Heartbeat+LVS+Ldirectord高可用&负载均衡
集群技术主要分为三大类:
高可用性(High Available Cluster),例:Linux-HA
负载均衡(Load balancing Cluster),例:LVS、MOSIX
高性能计算(High Performance Computing),例:Beowulf
我们这里使用 RHEL5.2,LVS,Linux-HA,Ldirectord,构造一个高可用的负载均
衡集群系统。如图:
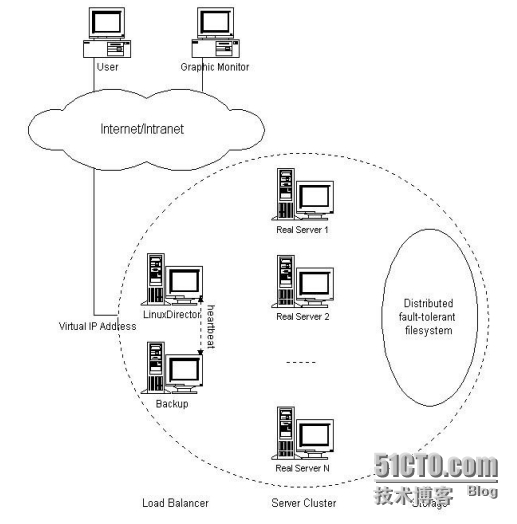
Load Balancer 是整个集群系统的前端,负责把客户请求转发到 Real
Server 上。
Backup 是备份 Load Balancer,当 Load Balancer 不可用时接替它,成为
实际的 Load Balancer。
Load Balancer 通过 Ldirectord 监测各 Real Server 的健康状况。在 Real
Server 不可用时把它从群中剔除,恢复时重新加入。
Server Array(服务器群)
Server Array 是一组运行实际应用服务的机器,比如 WEB, Mail, FTP, DNS,
Media 等等。
在实际应用中,Load Balancer 和 Backup 也可以兼任 Real Server 的角色。
各服务器 IP 分配:
实验环境:rhel6.5 iptables&selinux disabled 时间同步
Virtual IP: 192.168.2.111
Load Balancer: 192.168.2.36
Backup: 192.168.2.46
Real Server 1: 192.168.2.38
Real Server 2: 192.168.2.39(四台主机都做自己的解析)
HeartBeat
HeartBeat 是 Linux-HA 的高可用性集群软件,它的主要作用是:
安装在 Load Balancer 和 Backup 上,运行于 active/standby 模式。
当 Load Balancer 失效时,Backup 自动激活,成为实际的 Load Balancer。
切换到 active 模式时,按顺序启动 Virtual IP、IPVS 和 Ldirectord。
切换到 standby 模式时,按顺序关闭 Ldirectord、IPVS 和 Virtual IP。
软件包安装与配置


安装完成后进入到/etc/ha.d目录下 在desktop37上同样安装这三个包
[root@desktop36 ha.d]# ls
harc ldirectord.cf README.config shellfuncs
rc.d resource.d
查看那个README.config文件
[root@desktop36 ha.d]# less README.config
 |
你会看到heartbeat的配置文件在 /usr/share/doc/heartbeat-3.0.4/
进到这个目录下
[root@desktop36 heartbeat-3.0.4]# ls
apphbd.cf AUTHORS COPYING ha.cf README
authkeys ChangeLog COPYING.LGPL haresources
把这三个标注为红色的文件cp到/etc/ha.d/下
[root@desktop36 heartbeat-3.0.4]# cp authkeys haresources ha.cf /etc/ha.d/
主配置文件(/etc/ha.d/ha.cf):
debugfile /var/log/ha-debug
调试日志文件文件,取默认值
logfile /var/log/ha-log
系统运行日志文件,取默认值
logfacility local0
日志等级,取默认值
keepalive 2
心跳频率,自己设定。1:表示 1 秒;200ms:表示 200 毫秒
deadtime 30
节点死亡时间阀值,就是从节点在过了 30 后还没有收到心跳就认为主节点死亡,自己设定
warntime 10
发出警告时间,自己设定
initdead 120
