Node.js C++扩展实现
因为有了Node.js,JavaScript可以被用于服务端编程。通过各种扩展,Node.js可以变得非常强大。今天分享下怎样用C++创建Node.js扩展。
参考原文:Making Dynamsoft Barcode SDK an Addon for Node.js
搭建Nodejs开发环境
要构建扩展,需要安装node-gyp:
npm install -g node-gyp
这个库里面包涵了JavaScript v8引擎所需要的头文件以及依赖库。
创建一个C/C++文件dbr.cc以及配置文件binding.gyp。打开配置文件,在里面加入扩展名和源代码文件:
{
"targets": [
{
"target_name": "dbr",
"sources": [ "dbr.cc" ]
}
]
}
现在就可以用来构建dbr.node,用于Node.js的动态链接库,相当于DLL。在命令行中输入:
node-gyp configure install
这行命令干了两件事,首先生成了Visual Studio的工程文件。然后调用VS的编译器生成了动态链接库。可以看下生成的文件结构:
build / binding.sln / dbr.vcxproj / dbr.vcxproj.filters / config.gypi / Release / dbr.node / dbr.pdb / obj
更多内容可以参考官方文档Node.js addons。
把Dynamsoft Barcode SDK封装成Node.js扩展
接下来我们只需要使用Visual Studio来编写代码,构建工程就可以了。因为node-gyp在配置的时候已经把工程文件里的头文件路径和依赖库路径都加进去了,我们只需要做很小的修改。现在双击binding.sln导入工程。添加Dynamsoft Barcode SDK相关的头文件路径和库路径。最后添加post-build event用于拷贝DLL到生成目录:
copy "{installation directory}\Dynamsoft\Barcode Reader 2.0 Trial\Redist\C_C++\*.dll" "$(OutDir)"
现在开始编写C++代码。和Java,Python类似,在编写native代码的时候,需要首先注册native函数。初始化Barcode解码接口:
void Init(Handle<Object> exports) {
NODE_SET_METHOD(exports, "decodeFile", DecodeFile);
}
NODE_MODULE(dbr, Init)
接下来我们把获取的数据转换成v8数据类型。使用Local<Object>来存储一个Barcode结果,使用Local<Array>来存储所有的Local<Object>。最后通过回调函数把结果返回到JavaScript层。
void DecodeFile(const FunctionCallbackInfo<Value>& args) {
Isolate* isolate = Isolate::GetCurrent();
HandleScope scope(isolate);
// convert v8 string to char *
String::Utf8Value utfStr(args[0]->ToString());
char *pFileName = *utfStr;
int option_iMaxBarcodesNumPerPage = -1;
int option_llBarcodeFormat = -1;
pBarcodeResultArray pResults = NULL;
ReaderOptions option;
SetOptions(&option, option_iMaxBarcodesNumPerPage, option_llBarcodeFormat);
// decode barcode image file
int ret = DBR_DecodeFile(
pFileName,
&option,
&pResults
);
if (ret == DBR_OK){
int count = pResults->iBarcodeCount;
pBarcodeResult* ppBarcodes = pResults->ppBarcodes;
pBarcodeResult tmp = NULL;
// javascript callback function
Local<Function> cb = Local<Function>::Cast(args[1]);
const unsigned argc = 1;
// array for storing barcode results
Local<Array> barcodeResults = Array::New(isolate);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
tmp = ppBarcodes[i];
Local<Object> result = Object::New(isolate);
result->Set(String::NewFromUtf8(isolate, "format"), Number::New(isolate, tmp->llFormat));
result->Set(String::NewFromUtf8(isolate, "value"), String::NewFromUtf8(isolate, tmp->pBarcodeData));
barcodeResults->Set(Number::New(isolate, i), result);
}
// release memory
DBR_FreeBarcodeResults(&pResults);
Local<Value> argv[argc] = { barcodeResults };
cb->Call(isolate->GetCurrentContext()->Global(), argc, argv);
}
}
文档可以参考v8.h以及Chrome V8
现在创建一个JavaScript脚本文件测试一下:
var dbr = require('./build/Release/dbr');
var readline = require('readline');
var rl = readline.createInterface({
input: process.stdin,
output: process.stdout
});
rl.question("Please input a barcode image path: ", function(answer) {
// e.g. F:\git\Dynamsoft-Barcode-Reader\Images\AllSupportedBarcodeTypes.tif
dbr.decodeFile(
answer,
function(msg){
var result = null;
for (index in msg) {
result = msg[index]
console.log(result['format']);
console.log(result['value']);
console.log("##################");
}
}
);
rl.close();
});
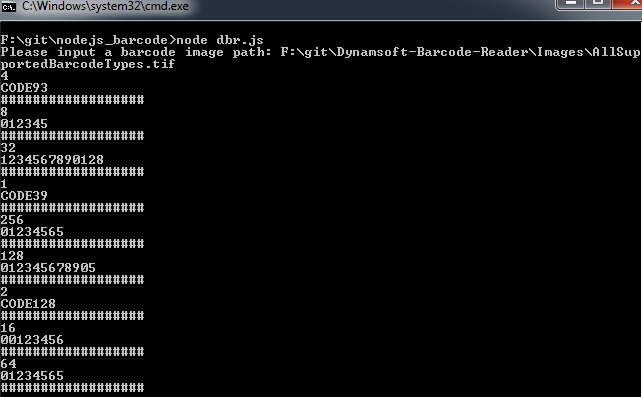
最后通过命令行运行查看结果:
源码
https://github.com/Dynamsoft/Dynamsoft-Barcode-Reader/tree/master/samples/Node.js