Linux之手动编译属于自己的微型内核
对于Linux爱好者来说自己手动定做一个属于自己的Linux系统是一件多么酷的事。
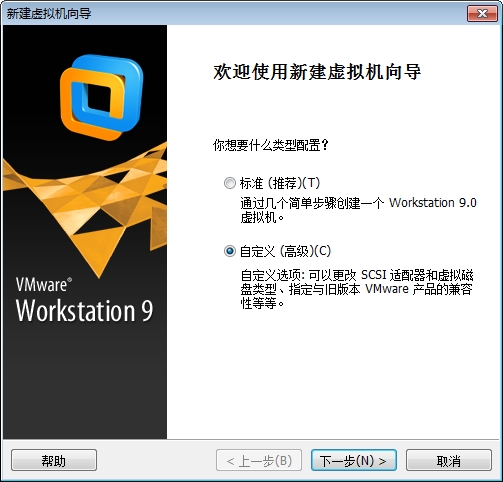
那么接下来我就给大家演示一下怎么制作一个属于自己的Linux吧。
为什么要制作属于自己的Linux呢?
我们目前用的Linux系统都是从网上或者官方那里得到的,是属于一种通用版,并不是根据自己的硬件特性定制的,不能最大的发挥Linux系统的优越性。因此这是不能满足我们这些Linux发烧友,制作属于自己的Linux让其发挥最大优越性能吧。
准备工作:我们制作的Linux是根据我们的硬件本身量身定制的,因此在制作前我们需要清楚的知道我们的目标主机(我们要安装微型Linux的主机)的硬件信息,制作系统前我们需要在宿主机(制作Linux的主机)上完成对系统的制作
整理一下心情让我们开始吧!!!
1、步骤规划
A、为内核提供CPU+Memory+Disk
B、提供文件系统
C、提供bash
D、提供init, --> bash
E、提供输入设备
F、提供TCP/IP协议栈,网络功能
一、查看设备硬件信息
[root@jsh ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo 查看CPU信息 processor: 0 vendor_id: GenuineIntel cpu family: 6 model: 42 model name: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-2450M CPU @ 2.50GHz 酷睿i5-2450M的 stepping: 7 cpu MHz: 2494.379 cache size: 3072 KB physical id: 0 siblings: 2 core id: 0 cpu cores: 2 双核心 apicid: 0 initial apicid: 0 fpu: yes fpu_exception: yes cpuid level: 13 wp: yes [root@jsh ~]# cat /proc/meminfo 查看内存信息 [root@jsh ~]# lspci 查看桥设备信息 [root@jsh ~]# lsusb 查看usb信息
下载内核源代码:www.kernel.org
我们此次实验使用的是3.13.6版本的内核源码
二、为目标磁盘创建文件系统
