Nginx
Nginx荣获2012年度云计算开发奖,全球第二大Web服务器;开源、高性能、高并发、简单配置,解决了C10k问题。
但在稳定性方面交老道的Apache稍差一点。
Apache稳定、开源、跨平台,配置稍微复杂,存在C10k问题。
一、Nginx特性:
1、基本功能:
(1)、静态资源的web服务,能自动缓存打开的文件描述符。
(2)、反向代理服务器,负载均衡、缓存。
(3)、支持FastCGI协议,因此能够实现LNMP(Linux Nginx Mysql Php)。
(4)、高度模块化,但非DSO机制。支持多种过滤器(如gzip),SSI和图像大小调整等。
(5)、支持SSL.
2、扩展功能:
(1)、基于名称和IP做虚拟主机。
(2)、支持keepalive
(3)、支持平滑配置文件更新或程序版本升级。
(4)、定制访问日志,以及日志缓存以提高性能。
(5)、支持url rewrite
(6)、支持路径别名。
(7)、支持基于IP以及用户的认证。
(8)、支持速率限制,并发数限制等。
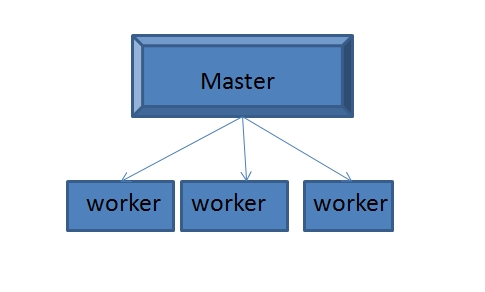
二、Nginx基本架构:
1、一个master,生成一个或者多个worker,一般而言worker数要小于物理cpu数量。
2、事件驱动,kqueue,epoll
3、支持非阻塞如mmap,AIO
4、支持sendfile,sendfile64
三、Nginx模块类别:
1、核心模块
2、标准http模块
3、可选的http模块
4、邮件模块
5、第三方扩展模块
四、Nginx的安装以及配置:
1、编译安装:
安装前确保Development Tools和Server Platform Development,
如未安装请执行#yum -y groupinstall "Development Tools" "Server Platform Development"
(1)、#yum -y install pcre-devel 为了解决依赖关系要装。
(2)、首先添加用户nginx,实现以此用户运行nginx服务进程。
#groupadd -r nginx
#useradd -r -g nginx nginx
(3)、#tar xf nginx1.4.7.tar gz
#cd nginx1.4.7
# .configure --prefix=/usr
--sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx
--conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
--error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log
--http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log
--pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid
--lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock
--user=nginx
--group=nginx
--with-http_ssl_module
--with-http_flv_module
--with-http_stub_status_module
--with-http_gzip_static_module
--with-client-body-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/client
--with-proxy-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/proxy
--with-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/fcgi
--with-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/uwsgi
--with-scgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/scgi
--with-pcre
#make && make install
然后启动#/usr/sbin/nginx ,并执行#ss -tnl 看下80端口。
(4)、开机启动加脚本:
#vi /etc/rc.d/initd./nginx 内容如下:
