Activity生命周期
Understand the Lifecycle Callbacks
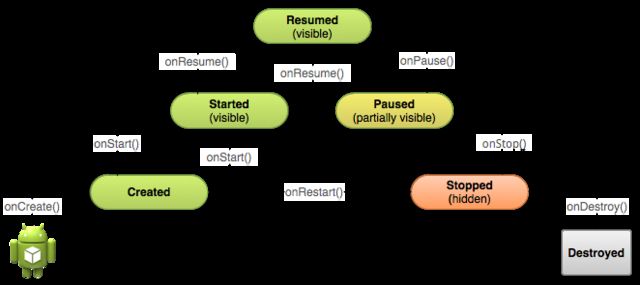
Figure 1. A simplified illustration of the Activity lifecycle, expressed as a step pyramid. This shows how, for every callback used to take the activity a step toward the Resumed state at the top, there's a callback method that takes the activity a step down. The activity can also return to the resumed state from the Paused and Stopped state.
- Does not crash if the user receives a phone call or switches to another app while using your app.
- Does not consume valuable system resources when the user is not actively using it.
- Does not lose the user's progress if they leave your app and return to it at a later time.
- Does not crash or lose the user's progress when the screen rotates between landscape and portrait orientation.
In this state, the activity is in the foreground and the user can interact with it. (Also sometimes referred to as the "running" state.)
Paused
In this state, the activity is partially obscured by another activity—the other activity that's in the foreground is semi-transparent or doesn't cover the entire screen. The paused activity does not receive user input and cannot execute any code.
Stopped
In this state, the activity is completely hidden and not visible to the user; it is considered to be in the background. While stopped, the activity instance and all its state information such as member variables is retained, but it cannot execute any code.
The other states (Created and Started) are transient and the system quickly moves from them to the next state by calling the next lifecycle callback method. That is, after the system calls onCreate(), it quickly callsonStart(), which is quickly followed by onResume().
Specify Your App's Launcher Activity
The main activity for your app must be declared in the manifest with an <intent-filter> that includes the MAIN action and LAUNCHER category. For example:
<activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
If either the MAIN action or LAUNCHER category are not declared for one of your activities, then your app icon will not appear in the Home screen's list of apps.
Create a New Instance
For example, the following example of the onCreate() method shows some code that performs some fundamental setup for the activity, such as declaring the user interface (defined in an XML layout file), defining member variables, and configuring some of the UITextView mTextView; // Member variable for text view in the layout
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// Set the user interface layout for this Activity
// The layout file is defined in the project res/layout/main_activity.xml file
setContentView(R.layout.main_activity);
// Initialize member TextView so we can manipulate it later
mTextView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text_message);
// Make sure we're running on Honeycomb or higher to use ActionBar APIs
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB) {
// For the main activity, make sure the app icon in the action bar
// does not behave as a button
ActionBar actionBar = getActionBar();
actionBar.setHomeButtonEnabled(false);
}
}
Pause Your Activity
You should usually use the onPause() callback to:
- Stop animations or other ongoing actions that could consume CPU.
- Commit unsaved changes, but only if users expect such changes to be permanently saved when they leave (such as a draft email).
- Release system resources, such as broadcast receivers, handles to sensors (like GPS), or any resources that may affect battery life while your activity is paused and the user does not need them.
For example, if your application uses the Camera, the onPause() method is a good place to release it.
@Override
public void onPause() {
super.onPause(); // Always call the superclass method first
// Release the Camera because we don't need it when paused
// and other activities might need to use it.
if (mCamera != null) {
mCamera.release()
mCamera = null;
}
}
Resume Your Activity
Be aware that the system calls this method every time your activity comes into the foreground, including when it's created for the first time. As such, you should implement onResume() to initialize components that you release during onPause() and perform any other initializations that must occur each time the activity enters the Resumed state (such as begin animations and initialize components only used while the activity has user focus).
The following example of onResume() is the counterpart to the onPause() example above, so it initializes the camera that's released when the activity pauses.
@Override
public void onResume() {
super.onResume(); // Always call the superclass method first
// Get the Camera instance as the activity achieves full user focus
if (mCamera == null) {
initializeCamera(); // Local method to handle camera init
}
}
Stop Your Activity
In extreme cases, the system might simply kill your app process without calling the activity's final onDestroy() callback, so it's important you use onStop() to release resources that might leak memory.
Although the onPause() method is called before onStop(), you should use onStop() to perform larger, more CPU intensive shut-down operations, such as writing information to a database.
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop(); // Always call the superclass method first
// Save the note's current draft, because the activity is stopping
// and we want to be sure the current note progress isn't lost.