们制作的Linux系统首先是存放在宿主机的一块硬盘上,制作好后把此硬盘给目标机,因此我们首先需要在宿主机上添加一块硬盘然后对此硬盘创建文件系统。
添加硬盘步骤
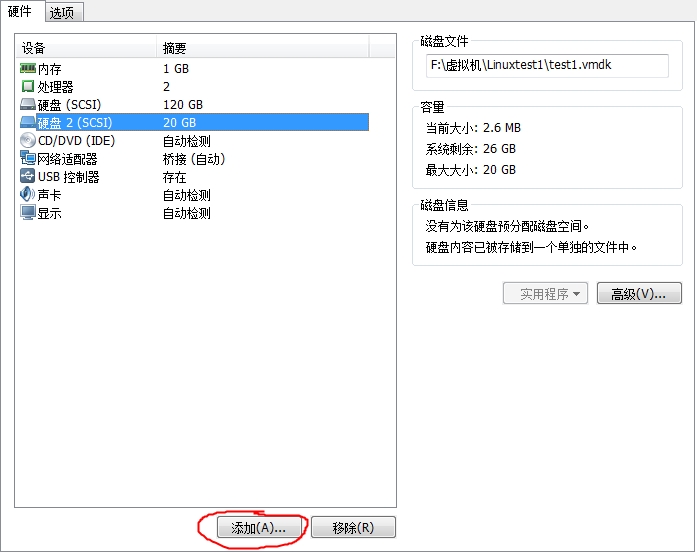
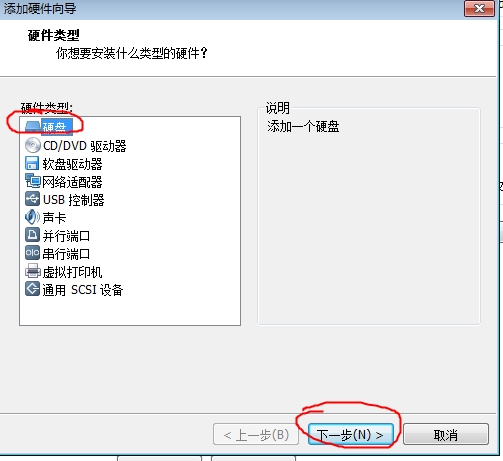
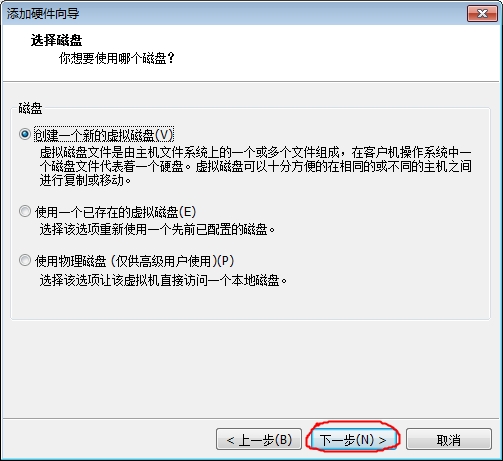
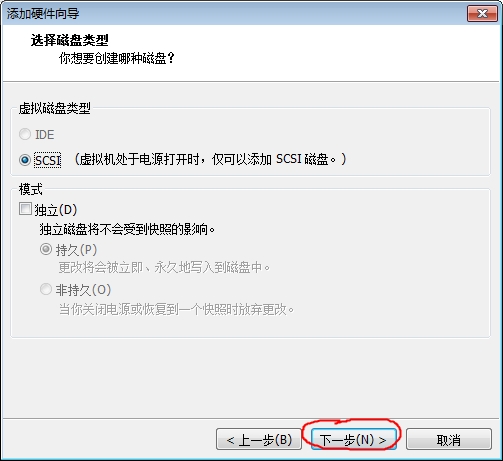
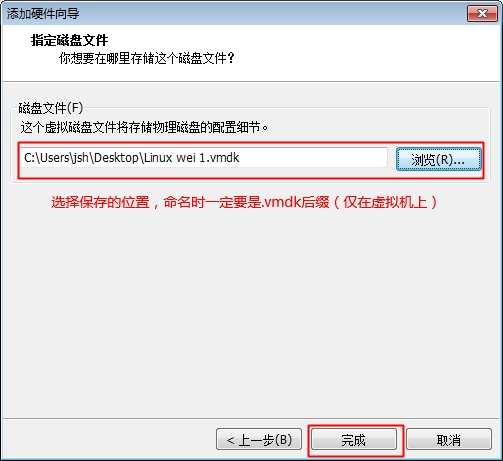
注:添加完要重新启动虚拟机才会识别此硬盘
添加完成后接下来就是创建文件系统了。
[root@jsh ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb 看好自己添加的是哪一块硬盘,此处我添加的是sbd
Command (m for help): n 创建分区
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
P 创建主分区
Partition number (1-4): 1 创建第一个主分区
First cylinder (1-2610, default 1):
Using default value 1
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-2610, default 2610): +50M
给第一个主分区分配50M空间用来存放内核
Command (m for help): n 再创建一个分区
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
P 创建主分区
Partition number (1-4): 2 创建第二个主分区
First cylinder (8-2610, default 8):
Using default value 8
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (8-2610, default 2610): +512M
给第二个主分区分配512M空间来存放根文件系统
Command (m for help): w 保存并退出
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
[root@jsh ~]# mke2fs -t ext4 /dev/sdb{1,2} 格式化sdb1和sdb2,文件系统为ext4