#!/bin/sh
#
# nginx - this script starts and stops the nginx daemon
#
# chkconfig: - 85 15
# description: Nginx is an HTTP(S) server, HTTP(S) reverse \
# proxy and IMAP/POP3 proxy server
# processname: nginx
# config: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
# config: /etc/sysconfig/nginx
# pidfile: /var/run/nginx.pid
# Source function library.
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
# Source networking configuration.
. /etc/sysconfig/network
# Check that networking is up.
[ "$NETWORKING" = "no" ] && exit 0
nginx="/usr/sbin/nginx"
prog=$(basename $nginx)
NGINX_CONF_FILE="/etc/nginx/nginx.conf"
[ -f /etc/sysconfig/nginx ] && . /etc/sysconfig/nginx
lockfile=/var/lock/subsys/nginx
make_dirs() {
# make required directories
user=`nginx -V 2>&1 | grep "configure arguments:" | sed 's/[^*]*--user=\([^ ]*\).*/\1/g' -`
options=`$nginx -V 2>&1 | grep 'configure arguments:'`
for opt in $options; do
if [ `echo $opt | grep '.*-temp-path'` ]; then
value=`echo $opt | cut -d "=" -f 2`
if [ ! -d "$value" ]; then
# echo "creating" $value
mkdir -p $value && chown -R $user $value
fi
fi
done
}
start() {
[ -x $nginx ] || exit 5
[ -f $NGINX_CONF_FILE ] || exit 6
make_dirs
echo -n $"Starting $prog: "
daemon $nginx -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE
retval=$?
echo
[ $retval -eq 0 ] && touch $lockfile
return $retval
}
stop() {
echo -n $"Stopping $prog: "
killproc $prog -QUIT
retval=$?
echo
[ $retval -eq 0 ] && rm -f $lockfile
return $retval
}
restart() {
configtest || return $?
stop
sleep 1
start
}
reload() {
configtest || return $?
echo -n $"Reloading $prog: "
killproc $nginx -HUP
RETVAL=$?
echo
}
force_reload() {
restart
}
configtest() {
$nginx -t -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE
}
rh_status() {
status $prog
}
rh_status_q() {
rh_status >/dev/null 2>&1
}
case "$1" in
start)
rh_status_q && exit 0
$1
;;
stop)
rh_status_q || exit 0
$1
;;
restart|configtest)
$1
;;
reload)
rh_status_q || exit 7
$1
;;
force-reload)
force_reload
;;
status)
rh_status
;;
condrestart|try-restart)
rh_status_q || exit 0
;;
*)
echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart|condrestart|try-restart|reload|force-reload|configtest}"
exit 2
esac
而后为此脚本赋予执行权限:
# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/init.d/nginx
添加至服务管理列表,并让其开机自动启动:
# chkconfig --add nginx
# chkconfig nginx on
而后就可以启动服务并测试了:
# service nginx start
2、nginx配置 /etc/nginx/nginx.conf:
注意:配置参数需要以分号结尾,否则就语法错误,语法格式:参数名 值1 [值2...];
分为两段:核心段和http段,重要参数如下:
参数配置请参考http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html
(1)、核心配置段{
A、正常运行必备的配置:
a、user username [groupname];
指定运行worker进程的用户和组
b、pid /path/to/pidfile_name;
指定nginx的pid文件
c、worker_rlimit_nofile #;
指定一个worker进程所能够打开的最大文件句柄数
d、worker_rlimit_sigpending #;
指定每个用户能够发往worker进程的信号的数量
B、优化性能相关的配置:
a、worker_processes #;
worker进程的个数,通常其值为CPU的物理核心数减1,即1个留给系统内核用。
b、worker_cpu_affinity cpumask ...;
如共6个cpu,启动四个cpu,则配置为
worker_processes 4;
worker_cpu_affinity 00000001 00000010 00000100 00001000;
c、worker_priority nice;
worker进程的优先级, nice的值为[-20,19],nice越小优先级越高。
d、ssl_engine device;
在存在ssl硬件加速器的服务器上,指定所使用的ssl硬件加速设备。
