关于霍夫找圆算法cvHoughCircles的
霍夫圆变换的函数为:
HoughCircles
利用 Hough 变换在灰度图像中找圆
CvSeq* cvHoughCircles( CvArr* image, void* circle_storage, int method, double dp, double min_dist, double param1=100, double param2=100, int min_radius=0, int max_radius=0 );
- image
- 输入 8-比特、单通道灰度图像.
- circle_storage
- 检测到的圆存储仓. 可以是内存存储仓 (此种情况下,一个线段序列在存储仓中被创建,并且由函数返回)或者是包含圆参数的特殊类型的具有单行/单列的CV_32FC3型矩阵(CvMat*). 矩阵头为函数所修改,使得它的 cols/rows 将包含一组检测到的圆。如果 circle_storage 是矩阵,而实际圆的数目超过矩阵尺寸,那么最大可能数目的圆被返回
. 每个圆由三个浮点数表示:圆心坐标(x,y)和半径.
- method
- Hough 变换方式,目前只支持CV_HOUGH_GRADIENT, which is basically 21HT, described in [Yuen03].
- dp
- 累加器图像的分辨率。这个参数允许创建一个比输入图像分辨率低的累加器。(这样做是因为有理由认为图像中存在的圆会自然降低到与图像宽高相同数量的范畴)。如果dp设置为1,则分辨率是相同的;如果设置为更大的值(比如2),累加器的分辨率受此影响会变小(此情况下为一半)。dp的值不能比1小。
Resolution of the accumulator used to detect centers of the circles. For example, if it is 1, the accumulator will have the same resolution as the input image, if it is 2 - accumulator will have twice smaller width and height, etc.
- min_dist
- 该参数是让算法能明显区分的两个不同圆之间的最小距离。
Minimum distance between centers of the detected circles. If the parameter is too small, multiple neighbor circles may be falsely detected in addition to a true one. If it is too large, some circles may be missed.
- param1
- 用于Canny的边缘阀值上限,下限被置为上限的一半。
The first method-specific parameter. In case of CV_HOUGH_GRADIENT it is the higher threshold of the two passed to Canny edge detector (the lower one will be twice smaller).
- param2
- 累加器的阀值。
The second method-specific parameter. In case of CV_HOUGH_GRADIENT it is accumulator threshold at the center detection stage. The smaller it is, the more false circles may be detected. Circles, corresponding to the larger accumulator values, will be returned first.
- min_radius
- 最小圆半径。
Minimal radius of the circles to search for.
- max_radius
- 最大圆半径。