创建两个目录,让这两个分区各自挂载
[root@jsh ~]# mkdir /mnt/{boot,sysroot} 在/mnt下创建boot和sysroot两个目录
[root@jsh ~]# mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/boot/ 把sdb1挂载至/mnt/boot/
[root@jsh ~]# mount /dev/sdb2 /mnt/sysroot/ 把sdb2挂载至/mnt/sysroot/
为目标机提供根文件系统
[root@jsh ~]# cd /mnt/sysroot/
注:在此目录下我们有一个脚本,是用来复制程序以及程序所依赖的库文件用的脚本
给大家提供这个脚本的代码
[root@jsh sysroot]# vim bincp.sh
#!/bin/bash
#
target=/mnt/sysroot/
[ -d $target ] || mkdir $target
#!/bin/bash
#
target=/mnt/sysroot/
[ -d $target ] || mkdir $target
preCommand() {
if which $1 &> /dev/null; then
commandPath=`which --skip-alias $1`
return 0
else
echo "No such command."
return 1
fi
}
commandCopy() {
commandDir=`dirname $1`
[ -d ${target}${commandDir} ] || mkdir -p ${target}${commandDir}
[ -f ${target}${commandPath} ] || cp $1 ${target}${commandDir}
}
libCopy() {
for lib in `ldd $1 | egrep -o "/[^[:space:]]+"`; do
libDir=`dirname $lib`
[ -d ${target}${libDir} ] || mkdir -p ${target}${libDir}
[ -f ${target}${lib} ] || cp $lib ${target}${libDir}
done
}
read -p "Plz enter a command: " command