e、timer_resolution T;
每次内核事件调用返回时,都会调用系统的gettimeofday()来更新nginx缓存时钟,timer_relolution用于定义每隔多久更新一次缓存时钟;X86_64系统上,调用gettimeofday()代价较小,可以忽略此项;X86_32系统上代价较大。
C、事件相关的配置:
a、accept_mutex [on|off];
是否打开nginx负载均衡锁;此锁能够让多个worker轮流地与客户端建立连接;即实现worker间负载均衡。
b、lock_file /path/to/lock_file;
lock文件;如果accept_mutex为off,那么lock_file 失效。
c、accept_mutex_delay #ms;
accept锁模式中,一个worker进程为取得accept锁的等待时长。默认为 500ms。如果某worker进程在每次师徒取得锁时失败,至少要等待#ms才能再次请求锁。
d、multi_accept{on|off};
是否允许一次性地响应多个用户请求;默认为off,默认一个一个请求被响应处理。
e、use [epoll|rtsig|select|poll];
定义使用的事件模型,建议让nginx自动选择,在linux一般选择epoll;
f、worker_connections #;
每个worker能够并发响应的最大请求数;
D、用于调试、定位问题:只在调试nginx时使用。
a、daemon [on|off];
是否让nginx运行于后台;默认为on,调试时为off,使得所有信息输出到控制台,方便查看信息。
b、master_process [on|off];
是否让master管理多个worker运行,默认为on;调试时为off,以方便追踪问题。
c、error_log /path/to/error_log level;
错误日志文件以及级别,默认为error级别;调试时可以使用debug级别,
但要求在编译时必须使用--with_debug启动debug功能。
}
(2)http配置段{
说明:Nginx必须使用虚拟主机配置站点;
每个虚拟主机使用一个server{}段配置;
非虚拟主机的配置或者公共配置,需要配置在server{}外。
具体格式如下:
directive value;
...
server{
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location{
}
}
server{
}
...
A、重要配置详情:
a、server{}:
定义一个虚拟主机,支持基于主机名或者IP的虚拟主机。
b、listen:
listen address[:port]
listen port
default_server:定义此server为http中默认的server;如果所有的server中没有任何一
个listen使用此参数,那么第一个server为默认server。
rcvbuf=SIZE:接收缓冲大小;
sndbuf=SIZE:发送缓冲大小;
ssl:https server
c、server_name相关:
server_name NAME...;可以跟多个主机名;当nginx收到一个请求时,会取出其首部的server的值,而后跟众server_name进行比较。
server_name_hash_bucket_size 32|64|128;为了实现快速查找主机名,nginx使用hash表保存主机名;
d、location相关:
根据用户请求的URI,匹配指定的各location,匹配到时将被location来处理。
location定义在server或者location中,location可以出现多次,但不能放在http上下文中。
location [ =|~|~*|^~ ] uri { ... }
location @name {...}
=:精确匹配
~:正则表达式模式匹配,匹配时区分字符大小写。
~*:正则表达式模式匹配,匹配时忽略字符大小写。
^~:uri前半部分匹配,不检查正则表达式。

e、文件路径定义:
root path:设置web资源路径,用于指定请求的根文件目录,通常定义在location中。
如:location / {
root /www/html;
index index.html index.htm
}
location ^~ /images/ {
root /web;
}
http://www.a.org/images/b.html
b.html放置用于/web/images/下
alias path:用于配置路径别名,只能用于location中。
如:location / {
root /www/html;
index index.html index.htm
}
location ^~ /images/ {
alias /web;
}
http://www.a.org/images/b.html
b.html放置用于/web/下
注意:root path和alias path配置时,b.html的放置路径。
index file...:定义默认页,自左而右匹配。
如:location / {
root /www/html;
index index.html index.htm
}
error_page code ...[=[reponse]] uri;当对于某个请求返回错误是,如果匹配上了error_page指令中设定的code,则重定向指定的页面。如error_page 404 /404.html,error_page可以定义在server或者location中。
如:location / {
root /www/html;
index index.html index.htm
error_page 404 /404.html
}
try_files path1 [path2] uri;错误重定向。
如:location /tryfile {
root /www/html;
index index.html index.htm
try_files $uri /tryfile.html
}
f、网络连接相关的配置:
keepalive_timeout time;设置保持连接的超时时长,默认为75s中。

keepalive_request n;在一次长连接上允许承载的最大请求数;

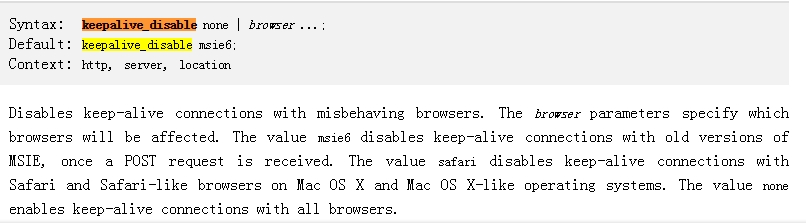
keepalive_disable [msie6|safari|none];对指定的浏览器禁止使用长连接。
tcp_nodelay {on|off} ;对keepalive连接是否使用tcp_nodelay选项。

client_header_timeout time;读取http请求首部的超时时长。
send_timeout time;发送响应的超时时长。
g、对客户端请求的限制:
limit_except method...{...};排除请求方法。
 Please note that this will limit access to all methods except GET and HEAD.
