现实企业级Java开发中,有时候我们会碰到下面这些问题:
OutOfMemoryError,内存不足
内存泄露
线程死锁
锁争用(Lock Contention)
Java进程消耗CPU过高
......
这些问题在日常开发中可能被很多人忽视(比如有的人遇到上面的问题只是重启服务器或者调大内存,而不会深究问题根源),但能够理解并解决这些问题是Java程序员进阶的必备要求。本文将对一些常用的JVM性能调优监控工具进行介绍,希望能起抛砖引玉之用。本文参考了网上很多资料,难以一一列举,在此对这些资料的作者表示感谢!关于JVM性能调优相关的资料,请参考文末。
A、 jps(Java Virtual Machine Process Status Tool)
jps主要用来输出JVM中运行的进程状态信息。语法格式如下:
如果不指定hostid就默认为当前主机或服务器。
命令行参数选项说明如下:
1 |
-q 不输出类名、Jar名和传入main方法的参数 |
比如下面:
1 |
root@ubuntu :/# jps -m -l |
2 |
2458 org.artifactory.standalone.main.Main /usr/local/artifactory-2.2.5/etc/jetty.xml |
3 |
29920 com.sun.tools.hat.Main -port 9998 /tmp/dump.dat |
4 |
3149 org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap start |
5 |
30972 sun.tools.jps.Jps -m -l |
6 |
8247 org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap start |
7 |
25687 com.sun.tools.hat.Main -port 9999 dump.dat |
B、 jstack
jstack主要用来查看某个Java进程内的线程堆栈信息。语法格式如下:
2 |
jstack [option] executable core |
3 |
jstack [option] [server-id@]remote-hostname-or-ip |
命令行参数选项说明如下:
1 |
-l long listings,会打印出额外的锁信息,在发生死锁时可以用jstack -l pid来观察锁持有情况 |
2 |
-m mixed mode,不仅会输出Java堆栈信息,还会输出C/C++堆栈信息(比如Native方法) |
jstack可以定位到线程堆栈,根据堆栈信息我们可以定位到具体代码,所以它在JVM性能调优中使用得非常多。下面我们来一个实例找出某个Java进程中最耗费CPU的Java线程并定位堆栈信息,用到的命令有ps、top、printf、jstack、grep。
第一步先找出Java进程ID,我部署在服务器上的Java应用名称为mrf-center:
1 |
root@ubuntu :/# ps -ef | grep mrf-center | grep -v grep |
2 |
root 21711 1 1 14:47 pts/3 00:02:10 java -jar mrf-center.jar |
得到进程ID为21711,第二步找出该进程内最耗费CPU的线程,可以使用ps -Lfp pid或者ps -mp pid -o THREAD, tid, time或者top -Hp pid,我这里用第三个,输出如下:
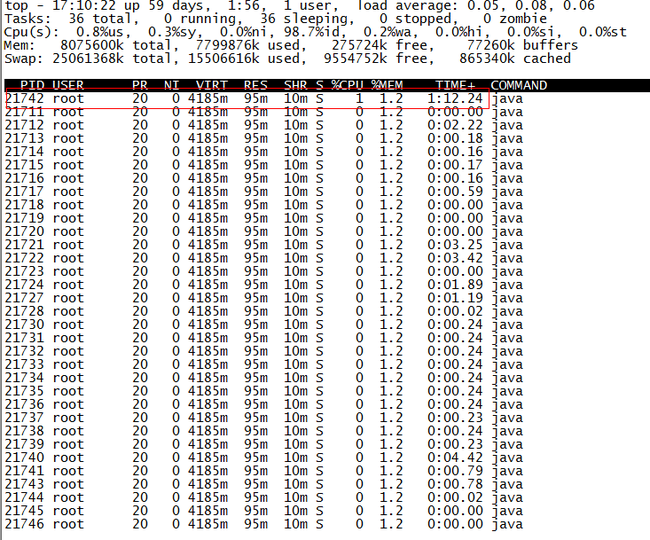
TIME列就是各个Java线程耗费的CPU时间,CPU时间最长的是线程ID为21742的线程,用
得到21742的十六进制值为54ee,下面会用到。
OK,下一步终于轮到jstack上场了,它用来输出进程21711的堆栈信息,然后根据线程ID的十六进制值grep,如下:
1 |
root@ubuntu :/# jstack 21711 | grep 54ee |
2 |
"PollIntervalRetrySchedulerThread" prio=10 tid=0x00007f950043e000 nid=0x54ee in Object.wait() [0x00007f94c6eda000] |
可以看到CPU消耗在PollIntervalRetrySchedulerThread这个类的Object.wait(),我找了下我的代码,定位到下面的代码:
02 |
getLog().info("Thread [" + getName() + "] is idle waiting..."); |
03 |
schedulerThreadState = PollTaskSchedulerThreadState.IdleWaiting; |
04 |
long now = System.currentTimeMillis(); |
05 |
long waitTime = now + getIdleWaitTime(); |
06 |
long timeUntilContinue = waitTime - now; |
07 |
synchronized(sigLock) { |
10 |
sigLock.wait(timeUntilContinue); |
13 |
catch (InterruptedException ignore) { |