until [ "$command" == 'quit' ]; do
if preCommand $command ; then
commandCopy $commandPath
libCopy $commandPath
fi
read -p "Plz enter a command: " command
done
注:若复制此脚本的话那么之前创建的文件路径必须与我们之前创建的路径一样,否则此脚本执行时会报错的。
[root@jsh sysroot]# chmod +x bincp.sh 给此脚本一个执行权限 [root@jsh sysroot]# bash bincp.sh 执行此脚本 Plz enter a command: bash 复制bash程序 Plz enter a command: cat 复制cat命令 Plz enter a command: ls 复制ls命令 Plz enter a command: ifconfig 复制ifconfig命令 Plz enter a command: quit 退出 [root@jsh sysroot]#
为目标机提供根下的目录
[root@jsh sysroot]# mkdir -pv etc proc sys dev usr var tmp home root boot sbin
三、为目标磁盘安装grub
[root@jsh ~]# grub-install --root-directory=/mnt /dev/sdb [root@jsh ~]# ls /mnt/boot/ grub lost+found 此时我们就能看到boot目录下有一个grub目录
四、编译内核
然后我们给grub提供配置文件就行了,配置文件在内核源码中,因此我们需要解压内核源码
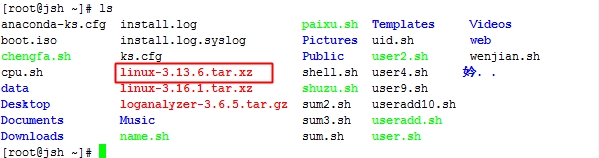
此内核是我之前下载好的
[root@jsh ~]# tar xf linux-3.13.6.tar.xz -C /usr/src/ 我们把它解压到/usr/src/下


[root@jsh linux]# make menuconfig 执行此命令,去选择我们用到的功能
注:执行此步骤会弹出一个图形化界面,如果你的系统不支持图形化操作请自行安装开发环境
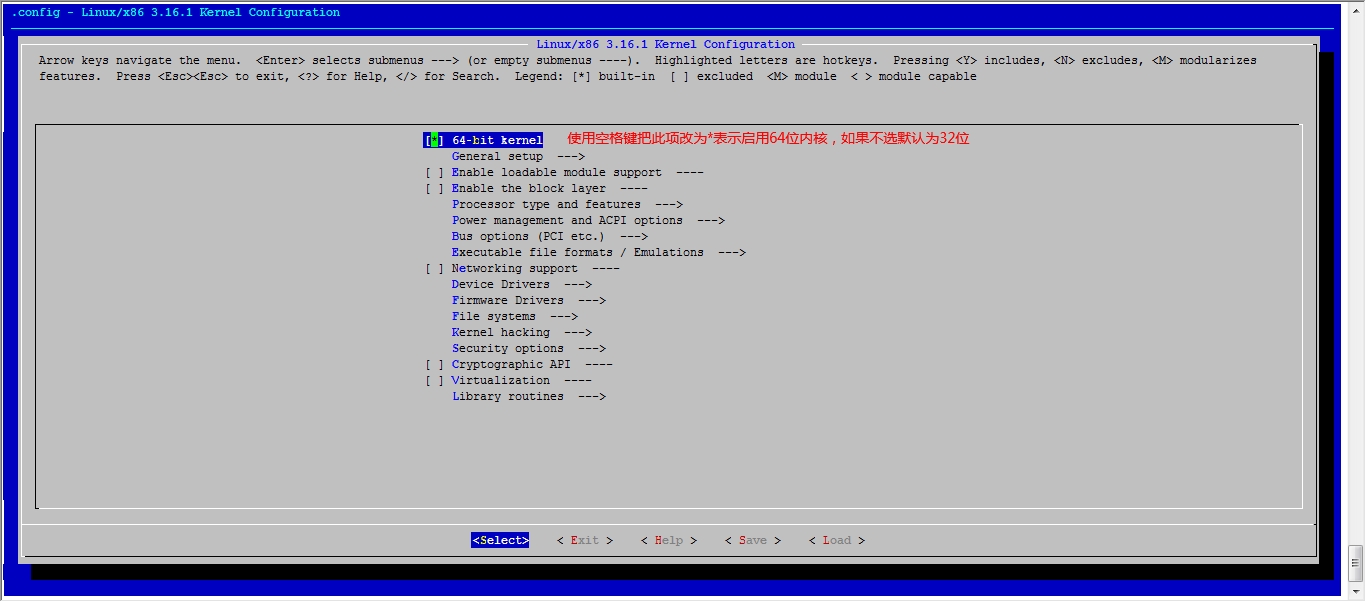
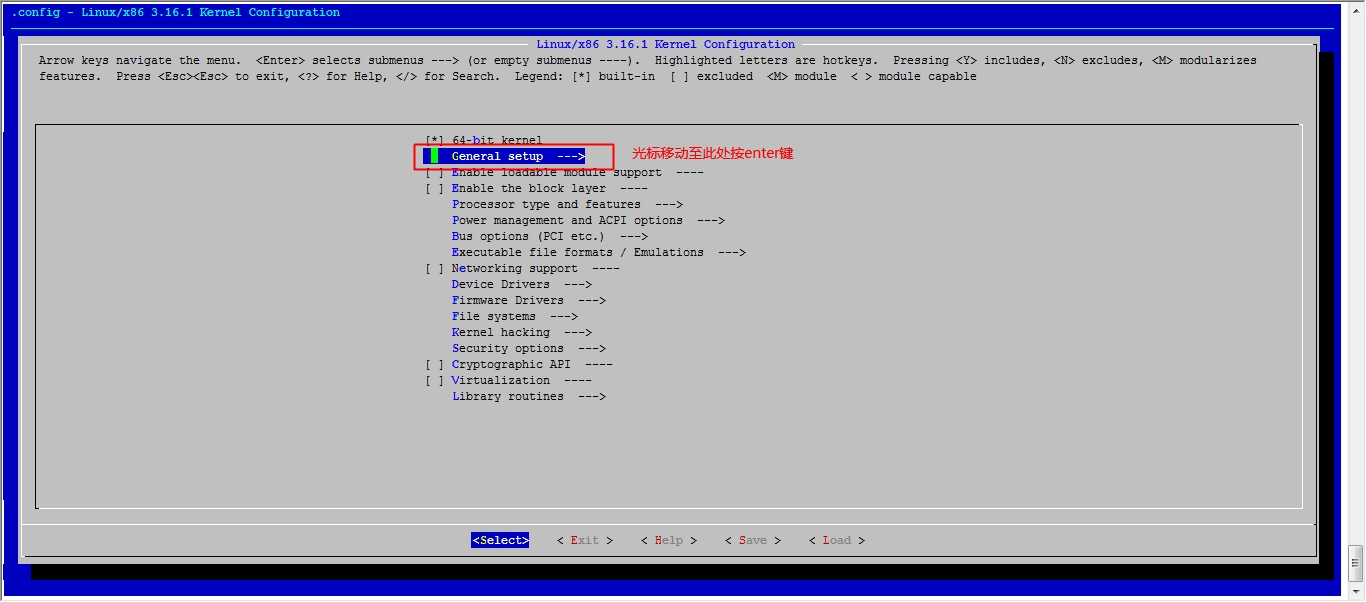
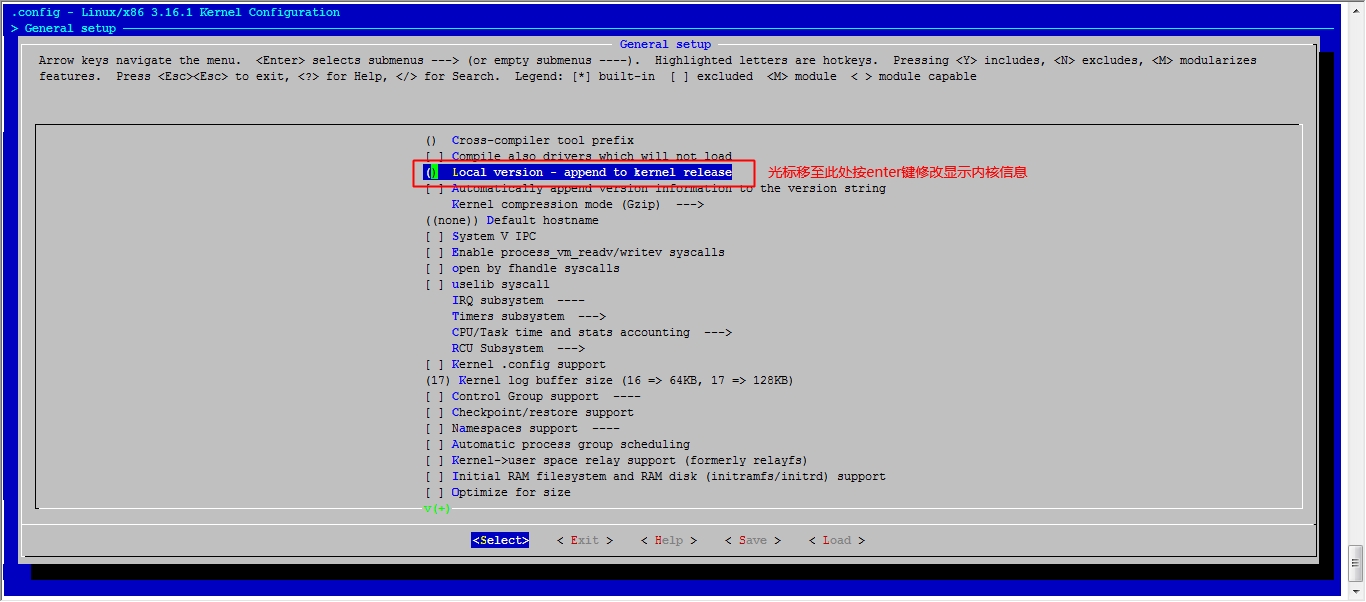