Please note that this will limit access to all methods except GET and HEAD.
client_max_body_size SIZE;http请求的包体的最大值,常用于限定客户所能请求的最大包体;
根据请求首部中的Content-length来检测,以免无用的传输。如:上传附件的限制。
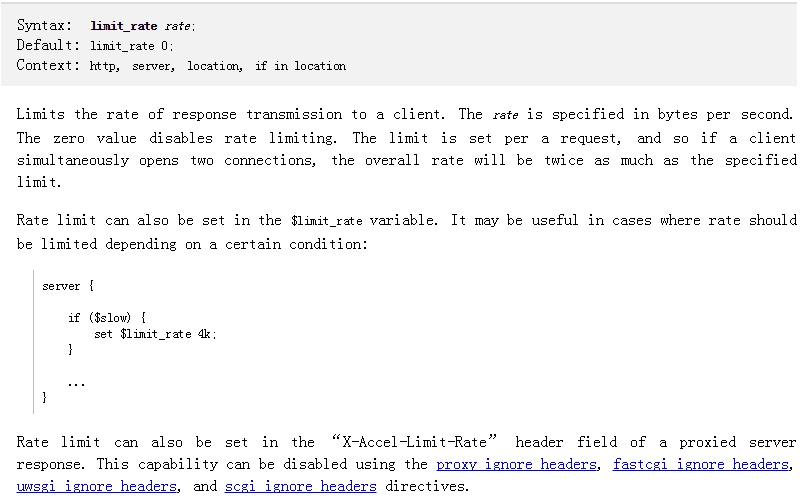
limit_rate speed;限制客户端每秒传输的字节数,默认为0,表示没有限制。
limit_rate_after time;nginx向客户发送响应报文时,如果时长超出此处制定的时长,则后续的发送过程开始限速;如:下载网站需要限速,web站点一般就不需要限速了 哈哈...