它是轮询任务的空闲等待代码,上面的sigLock.wait(timeUntilContinue)就对应了前面的Object.wait()。
C、 jmap(Memory Map)和jhat(Java Heap Analysis Tool)
jmap用来查看堆内存使用状况,一般结合jhat使用。
jmap语法格式如下:
2 |
jmap [option] executable core |
3 |
jmap [option] [server-id@]remote-hostname-or-ip |
如果运行在64位JVM上,可能需要指定-J-d64命令选项参数。
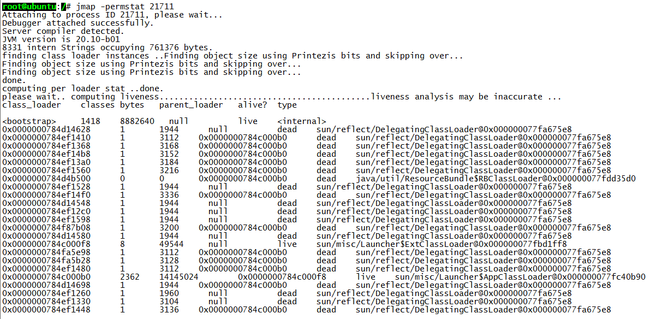
打印进程的类加载器和类加载器加载的持久代对象信息,输出:类加载器名称、对象是否存活(不可靠)、对象地址、父类加载器、已加载的类大小等信息,如下图:
使用jmap -heap pid查看进程堆内存使用情况,包括使用的GC算法、堆配置参数和各代中堆内存使用情况。比如下面的例子:
01 |
root@ubuntu :/# jmap -heap 21711 |
02 |
Attaching to process ID 21711, please wait... |
03 |
Debugger attached successfully. |
04 |
Server compiler detected. |
05 |
JVM version is 20.10-b01 |
07 |
using thread-local object allocation. |
08 |
Parallel GC with 4 thread(s) |
13 |
MaxHeapSize = 2067791872 (1972.0MB) |
14 |
NewSize = 1310720 (1.25MB) |
15 |
MaxNewSize = 17592186044415 MB |
16 |
OldSize = 5439488 (5.1875MB) |
19 |
PermSize = 21757952 (20.75MB) |
20 |
MaxPermSize = 85983232 (82.0MB) |
25 |
capacity = 6422528 (6.125MB) |
26 |
used = 5445552 (5.1932830810546875MB) |
27 |
free = 976976 (0.9317169189453125MB) |
28 |
84.78829520089286% used |
30 |
capacity = 131072 (0.125MB) |
31 |
used = 98304 (0.09375MB) |
32 |
free = 32768 (0.03125MB) |
35 |
capacity = 131072 (0.125MB) |
37 |
free = 131072 (0.125MB) |
40 |
capacity = 35258368 (33.625MB) |
41 |
used = 4119544 (3.9287033081054688MB) |
42 |
free = 31138824 (29.69629669189453MB) |
43 |
11.683876009235595% used |
45 |
capacity = 52428800 (50.0MB) |
46 |
used = 26075168 (24.867218017578125MB) |
47 |
free = 26353632 (25.132781982421875MB) |
48 |
49.73443603515625% used |
使用jmap -histo[:live] pid查看堆内存中的对象数目、大小统计直方图,如果带上live则只统计活对象,如下:
01 |
root@ubuntu :/# jmap -histo:live 21711 | more |
03 |
num #instances #bytes class name |
04 |
---------------------------------------------- |
05 |
1: 38445 5597736 <constMethodKlass> |
06 |
2: 38445 5237288 <methodKlass> |
07 |
3: 3500 3749504 <constantPoolKlass> |
08 |
4: 60858 3242600 <symbolKlass> |
09 |
5: 3500 2715264 <instanceKlassKlass> |
10 |
6: 2796 2131424 <constantPoolCacheKlass> |
14 |
10: 1225 639656 <methodDataKlass> |
15 |
11: 14194 454208 java.lang.String |
16 |
12: 3809 396136 java.lang.Class |
19 |
15: 3028 266464 java.lang.reflect.Method |
20 |
16: 280 163520 <objArrayKlassKlass> |
21 |
17: 4355 139360 java.util.HashMap$Entry |
22 |
18: 1869 138568 [Ljava.util.HashMap$Entry; |
23 |