守护进程首次启动后应该等待 120 秒后再启动主服务器上的资源
udpport 694
心跳信息传递的 udp 端口,使用端口 694 进行 bcast 和 ucast 通信,取默认值
#baud 19200
串口波特率,与 serial 一起使用。
#serial /dev/ttyS0
采用串口来传递心跳信息。
bcast eth10
采用 udp 广播播来通知心跳
#ucast eth1 10.0.0.3
采用网卡 eth1 的 udp 单播来通知心跳,eth1 的 IP
#mcast eth0 225.0.0.1 694 1 0
采用 udp 多播播来通知心跳
auto_failback on
当主节点恢复后,是否自动切回
#stonith baytech /etc/ha.d/conf/stonith.baytech
stonith 用来保证共享存储环境中的数据完整性
watchdog /dev/watchdog
watchdog 能让系统在出现故障 1 分钟后重启该机器,这个功能可以帮助服务器在确实停止心
跳后能够重新恢复心跳。 如果使用该特性,修改系统中/etc/modprobe.conf, 添加如下行
options softdog nowayout=0
这样在系统启动的时候,在内核中装入"softdog"内核模块,用来生成实际的设备文件
/dev/watchdog
node desktop36.example.com
主节点名称,与 uname �Cn 保持一致。排在第一的默认为主节点,所以不要搞措顺序
node desktop46.example.com
副节点名称,与 uname �Cn 保持一致
ping 192.168.0.254
respawn hacluster /usr/lib64/heartbeat/ipfail
apiauth ipfail gid=haclient uid=hacluster
默认 heartbeat 并不检测除本身之外的其他任何服务,也不检测网络状况。
所以当网络中断时,并不会进行 Load Balancer 和 Backup 之间的切换。
可以通过 ipfail 插件,设置'ping nodes'来解决这一问题,但不能使用一个集群节点作为
ping 的节点。
资源文件(/etc/ha.d/haresources):
desktop36.example.com Ipaddr::192.168.2.111/24/eth0:0 ldirectord httpd
这个文件中定义了实现集群所需的各个软件的启动脚本,这些脚本必须放在/etc/init.d 或者
/etc/ha.d/resource.d 目录里 IPaddr 的作用是启动 Virutal IP,它是 HeartBeart 自带的一个
脚本;ldirectord 的作用是启动 ldirectord 监控程序,它会使 ldirectord.cf 中定义的 lvs 生效,
并监听其健康状;httpd 是 apache 服务的启动脚本。
认证文件(/etc/ha.d/authkeys),文件的权限必须是 600:
auth 3
1 crc
#2 sha1 HI!
#3 md5 Hello!
配置 ip_forward
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
sysctl -p
以上是 desktop36.example.com 主心跳上的配置,进入 desktop46.example.com 备份心跳
重复以上安装配置,切记/etc/ha.d/目录下的 authkeys、haresources、 ha.cf
三个文件必须和 desktop36.example.com 上的相同.
分别在主备心跳上启动 heartbeat 服务:
|
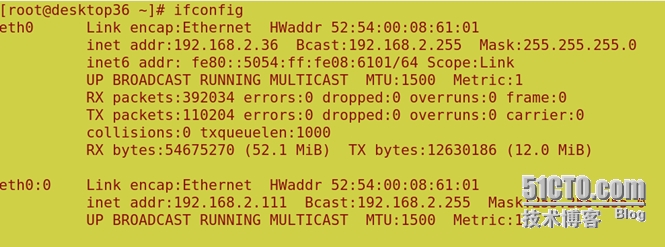
分别查看日志,是否有报错,服务正常的话 desktop36 上多了个 eth0:0 接口,若没有出现,
请等待一会,再使用 ifconfig 查看,若还是没有 eth0:0 接口出现,检查配置文件是否正确!
若停止 desktop36 上的 heartbeat 服务,则 desktop46 会接管,并产生一个 eth0:0 接口!