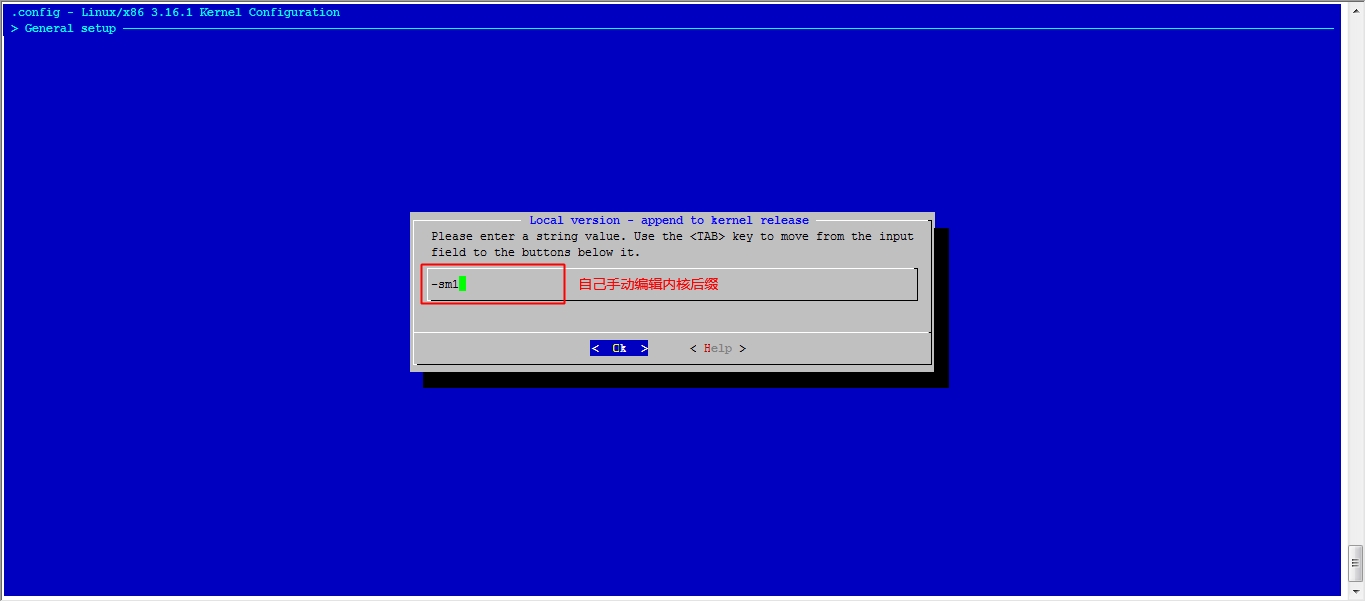
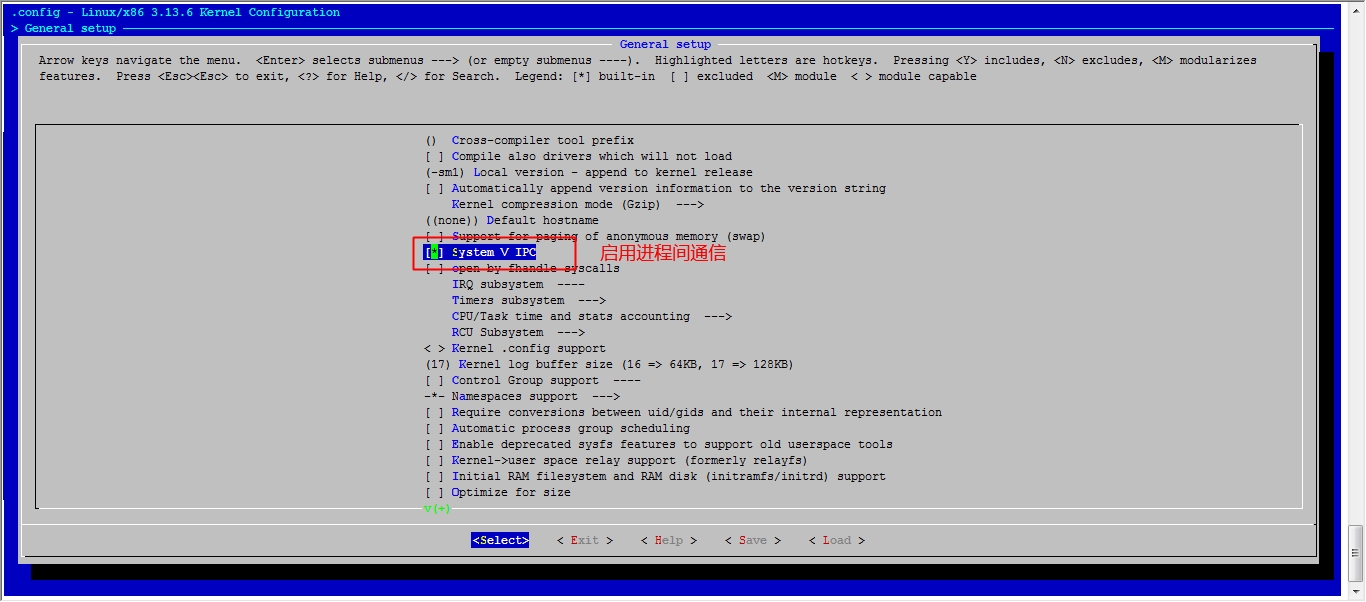
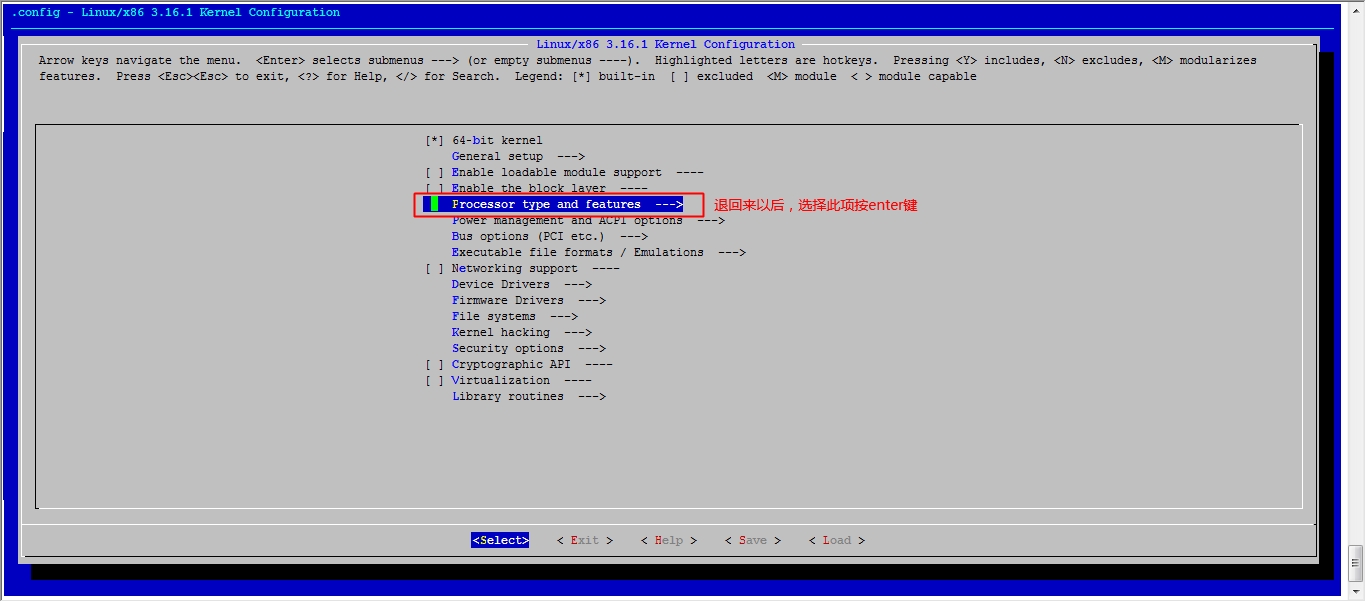
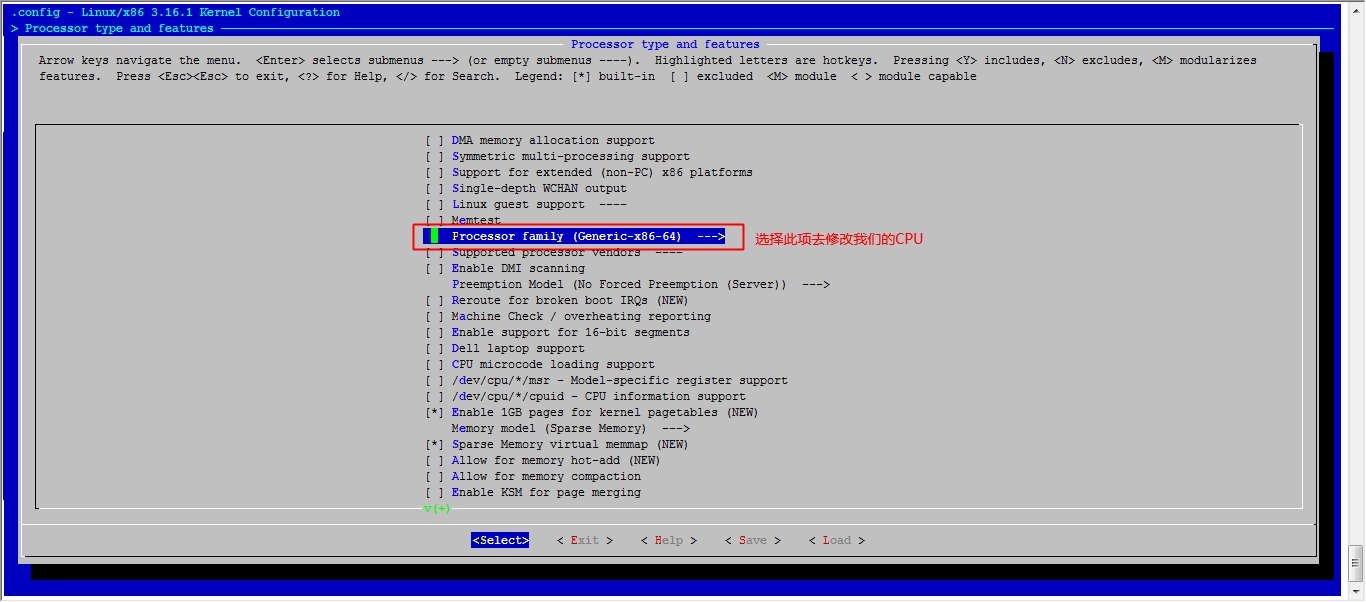
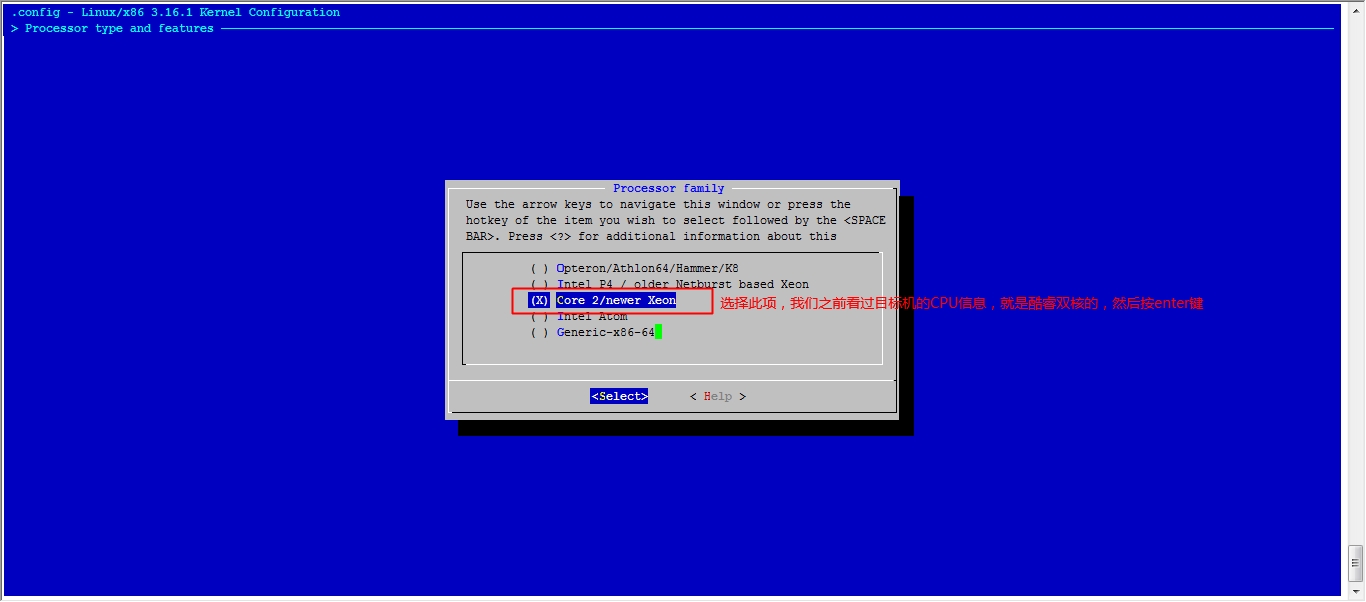
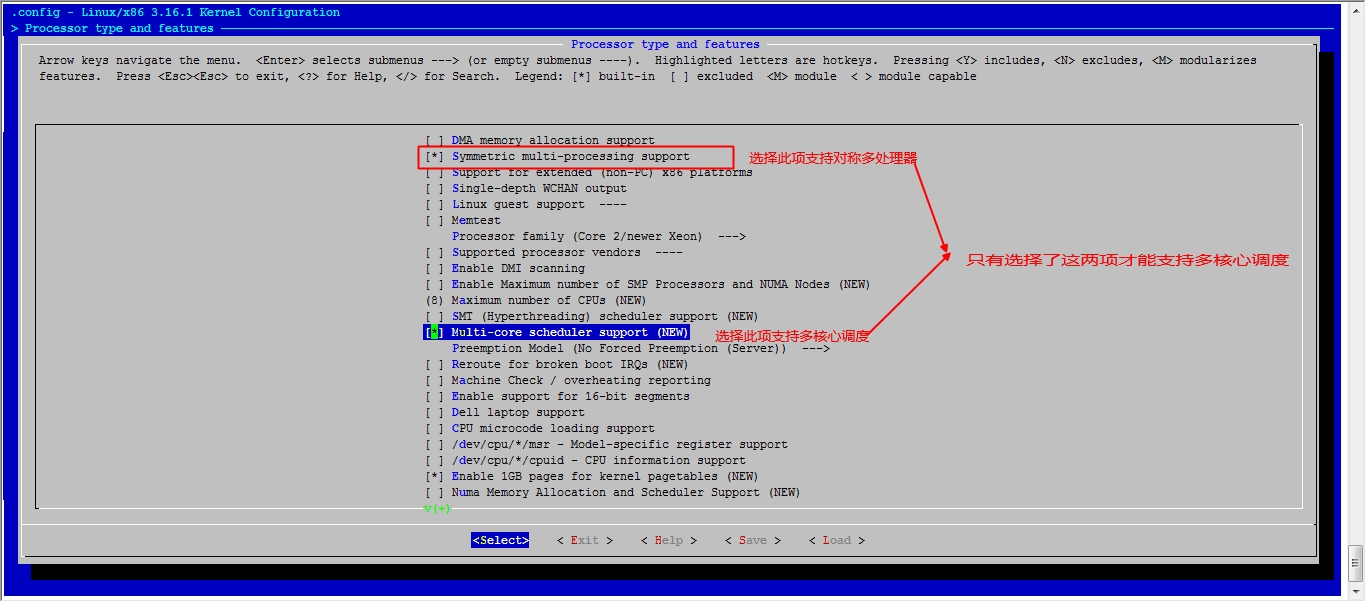
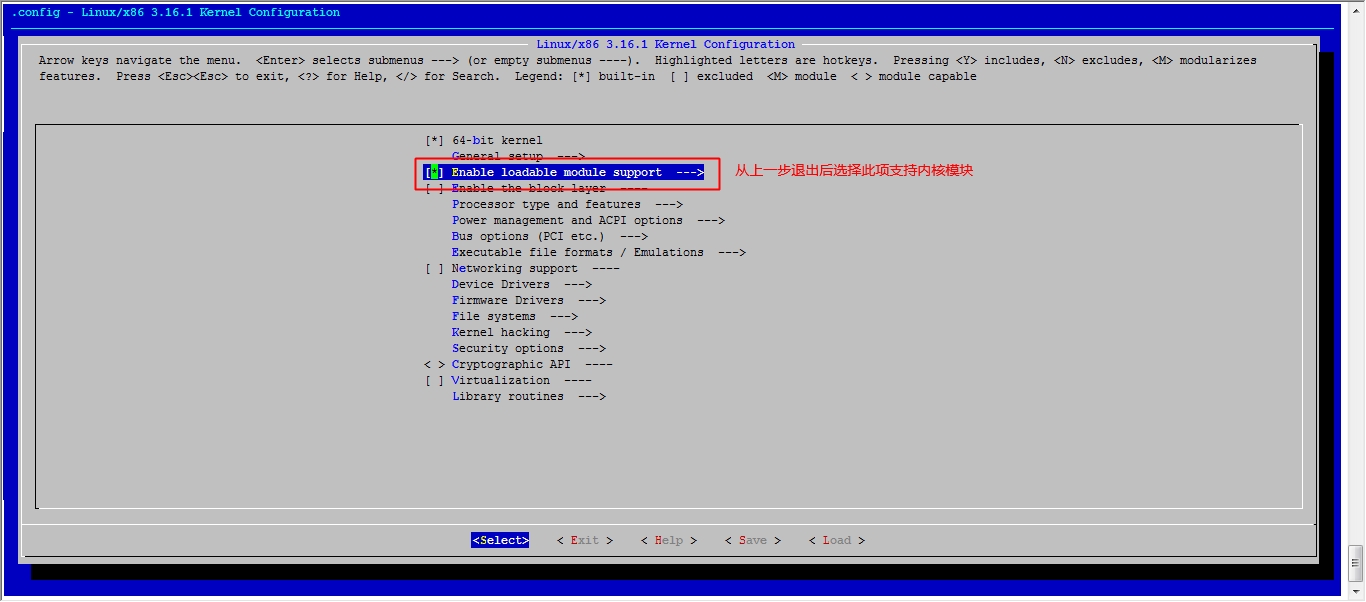
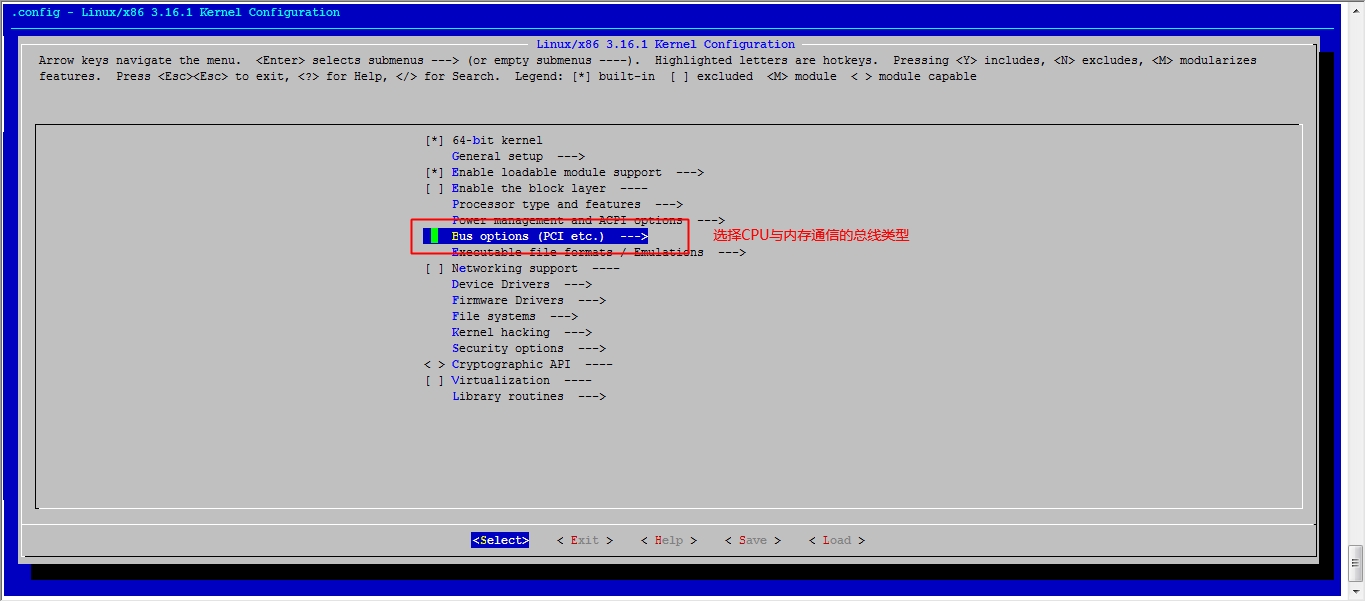
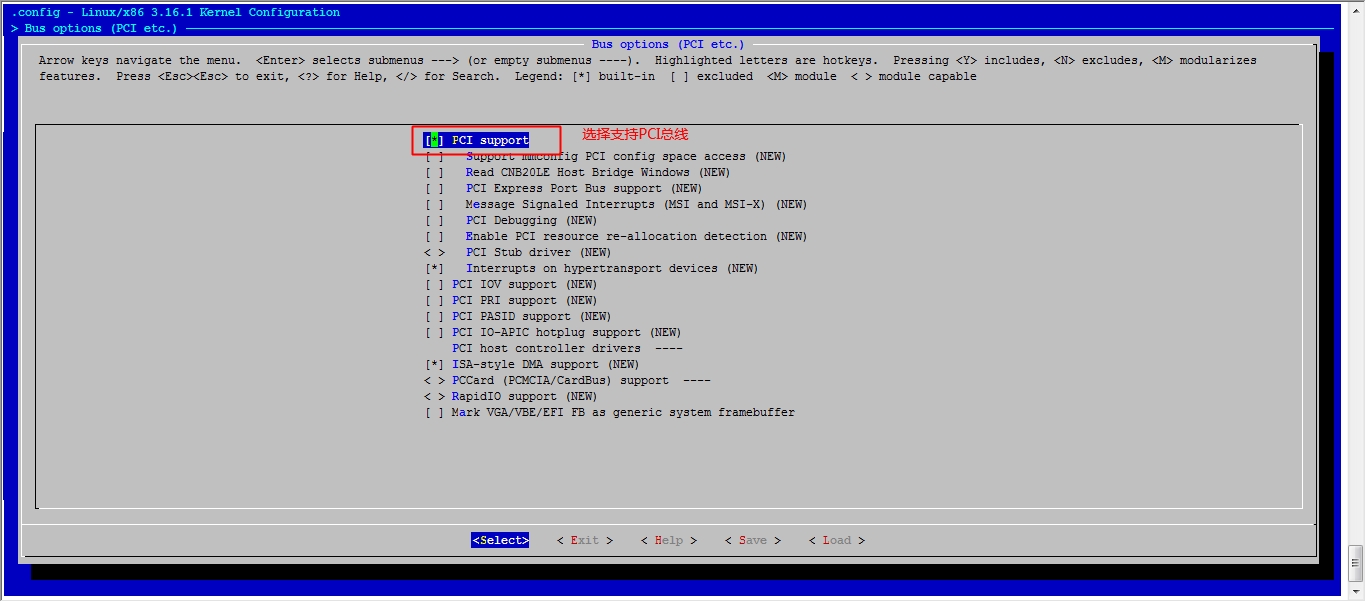
接下来我们就该选磁盘功能了
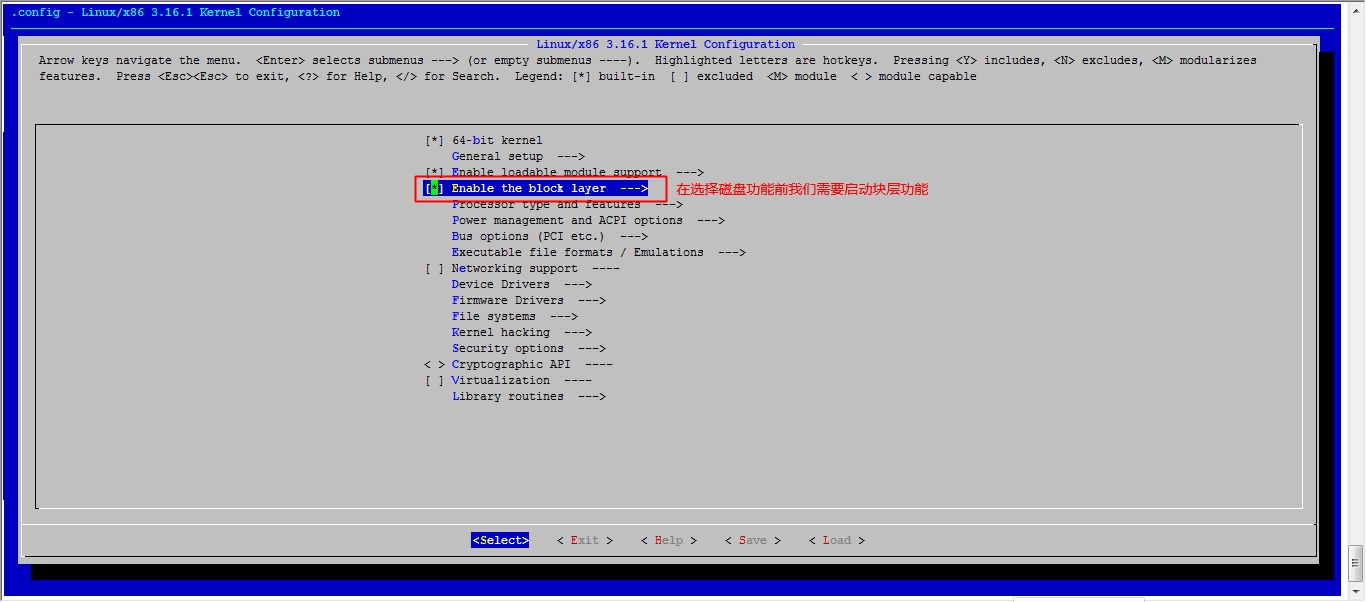
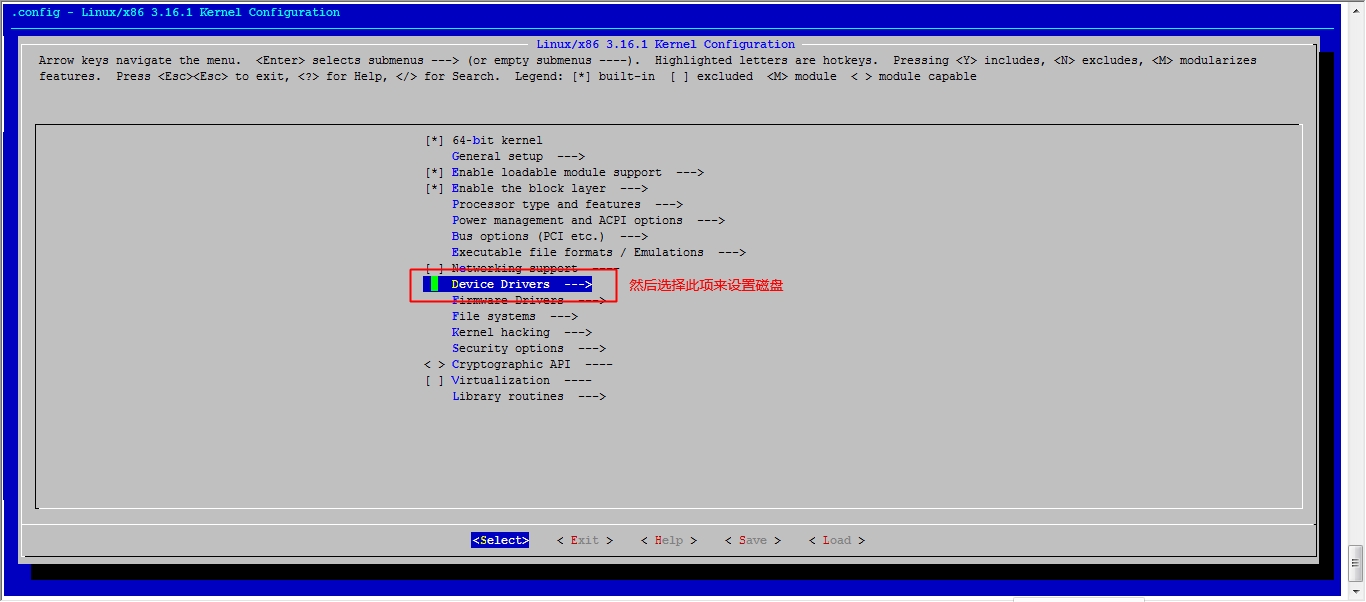
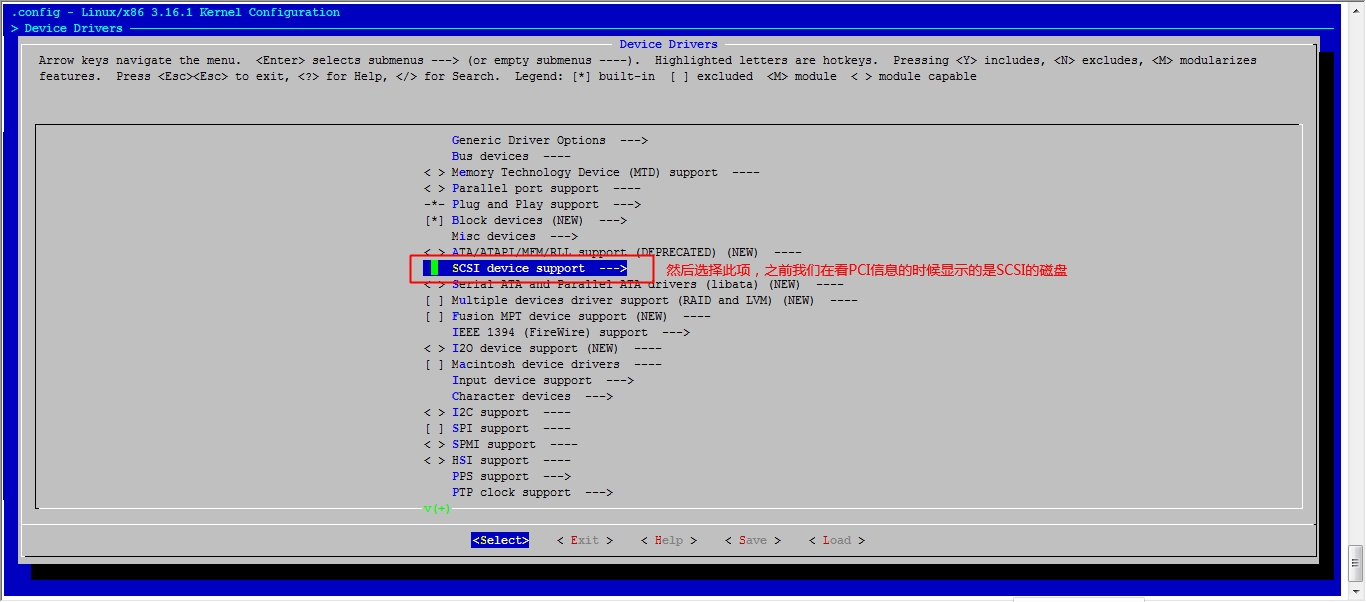
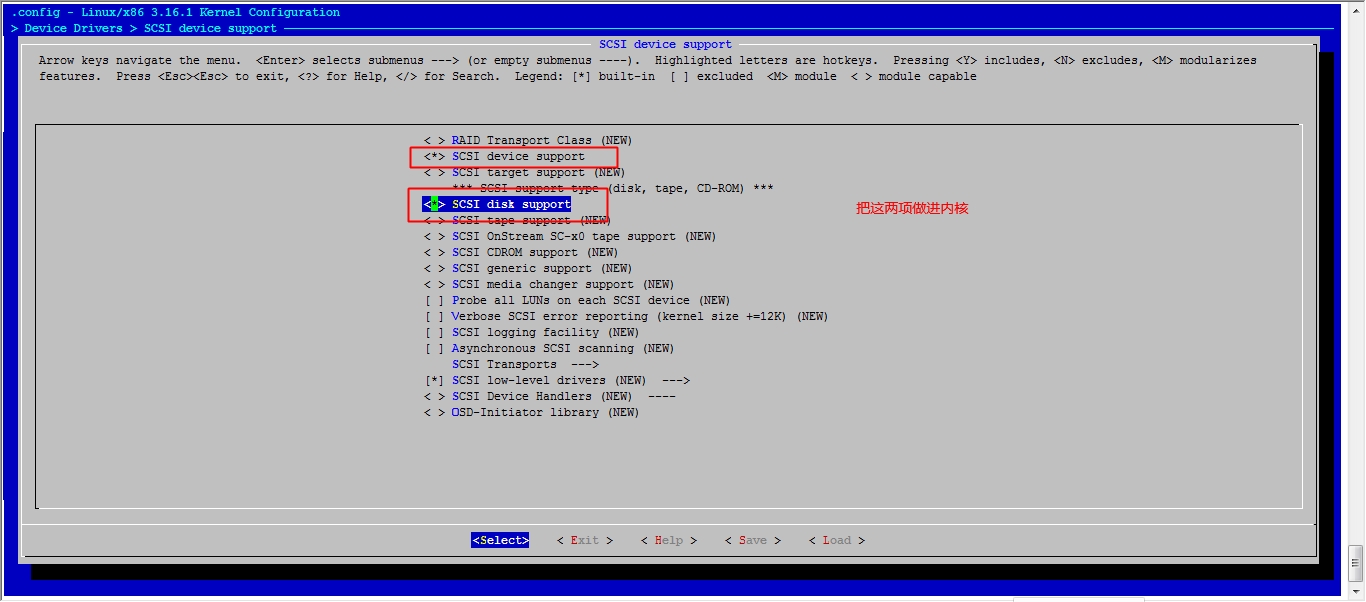
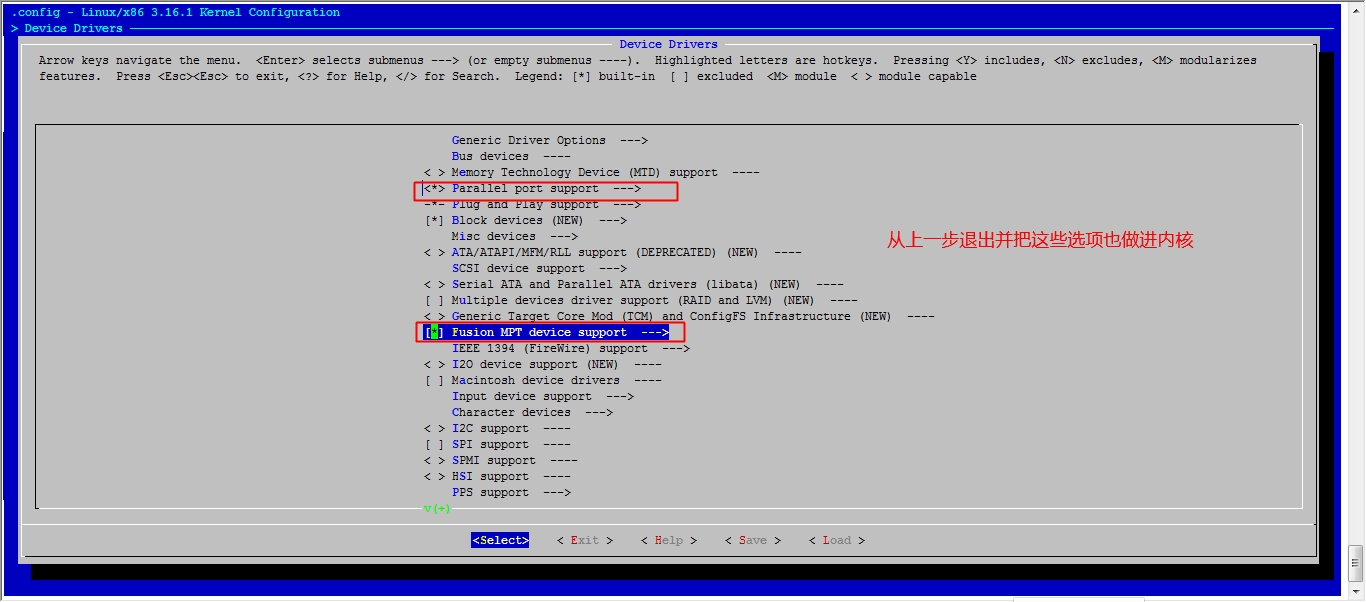
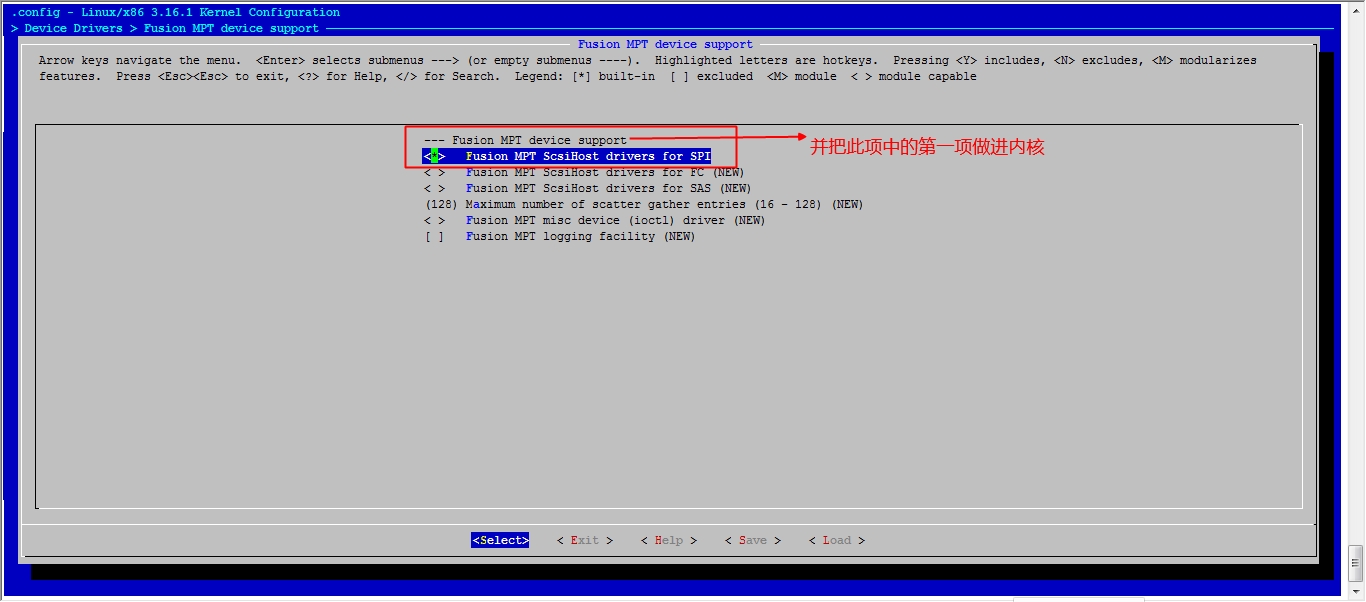
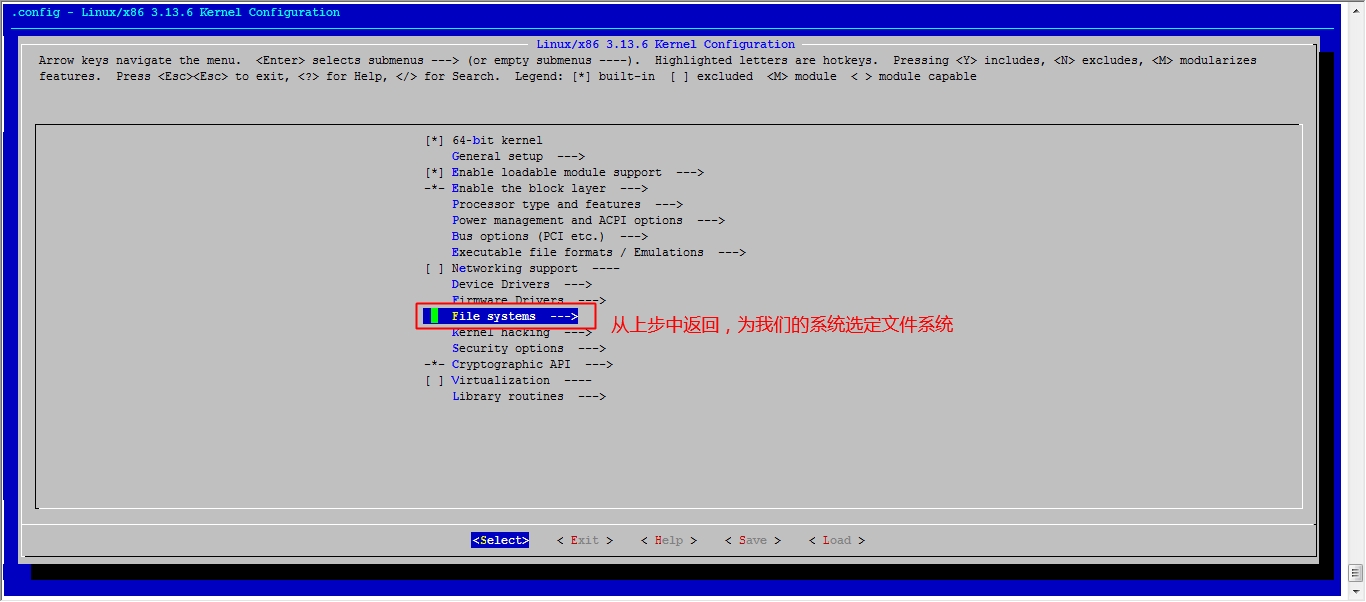
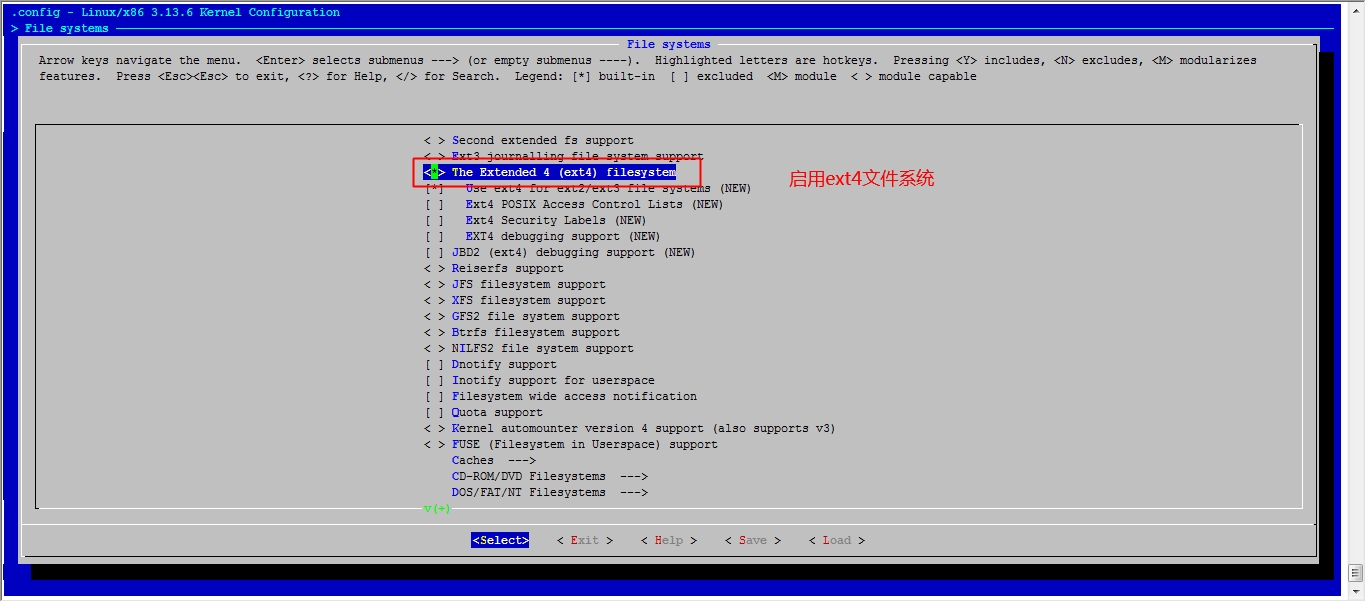
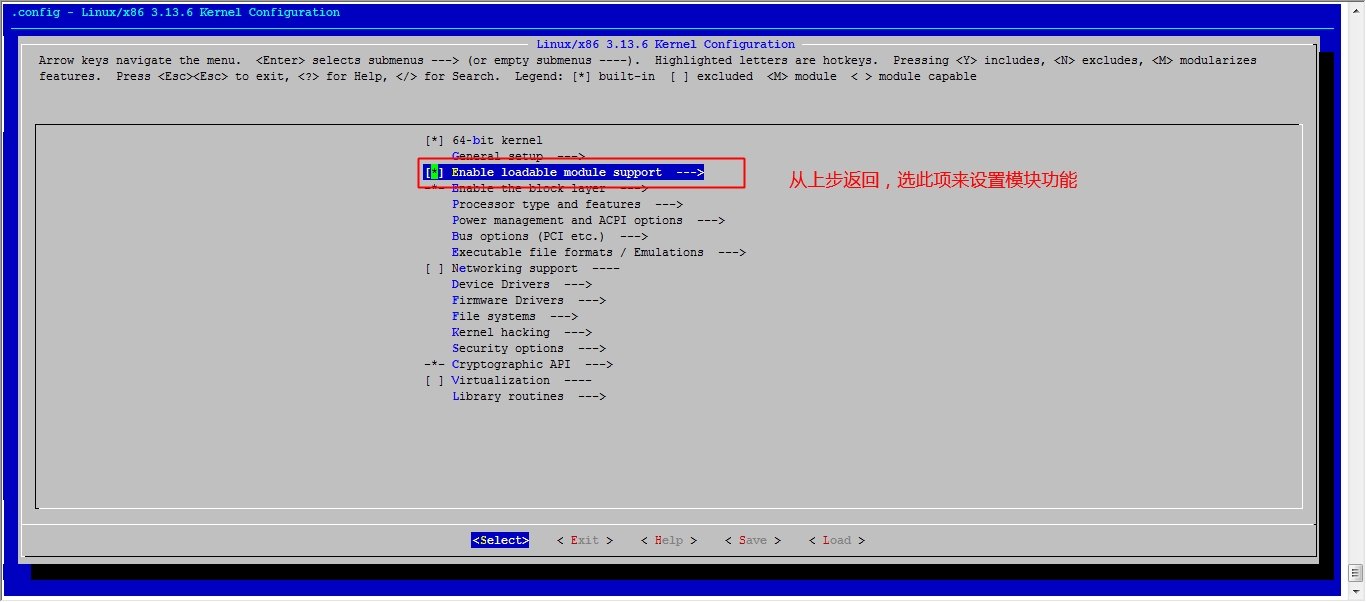
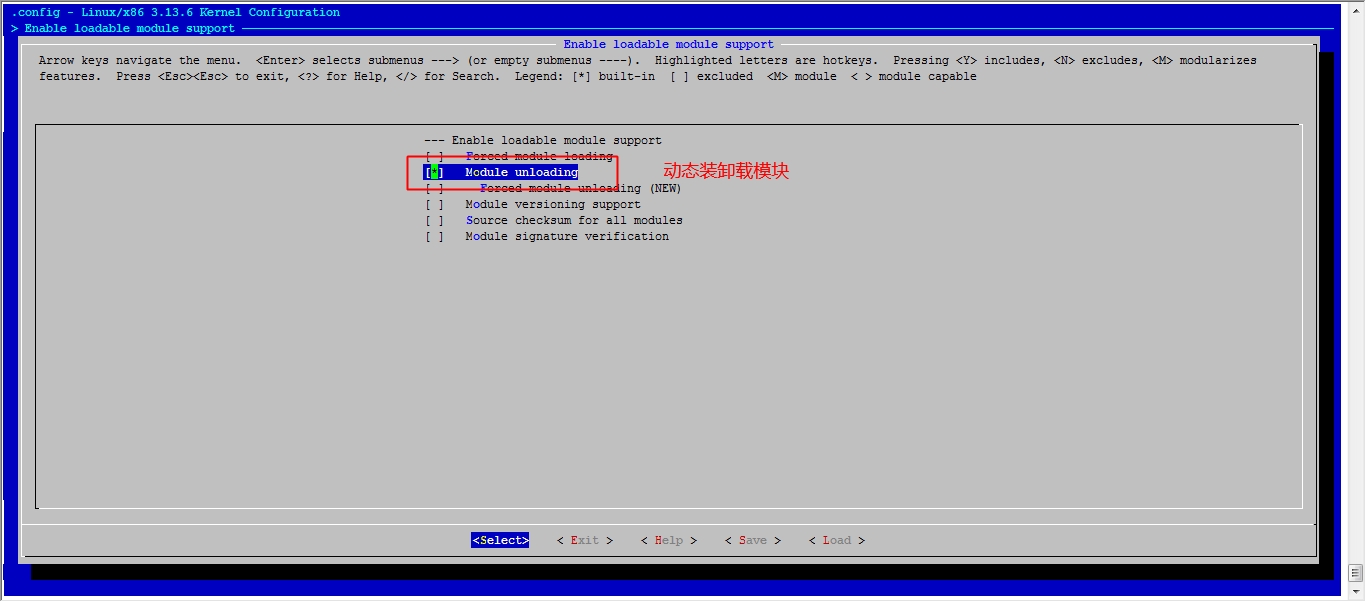
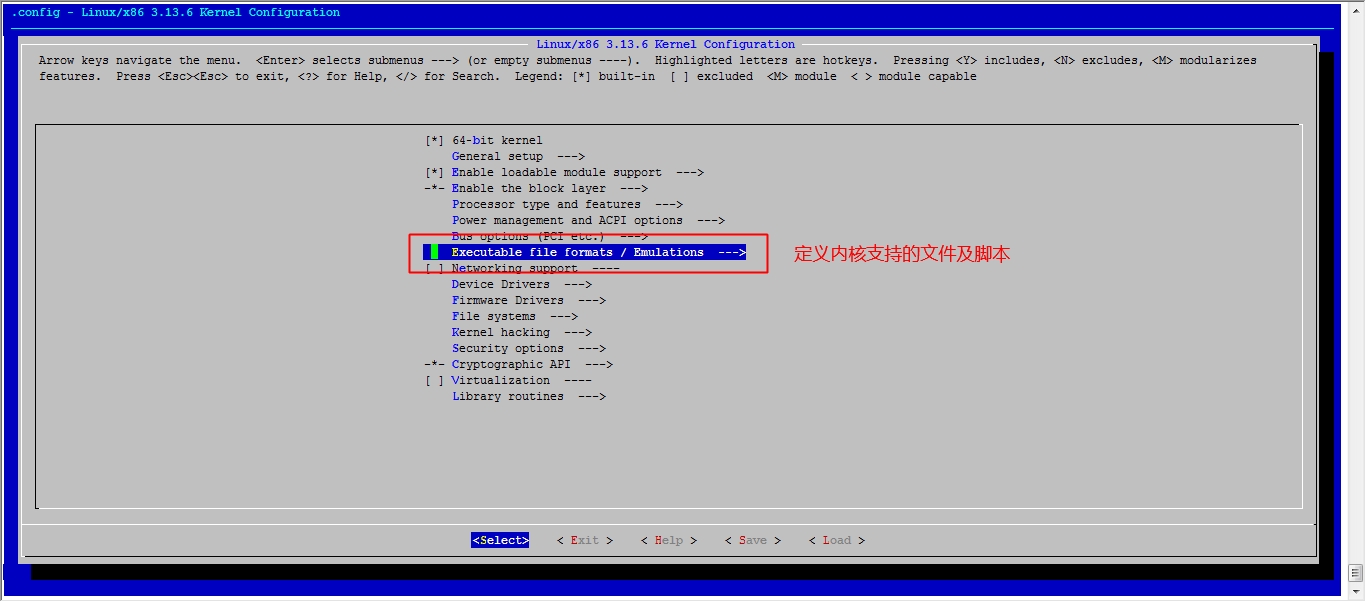
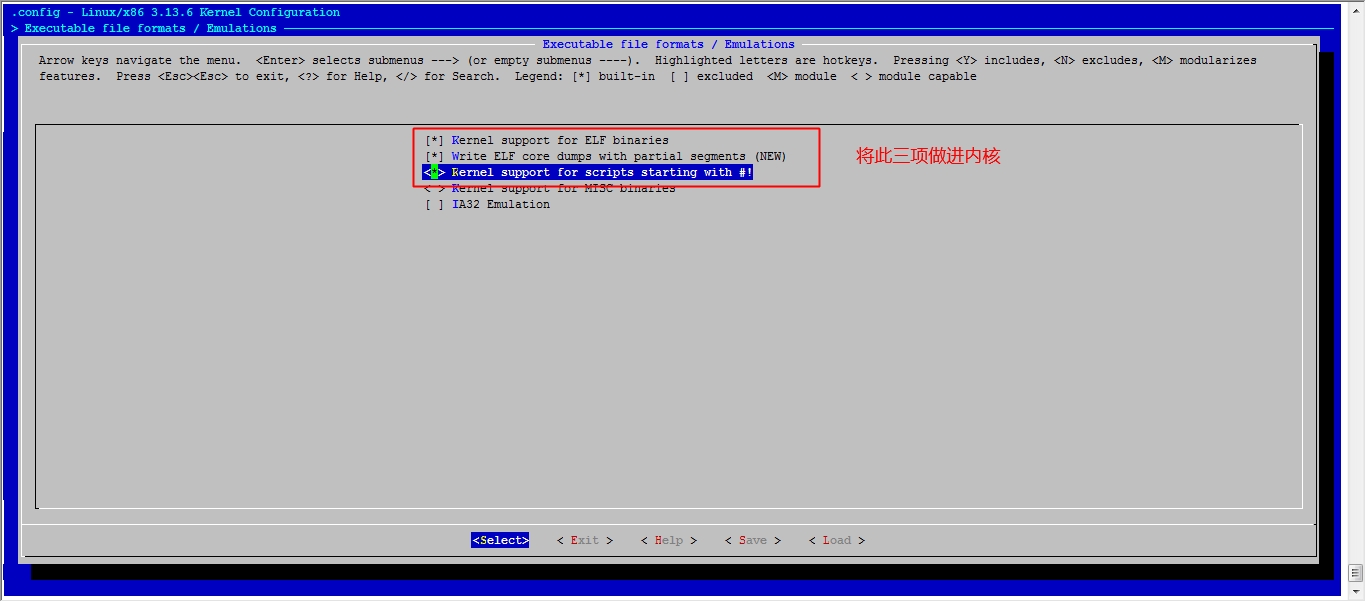
然后就可以保存退出了
[root@jsh linux]# make bzImage 编译内核
注:编译可能要花费一些时间,我们不防这会儿给提供一下grub配置文件
给grub提供配置文件
[root@jsh ~]# cd /mnt/boot/grub [root@jsh grub]# vim grub.conf timeout=5 default=0 title ce shi linux (3.13.6) root (hd0,0) kernel /bzImage ro root=/dev/sda2 init=/bin/bash
