nginx虚拟主机,反向代理实例
一、反向代理:
location匹配命令
~ #波浪线表示执行一个正则匹配,区分大小写
~* #表示执行一个正则匹配,不区分大小写
^~ #^~表示普通字符匹配,如果该选项匹配,只匹配该选项,不匹配别的选项,一般用来匹配目录
= #进行普通字符精确匹配
@ #"@" 定义一个命名的 location,使用在内部定向时,例如 error_page, try_files
location 匹配的优先级(与location在配置文件中的顺序无关)
= 精确匹配会第一个被处理。如果发现精确匹配,nginx停止搜索其他匹配。
普通字符匹配,正则表达式规则和长的块规则将被优先和查询匹配,也就是说如果该项匹配还需去看有没有正则表达式匹配和更长的匹配。
^~ 则只匹配该规则,nginx停止搜索其他匹配,否则nginx会继续处理其他location指令。
最后匹配理带有"~"和"~*"的指令,如果找到相应的匹配,则nginx停止搜索其他匹配;当没有正则表达式或者没有正则表达式被匹配的情况下,那么匹配程度最高的逐字匹配指令会被使用。
location 优先级官方文档
Directives with the = prefix that match the query exactly. If found, searching stops.
All remaining directives with conventional strings, longest match first. If this match used the ^~ prefix, searching stops.
Regular expressions, in order of definition in the configuration file.
If #3 yielded a match, that result is used. Else the match from #2 is used.
=前缀的指令严格匹配这个查询。如果找到,停止搜索。
所有剩下的常规字符串,最长的匹配。如果这个匹配使用^前缀,搜索停止。
正则表达式,在配置文件中定义的顺序。
如果第3条规则产生匹配的话,结果被使用。否则,如同从第2条规则被使用。
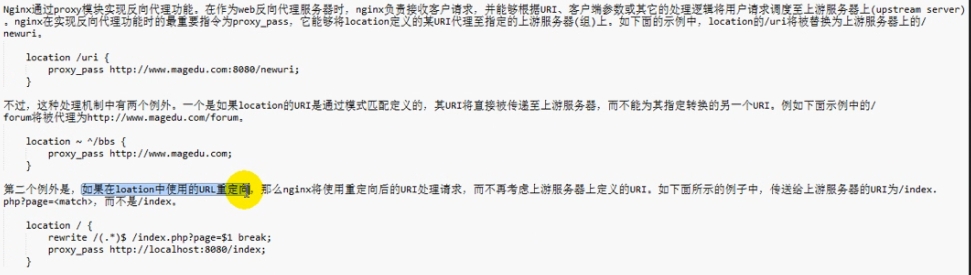
举例:第一种例外:
location ~* ^/bbs {
proxy_pass http://192.168.100.100:8080
proxy_pass http://192.168.100.100:8080/form 注:此写法不允许,会报错
}
则bbs是通过模式匹配到的,所以bbs则会被传到上游服务器,最后转到的是http://192.168.100.100:8080/bbs,而无需在proxy_pass指定其他路径。
二、主配置文件配置:
#user nobody;
worker_processes 4;
error_log logs/error.log debug_http;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
use epoll; #epoll是多路复用IO(I/O Multiplexing)中的一种方式,
worker_connections 1024; #单个后台worker process进程的最大并发链接数
# 并发总数是 worker_processes 和 worker_connections 的乘积
# 即 max_clients = worker_processes * worker_connections
# 在设置了反向代理的情况下,max_clients = worker_processes * worker_connections / 4 为什么
# 为什么上面反向代理要除以4,应该说是一个经验值
# 根据以上条件,正常情况下的Nginx Server可以应付的最大连接数为:4 * 8000 = 32000
# worker_connections 值的设置跟物理内存大小有关
# 因为并发受IO约束,max_clients的值须小于系统可以打开的最大文件数
# 而系统可以打开的最大文件数和内存大小成正比,一般1GB内存的机器上可以打开的文件数大约是10万左右
# 我们来看看360M内存的VPS可以打开的文件句柄数是多少:
# $ cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max
# 输出 34336
# 32000 < 34336,即并发连接总数小于系统可以打开的文件句柄总数,这样就在操作系统可以承受的范围之内
# 所以,worker_connections 的值需根据 worker_processes 进程数目和系统可以打开的最大文件总数进行适当地进行设置
# 使得并发总数小于操作系统可以打开的最大文件数目
# 其实质也就是根据主机的物理CPU和内存进行配置
# 当然,理论上的并发总数可能会和实际有所偏差,因为主机还有其他的工作进程需要消耗系统资源。
# ulimit -SHn 65535
}
http {
include mime.types; #设定mime类型,类型由mime.type文件定义
include /usr/local/nginx/conf/conf.d/*.conf; #包含其他文件
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
#sendfile 指令指定 nginx 是否调用 sendfile 函数(zero copy 方式)来输出文件,
#对于普通应用,必须设为 on,
#如果用来进行下载等应用磁盘IO重负载应用,可设置为 off,
#以平衡磁盘与网络I/O处理速度,降低系统的uptime.
#tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 120; #连接超时时间
tcp_nodelay on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
access_log logs/access.log;
error_log logs/error.log;
charset utf-8;
location / {
index index.html index.htm;
root html;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
三、虚拟主机:
conf.d目录下添加vhosts.conf
server {
listen 172.16.171.101:80;
server_name www.wushank.com;
charset utf-8;
error_log logs/wushank/error.log;
access_log logs/wushank/access.log;
location / {
root /var/www/html/wushank;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
listen 172.16.171.101:80;
server_name www.test.com;
charset utf-8;
error_log logs/test/error.log;
access_log logs/test/access.log;
location / {
root /var/www/html/test;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
listen 10.1.1.100:8000;
server_name localhost;
charset utf-8;
error_log logs/wang/error.log;
access_log logs/wang/access.log;
location / {
root /wang;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
四、反向代理配置:
upstream f5-test {
server 172.16.171.100:8080;
server 172.16.171.110:80;
server 172.16.171.120:80;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name 172.16.171.100 f5.sky.com;
location ~ \.php$ {
root /var/www/html;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
#设置反向代理的全局信息
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
client_max_body_size 50m;
client_body_buffer_size 256k;
proxy_connect_timeout 30;
proxy_send_timeout 30;
proxy_read_timeout 60;
proxy_buffer_size 16k;
proxy_buffers 4 32k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k;
proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k;
#根据URI对不同的目录进行反向代理
location /f5/ { 注:URL后有“/",则在转到上游URL后也需要有"/"
access_log logs/f5/access.log;
error_log logs/f5/error.log;
proxy_pass http://f5-test/f5/;
proxy_redirect default;
}
location /wushank { 注:URL后无“/",则在转到上游URL后也无"/"
access_log logs/wushank/access.log;
error_log logs/wushank/error.log;
proxy_pass http://f5-test/wushank;
proxy_redirect default;
}
}