h、文件操作的优化:
sendfile {on|off};是否启用sendfile功能。
aio {on|off};是否启用aio功能。
open_file_cache max=N [inactive=time]|off;
是否打开文件缓存功能:
max:缓存条目的最大值,当满了以后将根据LRU算法进行置换。
inactive:某缓存条目在指定时长内没被访问时,将自动被删除,默认为60s。
缓存的信息包括:
文件句柄、文件大小和上次修改时间。
已经打开的目录结构。
没有找到或者没有访问权限的信息。
open_file_cache_errors on|off;是否缓存文件找不到或者没有权限访问等相关信息。
open_file_cache_valid time;多长时间检查一次缓存中的条目是否超出非活动时长,默认60s
open_file_cache_min_use #;在inactive指定的时长内被访问超出此处指定的次数,才不会被删除
i、对客户端请求的特殊处理:
ignore_invalid_heads on|off;是否忽略不合法的http首部;on为默认,忽略不合法的http首部;off意味着请求首部中出现不合规的首部拒绝响应。
log_not_found on|off;是否将文件找不到的信息记录到错误日志中。
resolver address;指定nginx使用的dns服务器地址。
resover_timeout time;指定DNS解析超时时长,默认30s;
server_tokens on|off;是否在错误页面中显示nginx的版本号。
j、内存以及磁盘资源分配:
client_body_in_file_only
on|clean|off;
http的包体是否存储磁盘文件中;非off表示存储,默认为off
on|clean:clean请求结束后包体文件会被删除,on请求结束后包体文件不会被删除。
client_body_in_single_buffer on | off;
http的包体是否存储在内存buffer中,默认为off。
client_body_buffer_size size;nginx接收http包体的内存缓冲区大小,和client_body_in_single_buffer配合使用。client_body_temp_path dir_path [level1 [level2 [level3]]];定义http包体存放的临时目录,可以多级目录;和client_body_in_file_only配合使用。client_header_buffer_size size;正常情况下接收用户请求的http报文header部分时分配的buffer大小,默认为1k。large_client_header_buffers number size;定义存储超大http请求首部的内存buffer大小以及个数。connection_pool_size size;nginx对于每个建立成功的tcp练级诶都会预先分配一个内存池,此处即用于设定此内存池的初始大小,默认为256。
}
3、重要的内置变量:
$uri :当前请求的uri,不带参数;
$host:http请求报文中的host首部,不过请求中没有host,则以处理此请求的虚拟主机的主机名替代。
$request_uri:当前请求的uri,带完整参数;
$hostname:nginx服务器运行在的主机的主机名;
$remote_addr:客户端IP
$remote_port:客户端port
$remote_user:使用用户认证时,客户端用户输入的用户名;
$request_method:请求方法
$server_addr:服务器地址
$server_name:服务器名称
$server_port:服务器端口
$server_protocol:服务器想客户端发送响应时的协议,如http/1.1,http/1.0
五、配置使用Nginx:
1、Nginx虚拟主机的使用:
例如:配置两个虚拟主机:www.a.com和www.b.org
则需要在nginx.conf中配置两个server,具体配置如下:
server{
listen 80;
server_name www.a.com;
location /{
root /www/a.com;
index index.html index.htm index.php index.jsp;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location =/50x.html{
root html;
}
}
server{
listen 80 default_server;
server_name www.b.org;
root /www/b.org;
}
2、基于IP的访问控制:
access{
allow
deny
}
或者在server中直接写
allow
deny
例如仅允许 172.16.0.0/16这个网段访问,配置如下:
allow 172.16.0.0/16
deny all
3、基于用户做访问控制:
location /admin/ {
root /www/b.org;
auth_basic "admin_area";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.htpasswd;
}
4、autoindex模块:站点未配置主页时,将站点的所有页面以列表形式显示输出。
通常不打开,非常危险,只有建立下载站点时才打开。
location /download/ {
root /www/b.org;
autoindex on;
}
5、图片防盗链:
(1)、定义防盗链的步骤:
A、定义合规的引用:
valid_referers none|blocked|server_names|string ...;
B、拒绝不合规的引用:
if($invalid_referer){
rewrite ^/.*$ http://www.b.org/403.html 或者 return 404
}
(2)、例如:
location ~* \.(jpg|png|gif|jpeg)$ {
root /www/b.org;
valid_referers none blocked www.b.org *.b.org ~\.google\. ~\.baidu\.;
if($invalid_referer){
rewrite ^/.*$ http://www.b.org/403.html 或者 return 404
}
}
注意:~\.google\.允许google的爬虫