然后我们再来看一下已经编译好了
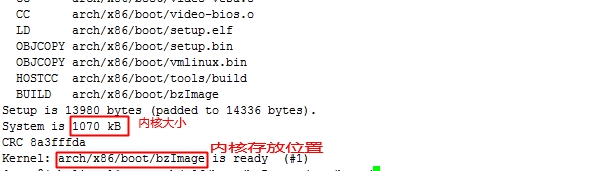
然后把编译好的内核放在我们之前创建的专门用于存放内核的目录下
[root@jsh linux]# cp arch/x86/boot/bzImage /mnt/boot/ [root@jsh linux]# sync 然后同步一下 [root@jsh boot]# chmod +x /mnt/boot/bzImage 给执行权限
然后把宿主机挂起创建目标主机就可以测试我们制作的系统是否能用了。
创建目标虚拟机
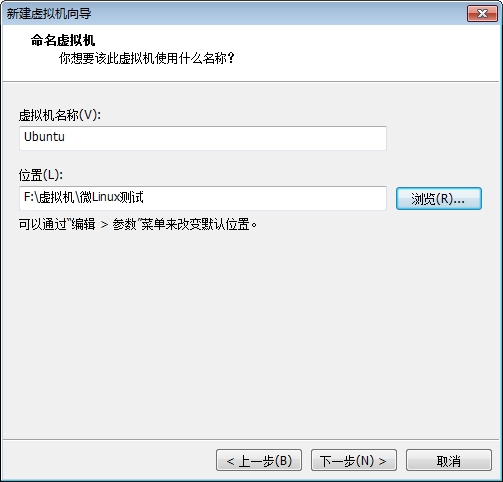
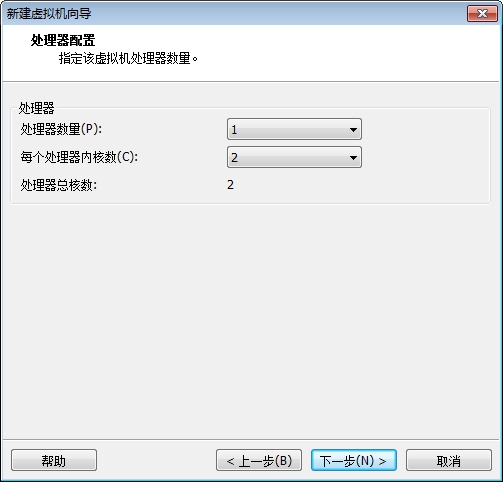
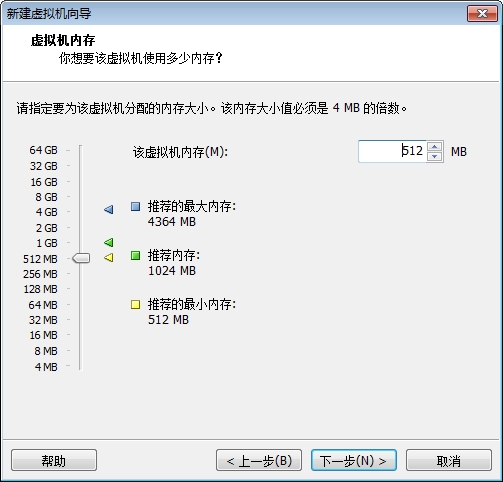
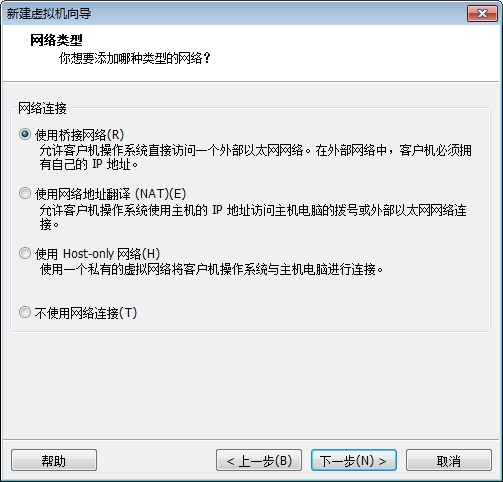
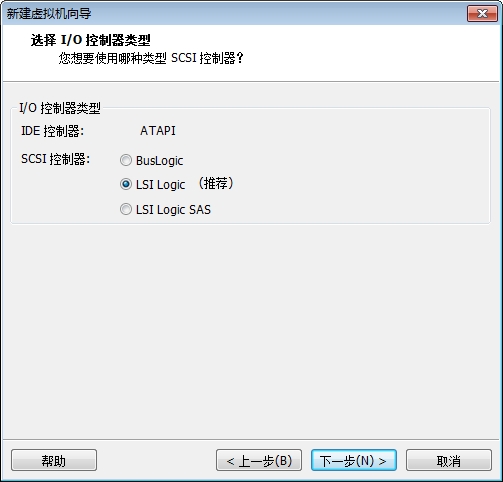
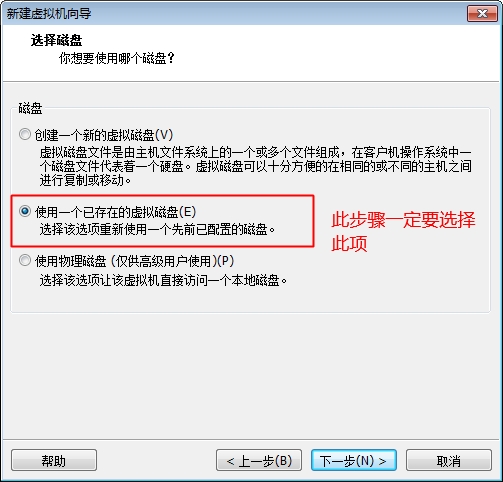
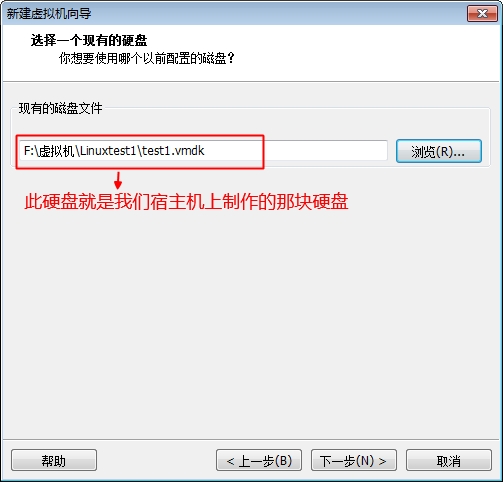
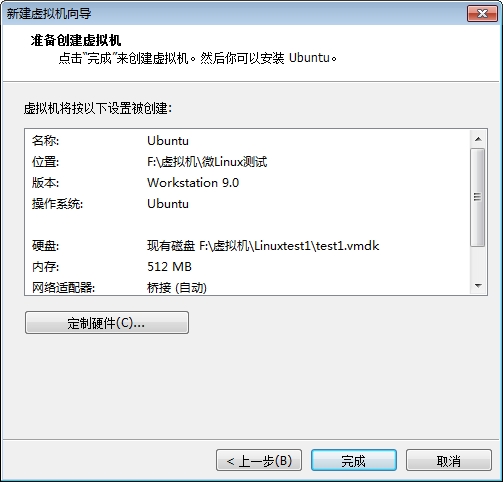
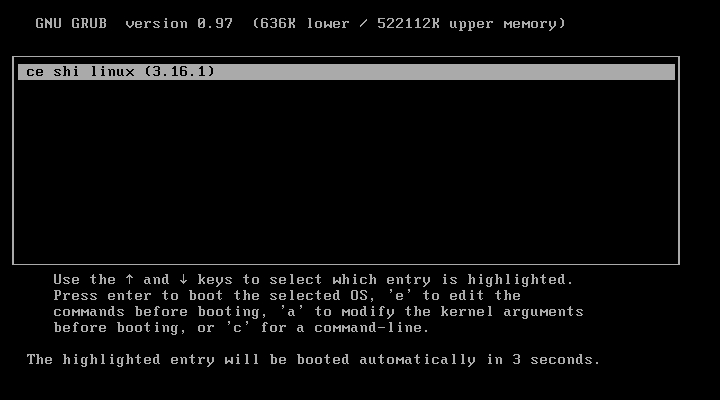
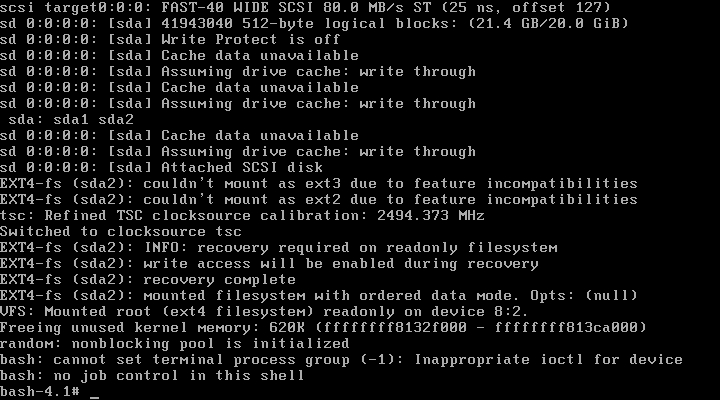
此时我们的系统已经能够正常的启动了,但是由于我们没有做好输入设备的驱动,这里的鼠标键盘是不能用的,接下来我们就开始配置内核的输入设备驱动吧。
首先把目标机关机,然后再次开启宿主机,(注:之前做目标机测试时我们要把宿主机挂起,现在我们再启用宿主机)
在宿主机下:
[root@jsh ~]# cd /usr/src/linux [root@jsh linux]# make menuconfig
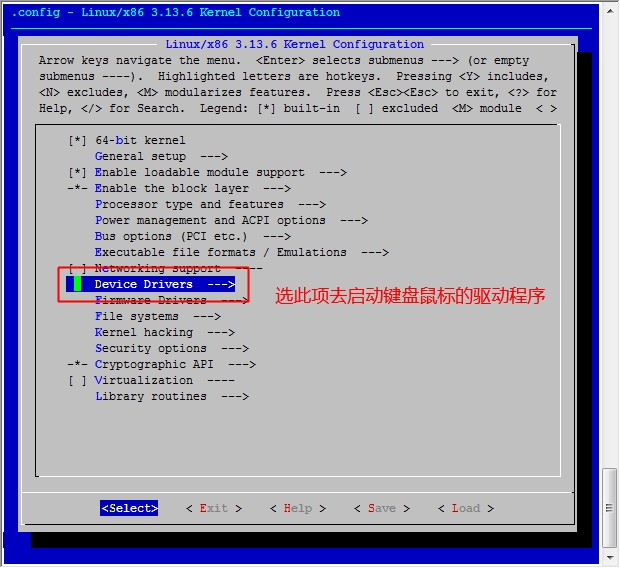
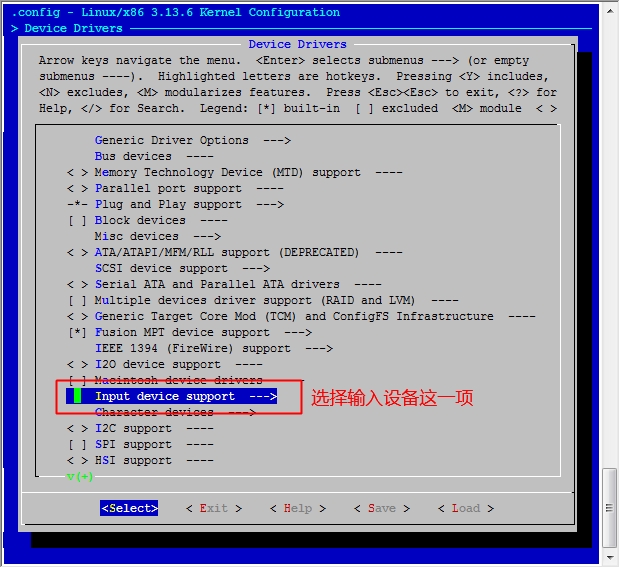
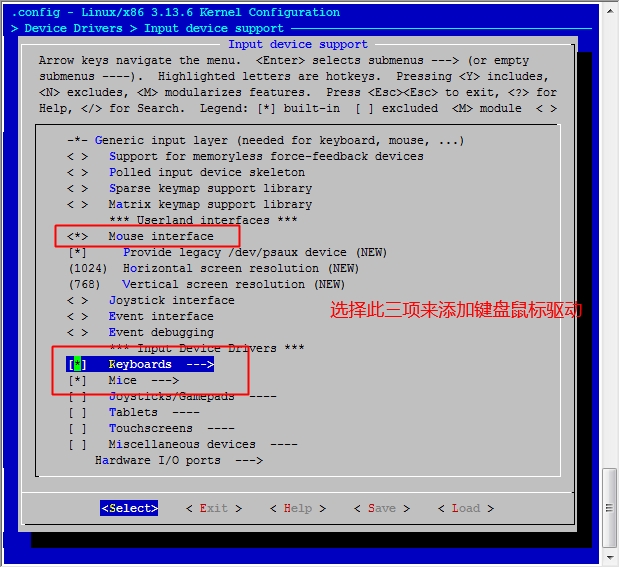
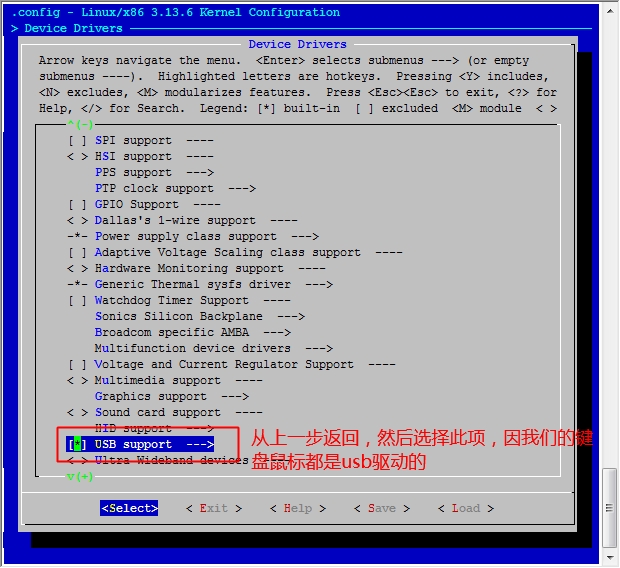