IPVS
IPVS 是 LVS 集群系统的核心软件,它的主要作用是:
安装在 Load Balancer 上,把发往 Virtual IP 的请求转发到 Real Server 上。
IPVS 的负载均衡机制有三种,这里使用 IP Tunneling 机制:
Virtual Server via NAT
Virtual Server via IP Tunneling
Virtual Server via Direct Routing
IPVS 的负载调度算法有十种:
轮叫(Round Robin)
加权轮叫(Weighted Round Robin)
少链接(Least Connections)
加权最少链接(Weighted Least Connections)
基于局部性的最少链接(Locality-Based Least Connections)
带复制的基于局部性最少链接(Locality-Based Least Connections with
Replication)
目标地址散列(Destination Hashing )
源地址散列(Source Hashing)
最短期望延迟(Shortest Expected Delay)
无须队列等待(Never Queue)
接下来在两台主备心跳上安装ipvsadm ; yum install ipvsadm -y
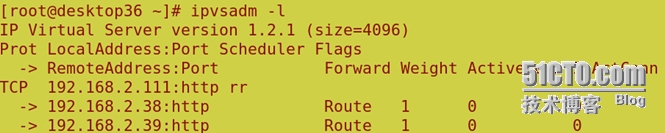
ipvsadm -A -t 192.168.2.111:80 -s rr 采用轮叫算法
ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.2.111:80 -r 192.168.2.38:80 -g
ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.2.111:80 -r 192.168.2.39:80 -g (把发往 Virtual IP 的请求转发到 Real Server 上。)
用ipvsadm -l 查看连接状况
配置 arp 机制:
在两台realserver上安装arptables_jf
[root@desktop38 ~]# yum install arptables_jf -y
[root@desktop39 ~]# yum install arptables_jf -y
[root@desktop38 ~]# ifconfig eth0:0 192.168.2.111 netmask 255.255.255.255
[root@desktop39 ~]# ifconfig eth0:0 192.168.2.111 netmask 255.255.255.255(添加虚拟IP)
[root@desktop38 ~]arptables -A IN -d 192.168.2.111 -j DROP
[root@desktop38 ~]arptables -A OUT -s 192.168.2.111 -j mangle --mangle-ip-s 192.168.2.38
[root@desktop39 ~]arptables -A IN -d 192.168.2.111 -j DROP
[root@desktop39 ~]arptables -A OUT -s 192.168.2.111 -j mangle --mangle-ip-s 192.168.2.39
/etc/init.d/arptables_jf save
/etc/init.d/arptables_jf start
这表示从虚拟IP进来的都DROP掉,从realIP出去的都是以虚拟IP的身份。
ldirectord
它的作用是:
监测 Real Server,当 Real Server 失效时,把它从 Load Balancer 列表中
删除,恢复时重新添加。
在两台主备心跳上安装ldirectord
yum localinstall ldirectord-3.9.2-1.2.x86_64.rpm
配置(/etc/ha.d/ldirectord.cf):
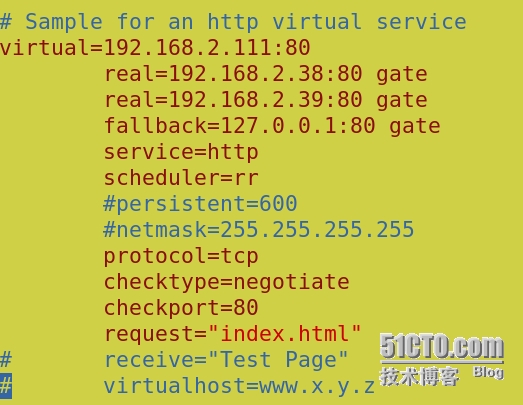
然后两台主备心跳都启动ldirectord
#/etc/init.d/ldirectord start
这时可能会出现一个问题 只要安装 yum install perl-IO-Socket-INET6 -y就OK了。
最后在两台realserver上安装httpd用来测试 并且在/var/www/html/下写入测试文件
echo `hostname` > /var/www/html/index.html 然后启动httpd
测试:
访问 http://192.168.2.111,看到页面在两个 realserver 上切换表示成功!
你也可以通过 ipvsadm -L 查看详细连接情况! OK!