Maximal radius of the circles to search for. By default the maximal radius is set to max(image_width, image_height).
The function cvHoughCircles finds circles in grayscale image using some modification of Hough transform.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
我的目标是在一直全是圆的图中找出所有圆,并用红色表圈出。
//霍夫变换寻找圆
img、img1、img2函数外定义。
void CdialogCVDlg::OnBnClickedBtnhoughcircles()
{
// TODO: Add your control notification handler code here
// TODO: Add your control notification handler code here
cvNamedWindow("a",1);
cvNamedWindow("b",1);
cvNamedWindow("c",1);
img = cvLoadImage("D:\ii.jpg",1); //原图
img1 = cvCreateImage (cvGetSize(img), IPL_DEPTH_8U, 1);//处理的图像必须是八位单通道的
if (img->nChannels == 1)
{
img1 = cvCloneImage (img);
}
else
{
cvCvtColor (img, img1, CV_RGB2GRAY); //转为单通道
}
CvMemStorage* storage=cvCreateMemStorage(0);
CvSeq* circle = 0;
//cvSmooth( img1, img1, CV_GAUSSIAN, 5, 5 ); //看了很多事例,要降噪处理,但测试的结果是
//找圆会有一定偏差,说明用这个要因图而异,噪声高的图才要用
circle = cvHoughCircles( //cvHoughCircles函数需要估计每一个像素梯度的方向,
//因此会在内部自动调用cvSobel,而二值边缘图像的处理是比较难的
img1,
storage,
CV_HOUGH_GRADIENT,
1, //累加器图像的分辨率,增大则分辨率变小
18, //很重要的一个参数,告诉两个圆之间的距离的最小距离,如果已知一副图像,可以先行计
//算出符合自己需要的两个圆之间的最小距离。
100, //canny算法的阈值上限,下限为一半(即100以上为边缘点,50以下抛弃,中间视是否相连而
//定)
25, //决定成圆的多寡 ,一个圆上的像素超过这个阈值,则成圆,否则丢弃
32,//最小圆半径,这个可以通过图片确定你需要的圆的区间范围
45 //最大圆半径
);
img2 = cvCreateImage (cvGetSize(img), IPL_DEPTH_8U, 3); //用一个三通道的图片来显示红色的
//圆圈
cvCvtColor (img1, img2, CV_GRAY2RGB); //转为3通道
for( int i = 0; i < circle->total; i++ )
{
float* p = ( float* )cvGetSeqElem( circle, i );
//霍夫圆变换
CvPoint pt = cvPoint( cvRound( p[0] ), cvRound( p[1] ) ); //圆心坐标(p(0),p(1))
cvCircle(
img2,
pt, //确定圆心
cvRound( p[2] ), //确定半径
CV_RGB( 255, 0, 0 ),
3
); //画圆函数
}
cvShowImage( "a", img );
cvShowImage("b",img1);
cvShowImage("c",img2);
}
//原图:
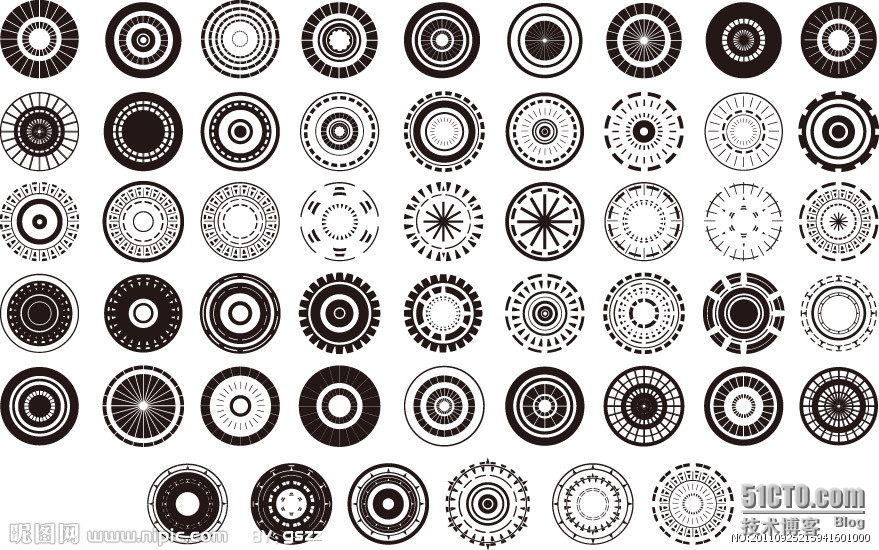
//效果图
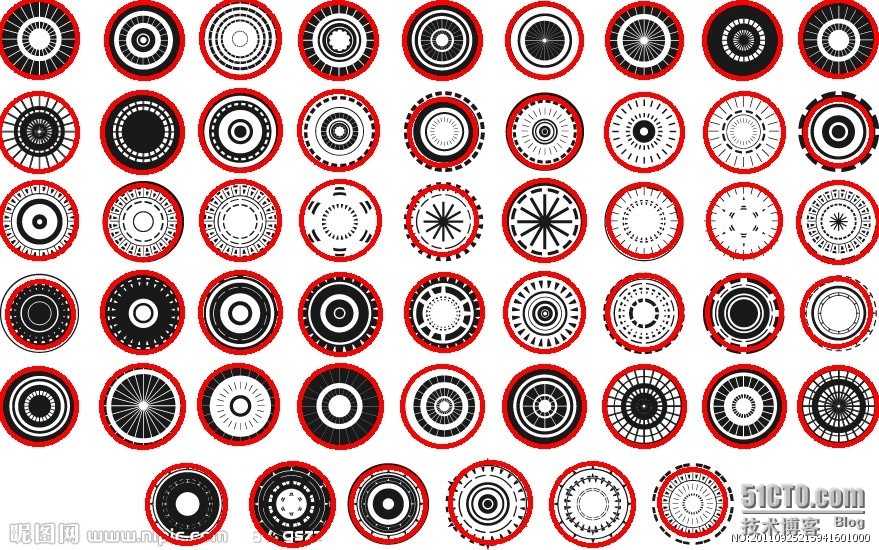
结论:只要调好参数,霍夫圆算法可以找出你的设定目标圆。