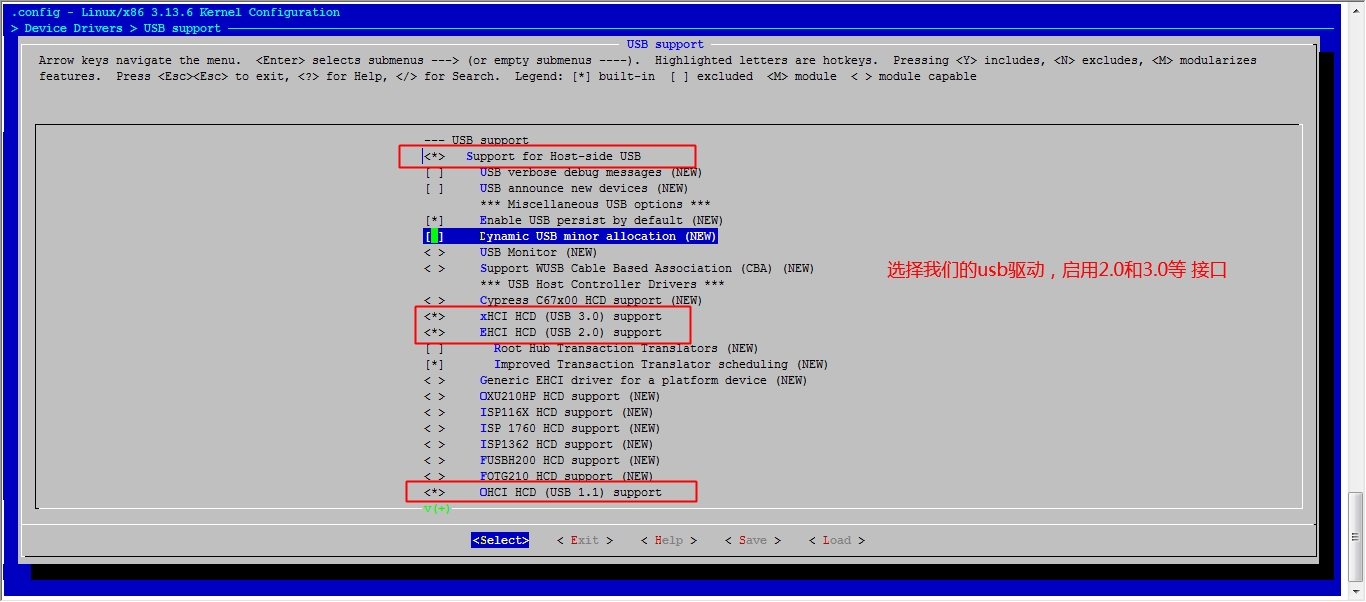
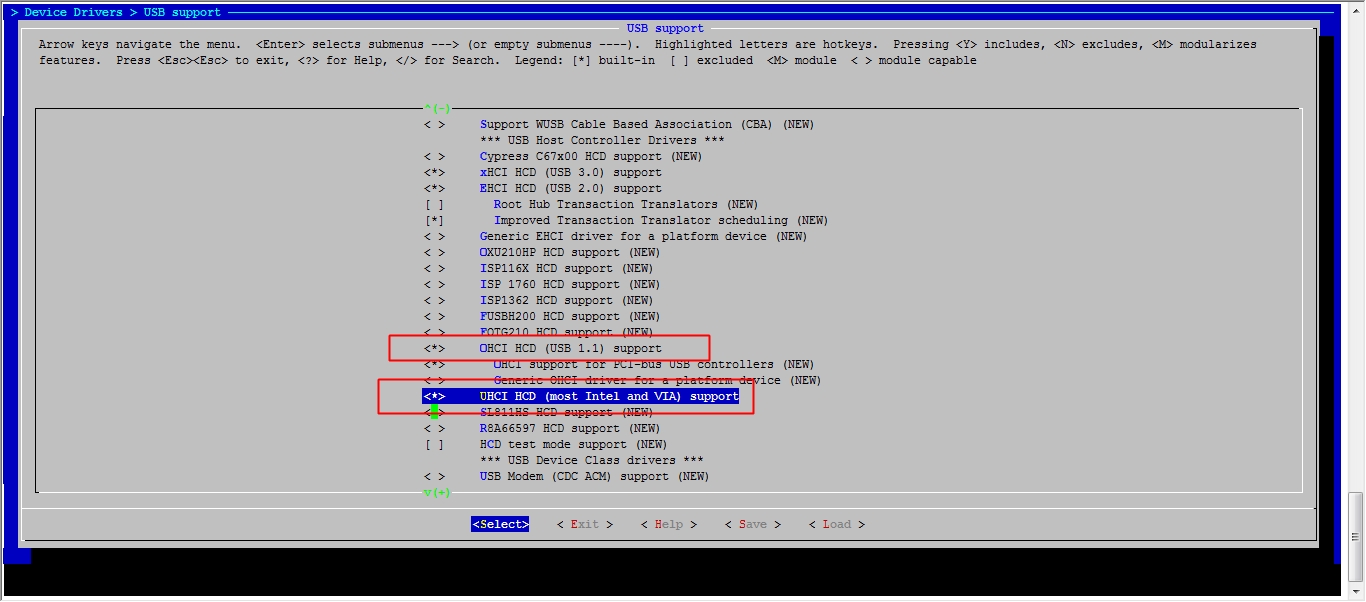
然后保存退出
[root@jsh linux]# make -j 3 编译 [root@jsh linux]# cp arch/x86/boot/bzImage /mnt/boot/ cp: overwrite `/mnt/boot/bzImage'? y 覆盖原文件 [root@jsh linux]# sync 同步
这就完成了键盘鼠标的驱动,如果这样启动的话还是有一个问题,我们需要让其启动时自动运行init,因此我们需要在/sbin下编辑文件
[root@jsh linux]# cd /mnt/sysroot/sbin [root@jsh sbin]# vim init #!/bin/bash echo -e "Welcom to \033[32mce shi\033[34mlinux." mount -n -t proc proc /proc mount -n -t sysfs sysfs /sys mount -n -o remount,rw /dev/sda2 /bin/bash [root@jsh sbin]# chmod +x init 给一个执行权限 [root@jsh sbin]# vim /mnt/boot/grub/grub.conf
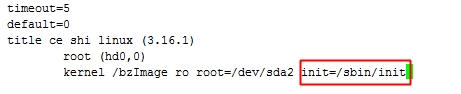
然后我们需要移植mount命令
[root@jsh ~]# bash bincp.sh bincp.sh这个脚本要实现创建 Plz enter a command: mount 移植mount命令 Plz enter a command: umount 移植umount命令 Plz enter a command: quit 退出 [root@jsh ~]#
好了,这样我们就可以启动一下试试了,首先挂起宿主机。然后开启目标机
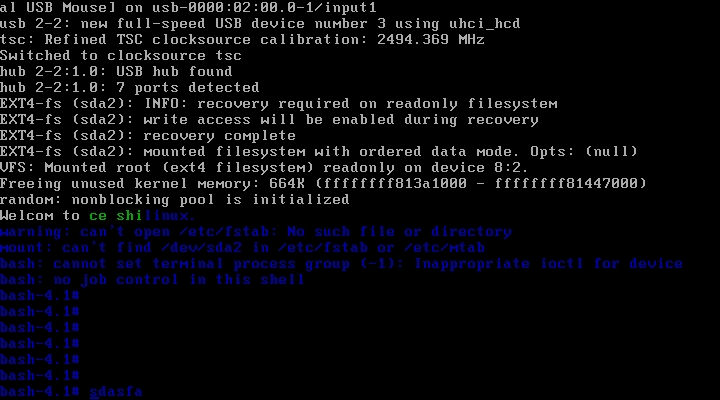
Ok这样就启动了,哈哈只不过字体颜色设置的有点奇怪,嘿嘿。
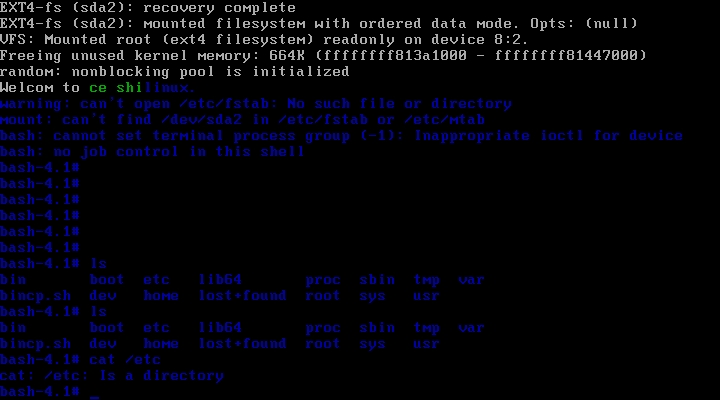
包括我们移植的命令也可以用哦,是不是有点小激动呢,但是总觉得怪怪的,跟我们的正常的系统还是有很多的不一样。
但是这样还有一个问题,我们可以看一下我们的设备文件

我们的dev下是空的,那怎么识别我们的sda1和sda2呢?
