack
我们在数据库里建一个表:
![]()
1 CREATE TABLE `http_auth` (
2 `username` char(255) NOT NULL,
3 `pass` char(25) DEFAULT NULL,
4 `uid` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
5 `gid` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
6 PRIMARY KEY (`username`)
7 ) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
![]()
导入数据:
1.mysqlimport -L -usmack -psmack -h192.168.0.26 smack /var/smack-data/http_auth.dat
2.在mysql命令行,执行 Loading data from file '/var/smack-data/http_auth.dat' into table 'http_auth' terminated by ','
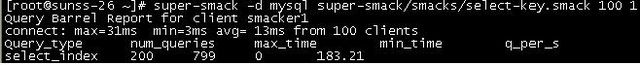
测试结果
输出的结果较为简略,只包含了查询的次数,最大耗时,最小耗时,每秒执行的查询,会按照查询类型进行分类计数之后输出
附修改后的select-key.smack文件:
![]()
1 // this is will be used in the table section
2 client "admin"
3 {
4 user "root";
5 host "192.168.0.24";
6 db "test";
7 pass "123456";
8 port "3306";
9 // socket "/tmp/mysql.sock"; // this only applies to MySQL and is
10 // ignored for PostgreSQL
11 }
12
13 // ensure the table exists and meets the conditions
14 table "http_auth"
15 {
16 client "admin"; // connect with this client
17 // if the table is not found or does not pass the checks, create it
18 // with the following, dropping the old one if needed
19 create "create table http_auth
20 (username char(25) not null primary key,
21 pass char(25),
22 uid integer not null,
23 gid integer not null
24 )";
25 min_rows "90000"; // the table must have at least that many rows
26 data_file "words.dat"; // if the table is empty, load the data from
27 //this file
28 gen_data_file "gen-data -n 90000 -f %12-12s%n,%25-25s,%n,%d";
29 // if the file above does not exist, generate it with the above shell command
30 // you can replace this command with anything that prints comma-delimited
31 // data to stdout, just make sure you have the right number of columns
32 }
33
34
35 //define a dictionary
36 dictionary "word"
37 {
38 type "rand"; // words are retrieved in random order
39 source_type "file"; // words come from a file
40 source "words.dat"; // file location
41 delim ","; // take the part of the line before ,
42 file_size_equiv "45000"; // if the file is greater than this
43 //divive the real file size by this value obtaining N and take every Nth
44 //line skipping others. This is needed to be able to target a wide key
45 // range without using up too much memory with test keys
46 }
47
48 //define a query
49 query "select_by_username"
50 {
51 query "select * from http_auth where username = '$word'";
52 // $word will be substitute with the read from the 'word' dictionary
53 type "select_index";
54 // query stats will be grouped by type
55 has_result_set "y";
56 // the query is expected to return a result set
57 parsed "y";
58 // the query string should be first processed by super-smack to do
59 // dictionary substitution
60 }
61
62 // define database client type
63 client "smacker1"
64 {
65 user "root"; // connect as this user
66 pass "123456"; // use this password
67 host "192.168.0.24"; // connect to this host
68 db "test"; // switch to this database
69 port "3306";
70 // socket "/tmp/mysql.sock"; // this only applies to MySQL and is
71 // ignored for PostgreSQL
72 query_barrel "2 select_by_username"; // on each round,
73 // run select_by_username query 2 times
74 }
75
76 main
77 {
78 smacker1.init(); // initialize the client
79 smacker1.set_num_rounds($2); // second arg on the command line defines
80 // the number of rounds for each client
81 smacker1.create_threads($1);
82 // first argument on the command line defines how many client instances
83 // to fork. Anything after this will be done once for each client until
84 // you collect the threads
85 smacker1.connect();
86 // you must connect after you fork
87 smacker1.unload_query_barrel(); // for each client fire the query barrel
88 // it will now do the number of rounds specified by set_num_rounds()
89 // on each round, query_barrel of the client is executed
90
91 smacker1.collect_threads();
92 // the master thread waits for the children, each child reports the stats
93 // the stats are printed
94 smacker1.disconnect();
95 // the children now disconnect and exit
96 }
97
![]()