19: 2443 97720 java.util.LinkedHashMap$Entry |
24 |
20: 2072 82880 java.lang.ref.SoftReference |
25 |
21: 1807 71528 [Ljava.lang.Object; |
26 |
22: 2206 70592 java.lang.ref.WeakReference |
27 |
23: 934 52304 java.util.LinkedHashMap |
28 |
24: 871 48776 java.beans.MethodDescriptor |
29 |
25: 1442 46144 java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap$HashEntry |
30 |
26: 804 38592 java.util.HashMap |
31 |
27: 948 37920 java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap$Segment |
32 |
28: 1621 35696 [Ljava.lang.Class; |
33 |
29: 1313 34880 [Ljava.lang.String; |
34 |
30: 1396 33504 java.util.LinkedList$Entry |
35 |
31: 462 33264 java.lang.reflect.Field |
36 |
32: 1024 32768 java.util.Hashtable$Entry |
37 |
33: 948 31440 [Ljava.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap$HashEntry; |
class name是对象类型,说明如下:
还有一个很常用的情况是:用jmap把进程内存使用情况dump到文件中,再用jhat分析查看。jmap进行dump命令格式如下:
1 |
jmap -dump:format=b,file=dumpFileName |
我一样地对上面进程ID为21711进行Dump:
1 |
root@ubuntu :/# jmap -dump:format=b,file=/tmp/dump.dat 21711 |
2 |
Dumping heap to /tmp/dump.dat ... |
dump出来的文件可以用MAT、VisualVM等工具查看,这里用jhat查看:
01 |
root@ubuntu :/# jhat -port 9998 /tmp/dump.dat |
02 |
Reading from /tmp/dump.dat... |
03 |
Dump file created Tue Jan 28 17:46:14 CST 2014 |
04 |
Snapshot read, resolving... |
05 |
Resolving 132207 objects... |
06 |
Chasing references, expect 26 dots.......................... |
07 |
Eliminating duplicate references.......................... |
09 |
Started HTTP server on port 9998 |
注意如果Dump文件太大,可能需要加上-J-Xmx512m这种参数指定最大堆内存,即jhat -J-Xmx512m -port 9998 /tmp/dump.dat。然后就可以在浏览器中输入主机地址:9998查看了:
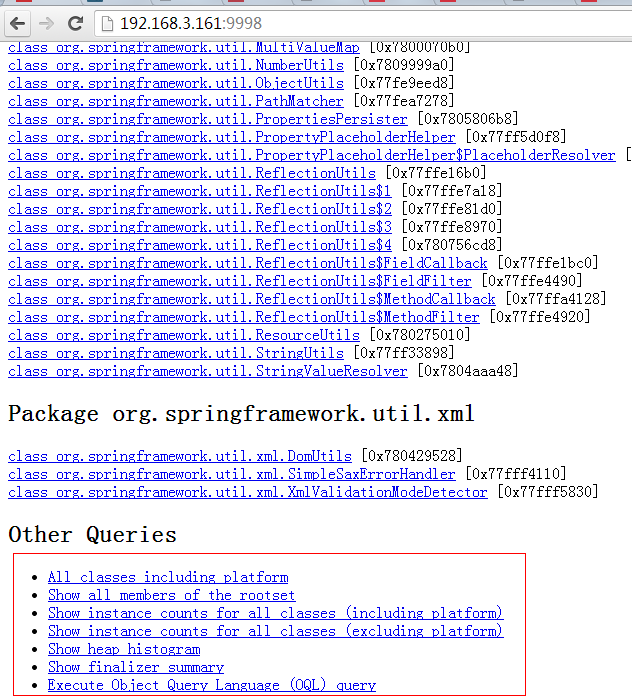
上面红线框出来的部分大家可以自己去摸索下,最后一项支持OQL(对象查询语言)。
D、jstat(JVM统计监测工具)
语法格式如下:
1 |
jstat [ generalOption | outputOptions vmid [interval[s|ms] [count]] ] |
vmid是Java虚拟机ID,在Linux/Unix系统上一般就是进程ID。interval是采样时间间隔。count是采样数目。比如下面输出的是GC信息,采样时间间隔为250ms,采样数为4:
1 |
root@ubuntu :/# jstat -gc 21711 250 4 |
2 |
S0C S1C S0U S1U EC EU OC OU PC PU YGC YGCT FGC FGCT GCT |
3 |
192.0 192.0 64.0 0.0 6144.0 1854.9 32000.0 4111.6 55296.0 25472.7 702 0.431 3 0.218 0.649 |
4 |
192.0 192.0 64.0 0.0 6144.0 1972.2 32000.0 4111.6 55296.0 25472.7 702 0.431 3 0.218 0.649 |
5 |
192.0 192.0 64.0 0.0 6144.0 1972.2 32000.0 4111.6 55296.0 25472.7 702 0.431 3 0.218 0.649 |
6 |
192.0 192.0 64.0 0.0 6144.0 2109.7 32000.0 4111.6 55296.0 25472.7 702 0.431 3 0.218 0.649 |