注:此时各设备文件是在内核的内存中的
我们还回到宿主机上
[root@jsh ~]# cd /usr/src/linux [root@jsh linux]# make menuconfig
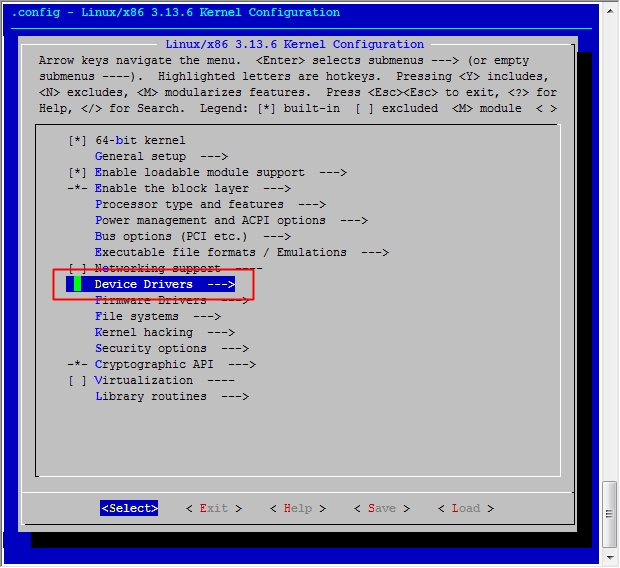
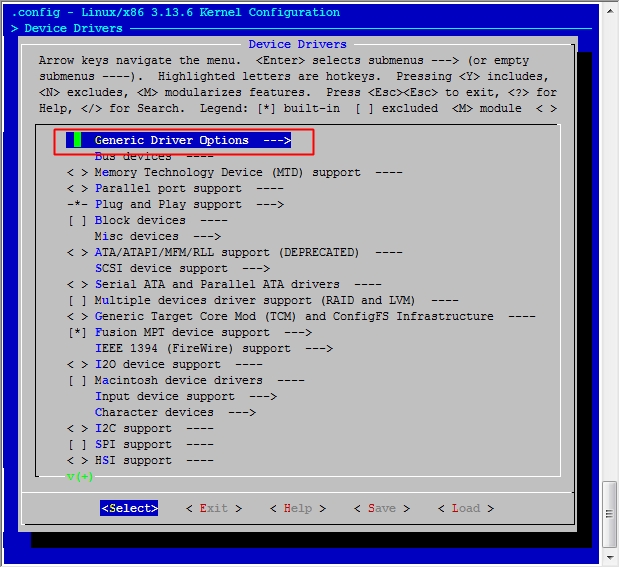
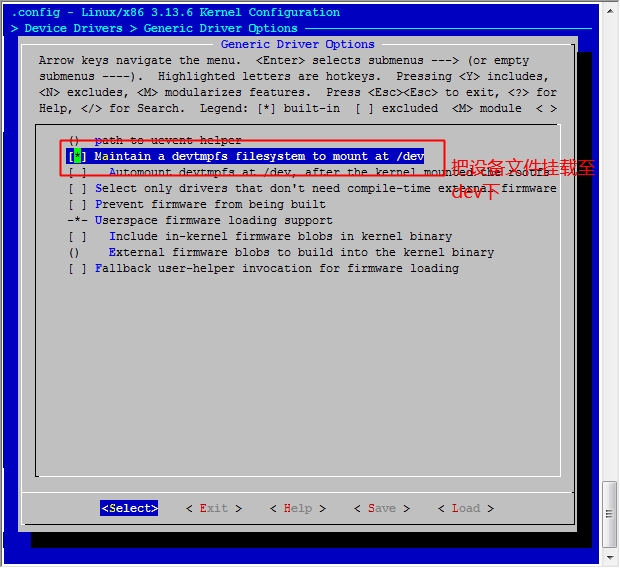
然后保存退出
[root@jsh linux]# make -j 3 [root@jsh linux]# cp arch/x86/boot/bzImage /mnt/boot/ cp: overwrite `/mnt/boot/bzImage'? y
编辑文件手动挂载
[root@jsh ~]# vim /mnt/sysroot/sbin/init
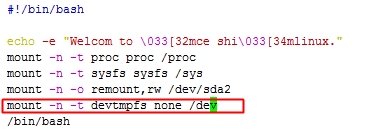
添加红色方框内容
好我们再来试一下,看看上边的设备文件有没有挂载上,首先挂起宿主机,然后再开启目标机。
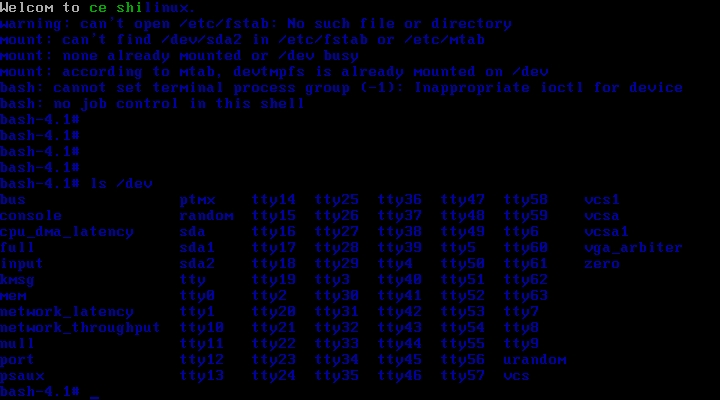
OK!成功了,呵呵怎么样是不是小有成就呢。
至此,我们的六个步骤中的前五个步骤都已经完成了,接下来就是最后一步了,配置网络功能。
在宿主机下
[root@jsh ~]# cd /usr/src/linux [root@jsh linux]# make menuconfig
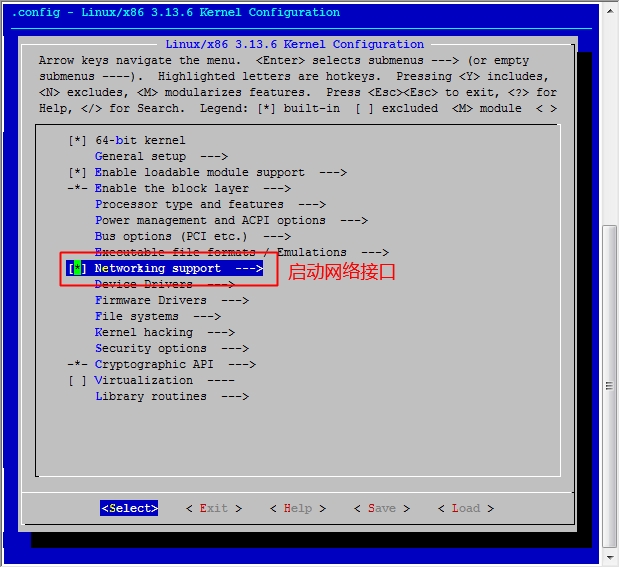
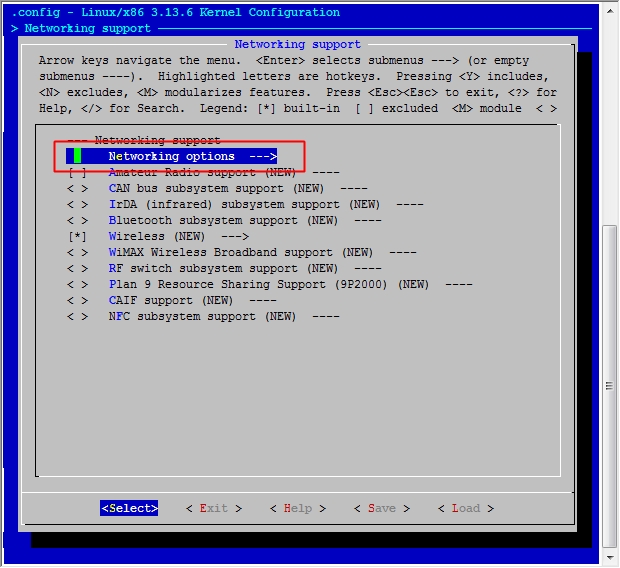
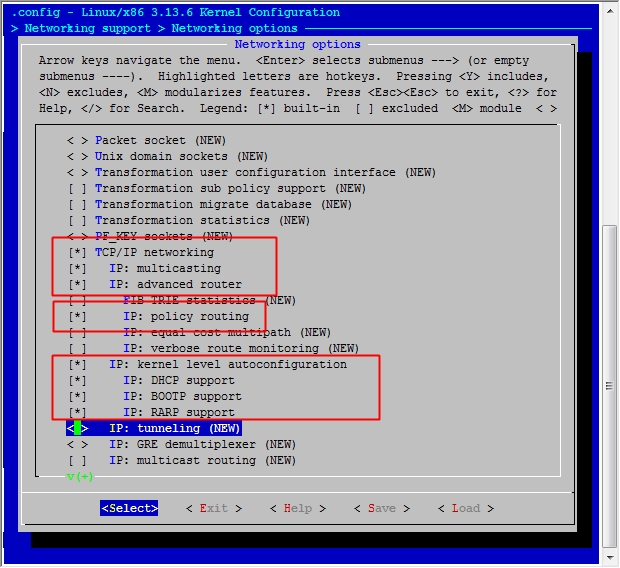
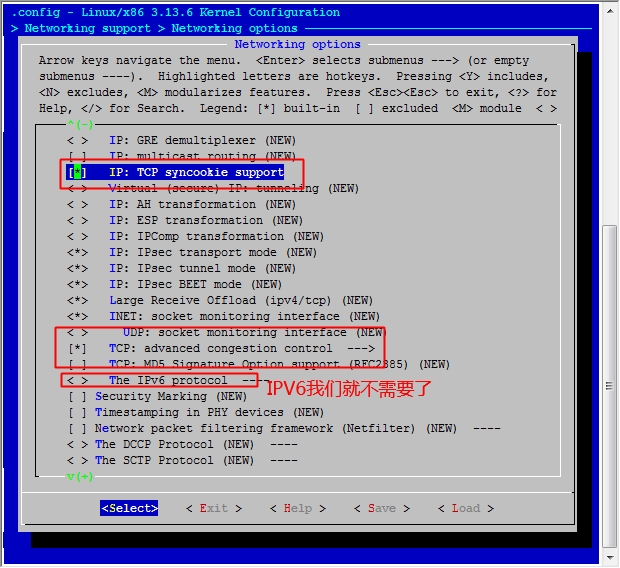
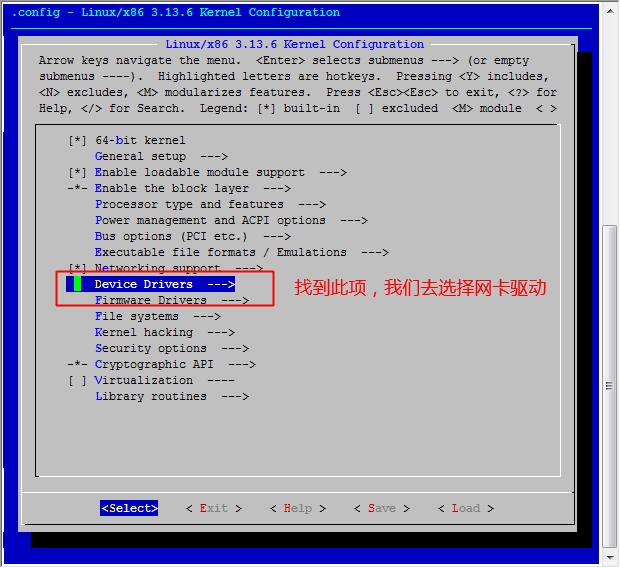
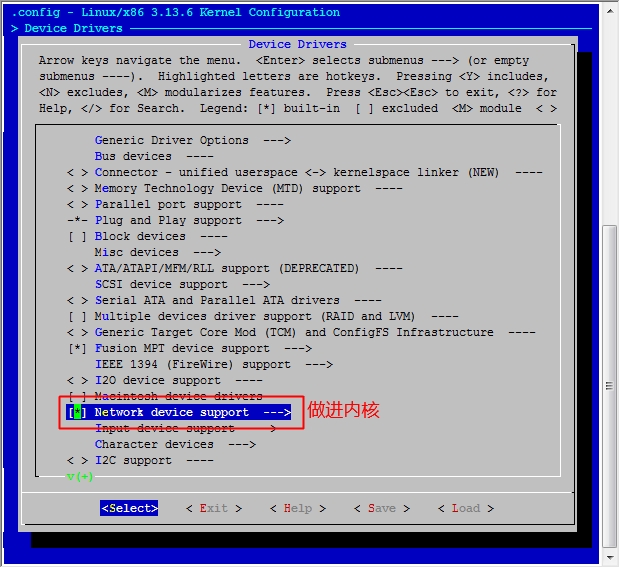
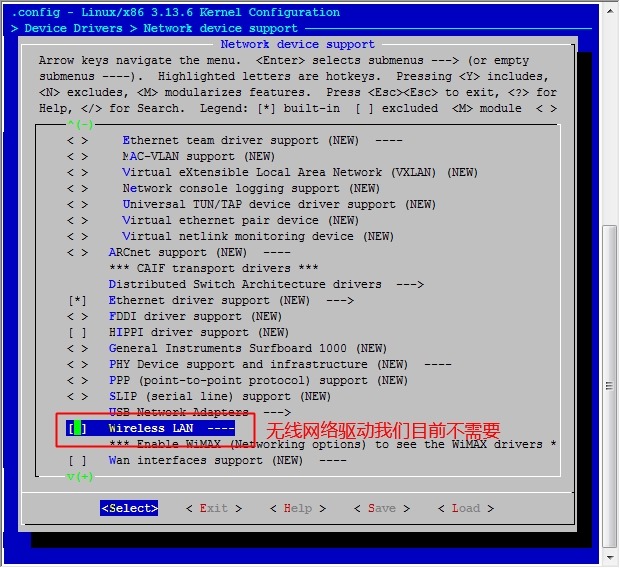
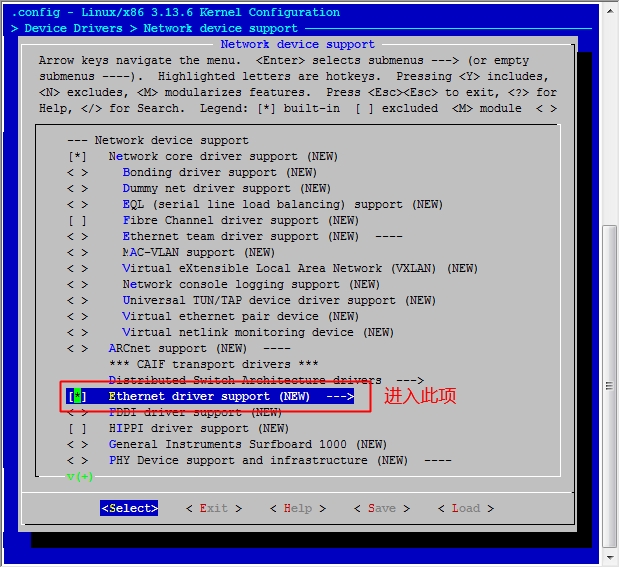
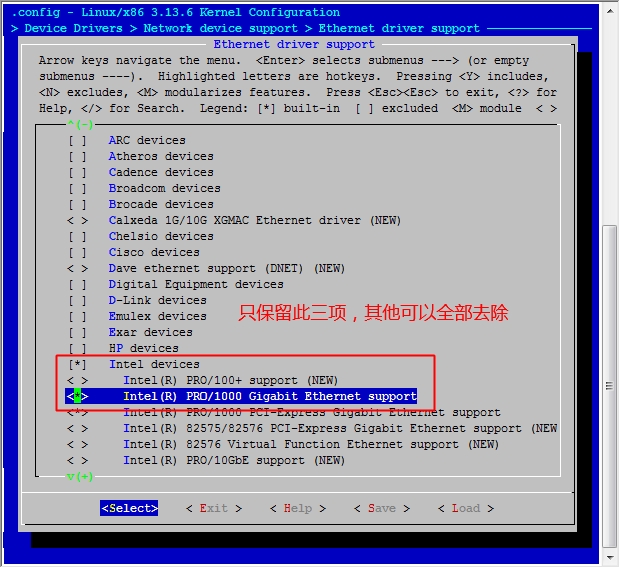
然后保存退出
[root@jsh linux]# make -j 3 [root@jsh linux]# cp arch/x86/boot/bzImage /mnt/boot/ cp: overwrite `/mnt/boot/bzImage'? y
移植一下网络相关的命令
[root@jsh ~]# bash bincp.sh Plz enter a command: route Plz enter a command: netstat Plz enter a command: ping Plz enter a command: quit
然后就能挂起宿主机,启动目标机了
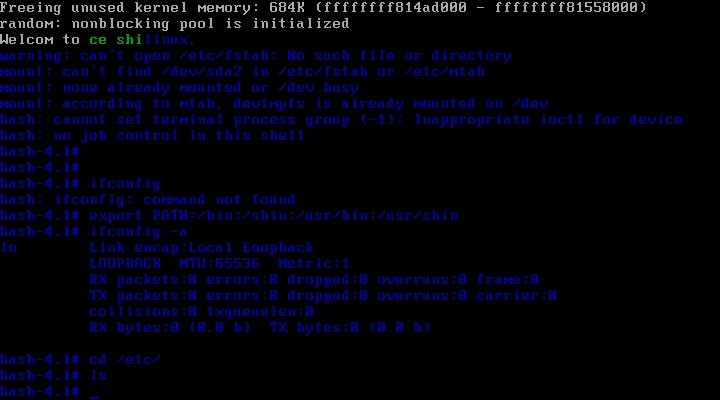
OK是不是很有成就感!!!