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put(NotePad.Notes.COLUMN_NAME_NOTE, getCurrentNoteText());
values.put(NotePad.Notes.COLUMN_NAME_TITLE, getCurrentNoteTitle());
getContentResolver().update(
mUri, // The URI for the note to update.
values, // The map of column names and new values to apply to them.
null, // No SELECT criteria are used.
null // No WHERE columns are used.
);
} When your activity is stopped, the Activity object is kept resident in memory and is recalled when the activity resumes.
Start/Restart Your Activity
You should usually use the onStart() callback method as the counterpart to the onStop() method, because the system calls onStart() both when it creates your activity and when it restarts the activity from the stopped state.For example, because the user might have been away from your app for a long time before coming back it, the onStart() method is a good place to verify that required system features are enabled:
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart(); // Always call the superclass method first
// The activity is either being restarted or started for the first time
// so this is where we should make sure that GPS is enabled
LocationManager locationManager =
(LocationManager) getSystemService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE);
boolean gpsEnabled = locationManager.isProviderEnabled(LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER);
if (!gpsEnabled) {
// Create a dialog here that requests the user to enable GPS, and use an intent
// with the android.provider.Settings.ACTION_LOCATION_SOURCE_SETTINGS action
// to take the user to the Settings screen to enable GPS when they click "OK"
}
}
@Override
protected void onRestart() {
super.onRestart(); // Always call the superclass method first
// Activity being restarted from stopped state
}
Destroy the Activity
Most apps don't need to implement this method because local class references are destroyed with the activity and your activity should perform most cleanup during onPause() and onStop().@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy(); // Always call the superclass
// Stop method tracing that the activity started during onCreate()
android.os.Debug.stopMethodTracing();
}
Recreating an Activity
The saved data that the system uses to restore the previous state is called the "instance state" and is a collection of key-value pairs stored in a Bundle object.
Caution: Your activity will be destroyed and recreated each time the user rotates the screen. When the screen changes orientation, the system destroys and recreates the foreground activity because the screen configuration has changed and your activity might need to load alternative resources (such as the layout).
To save additional data about the activity state, you must override the onSaveInstanceState() callback method. The system calls this method when the user is leaving your activity and passes it the Bundle object that will be saved in the event that your activity is destroyed unexpectedly. If the system must recreate the activity instance later, it passes the same Bundle object to both the onRestoreInstanceState() and onCreate() methods.
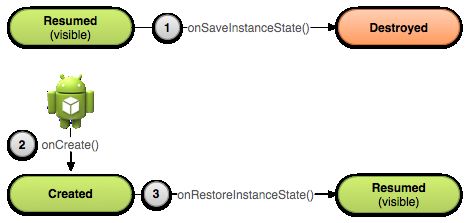
Figure 2. As the system begins to stop your activity, it calls onSaveInstanceState() (1) so you can specify additional state data you'd like to save in case the Activity instance must be recreated. If the activity is destroyed and the same instance must be recreated, the system passes the state data defined at (1) to both the onCreate() method (2) and theonRestoreInstanceState() method (3).
Save Your Activity State
To save additional state information for your activity, you must implement onSaveInstanceState() and add key-value pairs to the Bundle object. For example:static final String STATE_SCORE = "playerScore";
static final String STATE_LEVEL = "playerLevel";
...
@Override
public void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Save the user's current game state
savedInstanceState.putInt(STATE_SCORE, mCurrentScore);
savedInstanceState.putInt(STATE_LEVEL, mCurrentLevel);
// Always call the superclass so it can save the view hierarchy state
super.onSaveInstanceState(savedInstanceState);
}
Restore Your Activity State
When your activity is recreated after it was previously destroyed, you can recover your saved state from the Bundle that the system passes your activity. Both the onCreate() and onRestoreInstanceState() callback methods receive the same Bundle that contains the instance state information.For example, here's how you can restore some state data in onCreate():
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Always call the superclass first
// Check whether we're recreating a previously destroyed instance
if (savedInstanceState != null) {
// Restore value of members from saved state
mCurrentScore = savedInstanceState.getInt(STATE_SCORE);
mCurrentLevel = savedInstanceState.getInt(STATE_LEVEL);
} else {
// Probably initialize members with default values for a new instance
}
...
}
Instead of restoring the state during onCreate()
you may choose to implement onRestoreInstanceState()
, which the system calls after the onStart()
method. The system calls onRestoreInstanceState()
only if there is a saved state to restore, so you do not need to check whether the Bundle
is null: public void onRestoreInstanceState(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Always call the superclass so it can restore the view hierarchy
super.onRestoreInstanceState(savedInstanceState);
// Restore state members from saved instance
mCurrentScore = savedInstanceState.getInt(STATE_SCORE);
mCurrentLevel = savedInstanceState.getInt(STATE_LEVEL);
}