6、URL rewrite相关:
URL rewrite使用场景如京东早期的网址为www.360buy.com,现在网址www.jd.com,那么访问www.360buy.com必须自动跳转到www.jd.com;还有服务器升级,文件路径变更,也需要重定向;以及将url跳转等等;
(1)、rewrite regex replacement [flag];
A、flag的值:
last:一旦被当前规则匹配并重写后立即停止检查后续的其他rewrite的规则,而重写后的规则会重新发起请求。
break:一旦被当前规则匹配并重写后立即停止检查后续的其他rewrite的规则,而重写后的规则不会重新发起请求。
redirect:返回302临时重定向。
permanent:返回301永久重定向。
B、注意:如果出现死循环,nginx最多循环10次,超出之后会返回500错误。
一般将rewrite写在location中时都使用break,或者将rewrite写在if上下文中。
如:
location / {
root /www/b.org;
rewrite ^/images/(.*)$ /imgs/$1 break;
}
(2)、rewrite_log on|off :
是否把重写过程记录在错误日志中;默认为off。一般为off,繁忙的服务器一定为off。
(3)、return code:
用于结束rewrite规则,并且为客户返回状态码,可以使用的状态码有204 400 402-406,500-504等。
如:if($invalid_referer){
rewrite ^/.*$ return 404
}
7、gzip 压缩:
nginx将响应报文发送至客户端之前可以启用压缩功能,这样能够有效节约带宽,并提高响应至客户端的速度。通常编译nginx时默认会附带gzip压缩的功能,因此可以直接启用之。
http {
gzip on;
gzip_http_version 1.0;
gzip_comp_level 2;
gzip_types text/plain text/css text/xml text/javascript
application/x-javascript application/xml application/xml+ress application/javascript application/json;
gzip_disable msie6;
}
六、Nginx反向代理及负载均衡:Nginx比LVS好用,并易于配置。
1、正向代理:
帮一个网络内的多个客户端访问公网的服务叫正向代理,正向代理简言之就是代表客户端。
2、反向代理:
帮助服务器接收请求的服务叫反向代理,反向代理简言之就是代表服务器端。
3、nginx的两种常用用途:
(1)、静态内容的web服务器。
(2)、反向代理,处理并发连接处理能力很强,因为nginx是先缓存请求,然后一并发到后端服务器。
4、Nginx的proxy模块:Nginx通过proxy模块实现反向代理功能。
(1)、Nginx通过proxy模块实现反向代理功能。
Nginx在作为web反向代理服务器时,nginx负责接收客户请求,并能够根据URI、客户端参数或者其 他的处理逻辑将用户请求调度至上游服务器上。nginx在实现反向代理功能时的最重要的指令为 proxy_pass,它能够将location定义的某URI代理至指定的上游
服务器(组)上。如下面的示例中,location的/uri将被替换为上游服务器上的/newuri.
location /uri {
proxy_pass http://www.b.org:8080/newuri;
}
不过,这种处理机制中有两个例外。
第一个例外是,如果location的URI是通过模式匹配定义的,其URI将直接被传递到上游服务器,而 不能为其指定转换的另一个URI。例如:/bbs将被代理为http://www.b.org:8080/bbs
,即newuri就不要写了。
location ~^/bbs {
proxy_pass http://www.b.org:8080;
}
第二个例外是,如果location中使用的是URL重定向,那么nginx将使用重定向后的URI处理请求, 而不再考虑上游服务器上第一的URI。如下例,传递给上游服务器的URI为/index.php?page= <match>,而不是/index
location / {
rewrite /(.*)$ /index.php?page=$1 break;
proxy_pass http://www.b.org:8080/index;
}
(2)、proxy模块指令:
proxy模块可配置的指令参数非常多,它们分别用于定义proxy模块工作时的诸多属性,如连接超时 时长、代理时使用http协议版本等。
proxy_connect_timeout:nginx将一个请求发送至上游服务器(upstream server)之前等待的最大时长。默认60s
proxy_cookie_domain ;
将upstream server通过set-cookie首部设定为domain属性修改为指定的值,其值可以为一个字符、串、正则表达式的模式或一个引用变量。
proxy_cookie_path ;将upstream server通过set_cookie首部设定的path属性修改为指定的值,其值可以为一个字符串、、正则表达式的模式或一个引用变量。
proxy_hide_header ;设定发送给客户端的报文中需要隐藏的首部。
proxy_pass ;指定将请求代理至upstream server的url路径。
proxy_set_header ;将发送至upstream server的报文的某首部进行重写。
proxy_redirect ;重写location并刷新从upstream server收到的报文首部。
proxy_send_timeout;在连接断开之前两次发送至upstream server的写操作的最大间隔时长。
proxy_read_timeout;在连接断开之前两次发送至upstream server接收读操作的最大间隔时长。
5、Upstream 模块实现负载均衡。
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_upstream_module.html
(1)、upstream name {
server address [parameters];
},只能放在http段中,各server只能直接使用IP或者主机名,不要加协议。
示例如下:
http{
.....