要明白上面各列的意义,先看JVM堆内存布局:

可以看出:
2 |
年轻代 = Eden区 + 两个Survivor区(From和To) |
现在来解释各列含义:
1 |
S0C、S1C、S0U、S1U:Survivor 0/1区容量(Capacity)和使用量(Used) |
6 |
FGC、FGCT:Full GC次数和Full GC耗时 |
E、hprof(Heap/CPU Profiling Tool)
hprof能够展现CPU使用率,统计堆内存使用情况。
语法格式如下:
1 |
java -agentlib:hprof[=options] ToBeProfiledClass |
2 |
java -Xrunprof[:options] ToBeProfiledClass |
3 |
javac -J-agentlib:hprof[=options] ToBeProfiledClass |
完整的命令选项如下:
01 |
Option Name and Value Description Default |
02 |
--------------------- ----------- ------- |
03 |
heap=dump|sites|all heap profiling all |
04 |
cpu=samples|times|old CPU usage off |
05 |
monitor=y|n monitor contention n |
06 |
format=a|b text(txt) or binary output a |
07 |
file=<file> write data to file java.hprof[.txt] |
08 |
net=<host>:<port> send data over a socket off |
09 |
depth=<size> stack trace depth 4 |
10 |
interval=<ms> sample interval in ms 10 |
11 |
cutoff=<value> output cutoff point 0.0001 |
12 |
lineno=y|n line number in traces? y |
13 |
thread=y|n thread in traces? n |
14 |
doe=y|n dump on exit? y |
15 |
msa=y|n Solaris micro state accounting n |
16 |
force=y|n force output to <file> y |
17 |
verbose=y|n print messages about dumps y |
来几个官方指南上的实例。
CPU Usage Sampling Profiling(cpu=samples)的例子:
1 |
java -agentlib:hprof=cpu=samples,interval=20,depth=3 Hello |
上面每隔20毫秒采样CPU消耗信息,堆栈深度为3,生成的profile文件名称是java.hprof.txt,在当前目录。
CPU Usage Times Profiling(cpu=times)的例子,它相对于CPU Usage Sampling Profile能够获得更加细粒度的CPU消耗信息,能够细到每个方法调用的开始和结束,它的实现使用了字节码注入技术(BCI):
1 |
javac -J-agentlib:hprof=cpu=times Hello.java |
Heap Allocation Profiling(heap=sites)的例子:
1 |
javac -J-agentlib:hprof=heap=sites Hello.java |
Heap Dump(heap=dump)的例子,它比上面的Heap Allocation Profiling能生成更详细的Heap Dump信息:
1 |
javac -J-agentlib:hprof=heap=dump Hello.java |
虽然在JVM启动参数中加入-Xrunprof:heap=sites参数可以生成CPU/Heap Profile文件,但对JVM性能影响非常大,不建议在线上服务器环境使用。
其他JVM性能调优参考资料:
《Java虚拟机规范》
《Java Performance》
《Trouble Shooting Guide for JavaSE 6 with HotSpot VM》: http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/tsg-vm-149989.pdf
《Effective Java》
VisualVM: http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/guides/visualvm/
jConsole: http://docs.oracle.com/javase/1.5.0/docs/guide/management/jconsole.html
Monitoring and Managing JavaSE 6 Applications: http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/articles/javase/monitoring-141801.html
BTrace:https://kenai.com/projects/btrace



