Java面向对象小记(1)
1. 创建类 Person
创建对象的内存划分图:
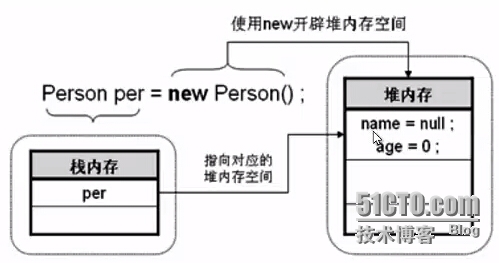
对属性赋值,操作为
对象.属性=赋值。
class Person{
String name;
int age;
public void tell(){
System.out.println("name:"+ name+" "+"age:"+age);
}
}
public class MethodDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Person per = null;
per = new Person();
per.name = "thystar"; //赋值
per.age = 22;
per.tell();
}
}
赋值后,堆内存空间中添加数据
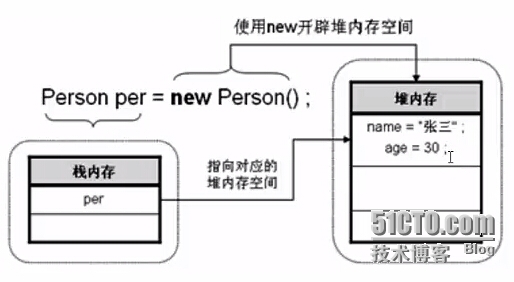
在极客学院上看到的解释,觉得很好就先记下来:http://www.jikexueyuan.com/course/111_2.html?ss=1
2. 面向对象的编程
类的封装性:
为了避免类中的属性被随意改动,将属性定义为private,用getter和setter方法调用:右键-->Source-->Generate Getters and Setters
class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void tell(){
System.out.println("name:"+ getName()+" "+"age:"+getAge());
}
}
public class MethodDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Person per = null;
per = new Person();
per.setName("thystar");
per.setAge(22);
per.tell();
}
}
极客学院改课程网址:http://www.jikexueyuan.com/course/113.html
匿名对象
class Student{
public void tell(){
System.out.println("Hello Thystar!");
}
}
public class Demo01 {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Student stu = new Student();
stu.tell();
// 匿名对象
new Student().tell(); //只能使用一次
}
}
构造方法
class Student{
public Student(){
System.out.println("Hello thystar");
}
}
public class Demo01 {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Student stu = new Student();
}
}
构造方法名称与类名一致,切没有返回值,但是可以传递参数。
class Student{
String name;
int age;
public Student(String name, int age){
System.out.println("name:"+ name+" "+"age:"+age);
}
}
public class Demo01 {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Student stu = new Student("thystar", 22);
}
}
构造方法由系统自动定义,其方法也可以重载。
极客学院改课程网址:http://www.jikexueyuan.com/course/113_3.html?ss=1
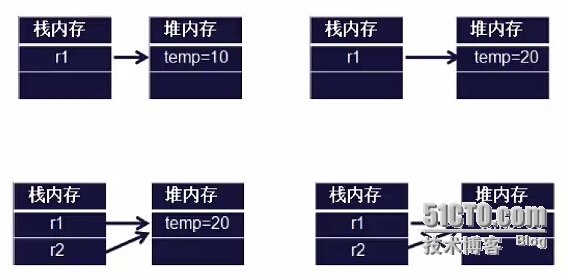
引用传递
class Ref1{
int temp = 10;
}
public class Demo02 {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Ref1 r1 = new Ref1();
r1.temp=20;
System.out.println(r1.temp);
tell(r1);
System.out.println(r1.temp);
}
public static void tell(Ref1 r2){
r2.temp = 30;
}
}
输出结果:
10
20
30
public class Demo3 {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String str1 = "Hello";
System.out.println(str1);
tell(str1);
System.out.println(str1);
}
public static void tell(String str){
str = "thystar";
}
}
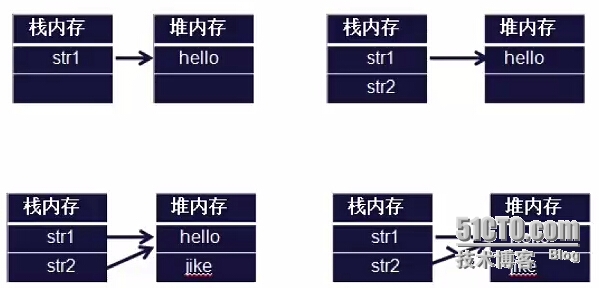
输出结果:
Hello
Hello
极客学院课程网址: http://www.jikexueyuan.com/course/114.html
this关键字
使用方法
表示类中的属性和调用方法
表示本类中的构造方法
表示当前对象
class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String n, int a){
this(); //调用本类中的构造方法
this.name = n;//表示属性
this.age = a;
}
public Person(){
System.out.println("xxxxxxxxxxxxxx");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void tell(){
System.out.println("name:"+ this.getName()+" "+"age:"+this.getAge());//调用方法
}
}
public class ThisDemo01 {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Person p = new Person("thystar", 22);
p.tell();
}
}
static 关键字
1. 使用static声明属性 ――》 static声明全局属性
2. 使用static声明方法――》 直接通过类名调用
3. 注意点: 使用static方法的时候,只能访问static声明的属性和方法,而非static声明的属性和方法是不能访问的。
静态的属性和方法要用类名直接进行调用。
极客学院地址:http://www.jikexueyuan.com/course/114_3.html?ss=2