upstream webservers {
server 172.16.1.8 weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=5;
server 172.16.1.18 weight=2 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=5;
server 127.0.0.1:8080 backup;
}
......
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.b.org;
location / {
proxy_pass http://webservers;
proxy_set_header X_Real_IP $remote_addr;
}
}
server {
listen 8080;
server_name 127.0.0.1;
root /www/backup;
}
......
}
server address [parameters];的parameters如下:
weight=#;设置权重
max_fails=#;最大失败尝试次数,默认为1
fail_timeout=#;失败尝试超时时长,默认为10s。
backup:当转发失败,转发至本机。
health_check:健康状态监测。
health_check [interval=time] [fails=number] [passes=number] [uri=uri] [match=name];
定义在location中。
interval:多长时间监测一次
fails:尝试失败次数,如果超过此次数,则认为失败。
passes:重新上线次数。
uri:监测是uri.
match:自定义状态监测。

ip_hash;用在upstream中,实际上就是源地址hash,实现session绑定。

(2)、缓存区、缓存:提高反向代理的性能。
缓存区设定:
nginx在默认情况下在将其响应给客户端之前会尽可能接收来自于upstream服务器的响应报文,它会将这些响应报文暂存于本机并尽量一次性地响应给客户端,然而在来自于客户端的请求或来自upstream服务器的响应过多时,nginx会试图将之存储于本地磁盘中,这将大大降低nginx的性能。因此在有着更多可用内存的场景中,应该将用于暂存这些报文的缓冲区调大至一个合理值。
proxy_buffer_size size:设定用于暂存来自于upstream服务器的第一个响应报文的缓冲区大小。
proxy_buffering on|off:启用缓冲upstream服务器的响应报文,否则,如果proxy_max_temp_file_size指令的值为0,来自upstream服务器的响应报文在接收到的那一刻
将同步发送至客户端;一般情况下,启用proxy_buffering并将proxy_max_temp_file_size设定为0能够启用缓存响应报文的功能,并能够避免将其缓存至磁盘中。
proxy_buffers 8 4k|8k:用于缓存来自upstream服务器的响应报文的缓冲区大小。8为8个缓冲区个数,4k|8k为缓冲区大小。
缓存:
nginx作为反向代理时,能够将来自upstream的响应缓存至本地(一般缓存到磁盘),并在后续的客户端请求同样内容时直接从本地构造响应报文。
proxy_cache zone|off:定义一个用于缓存的共享内存区域,其可被多个地方调用;缓存将遵从upstream服务器的响应报文首部中关于缓存的设定,如"Expires"、"Cache-Control:no-cache"、"Cache-control:max-age=XXX" 、"private"和"no-store"等,但nginx在缓存时不会考虑响应报文的"Vary"首部。为了确保私有信息不被缓存,所有关于用户的私有信息可以在upstream上通过"no-cache" or "max-age=0"来实现,也可在nginx设定proxy_cache_key必须包含用户特有数据如$cookie_xxx的方式实现,单最后这种方式在公共缓存上使用可能会有风险。因此,在响应报文中含有以下首部或者指定标志的报文将不会被缓存。
Set-Cookie
Cache-Control containing "no-cache","no-store","private",or a "max-age" with a non-numeric or 0 value
Expires with a time in the past
X-Accel-Expires:0