11. C#数据结构与算法 -- 顺序队列
理论基础:
队列(Queue)是插入操作限定在表的尾部而其它操作限定在表的头部进行的线性表。把进行插入操作的表尾称为队尾(Rear),把进行其它操作的头部称为队头(Front)。
对列的操作是按照先进先出(First In First Out)或后进后出( Last In Last Out)的原则进行的,因此,队列又称为FIFO表或LILO表。
与栈一样,队列的运算是定义在逻辑结构层次上的,而运算的具体实现是建立在物理存储结构层次上的。因此,把队列的操作作为逻辑结构的一部分,每个操作的具体实现只有在确定了队列的存储结构之后才能完成。
队列可以区分为顺序队列,链队列两种。
顺序队列类似于顺序栈,用一维数组来存放顺序队列中的数据元素。链队列同链栈一样,链队列通常用单链表来表示,它的实现是单链表的简化。
顺序队列在操作的过程中会出现“假溢出”。可以用循环顺序队列解决这种现象。
C#实现:
1 接口定义
C#语言的泛型接口来表示队列,接口中的方法成员表示基本操作。为了表示的方便与简洁,把泛型队列接口取名为IQueue<T>(实际上,在C#中泛型队列类是从IEnumerable<T>、ICollection和IEnumerable接口继承而来,没有IQueue<T>泛型接口)。
队列接口IQueue<T>的定义如下所示:
public interface IQueue<T>
{
/// <summary>
/// 队列长度
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
int GetLength();
/// <summary>
/// 判断是否为空
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
bool IsEmpty();
/// <summary>
/// 是否已满
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
bool Full();
/// <summary>
/// 清空队列
/// </summary>
void Clear();
/// <summary>
/// 入队
/// </summary>
/// <param name="item"></param>
void In(T item);
/// <summary>
/// 出队
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
T Out();
}
2 代码实现
实现提供的接口
public class CSeqQueue<T> : IQueue<T>
{
private int maxsize; //队列最大容量
private T[] data;//队列数据
private int front;//队头
private int rear;//队尾
public T this[int index]
{
get {return data[index]; }
set{ data[index] = value; }
}
public int MaxSize
{
get { return maxsize; }
set { maxsize = value; }
}
public int Front
{
get { return front; }
set { front = value; }
}
public int Rear
{
get { return rear; }
set { rear = value; }
}
public CSeqQueue(int size)
{
data =new T[size];
maxsize = size;
front = rear = -1;
}
//队列长度
public int GetLength()
{
return (rear - front + maxsize) % maxsize;
}
//清空队列
public void Clear()
{
front = rear = -1;
}
//判断是否为空
public bool IsEmpty()
{
if (front == rear)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//判断是否已满
public bool IsFull()
{
if (front == (rear+1)%maxsize)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//入队
public void In(T item)
{
if (IsFull())
{
Console.Write("Queue is full");
return;
}
data[++rear] = item;
}
//出队
public T Out()
{
if (IsEmpty())
{
Console.Write("Queue is empty");
return;
}
return data[++front];
}
}
C#中的队列:
C#2.0以下版本只提供了非泛型的Queue类,该类继承了ICollection、IEnumerable和ICloneable接口。
C#2.0提供了泛型的Queue<T>类,该类继承了IEnumerable<T>、ICollection和IEnumerable接口。
以下程序说明了泛型Queue<T>类的主要方法,并对在我们自定义的队列类中没有出现的成员方法进行了注释,
关于泛型Queue<T>类的更具体的信息,可参考.NET Framework的有关书籍。
public class Queue<T> : IEnumerable<T>, ICollection, IEnumerable
{
public void Clear();
//确定某元素是否在Queue<T>中。
//如果在Queue<T> 中找到 item,则为true;否则为false。
public bool Contains(T item);//从指定数组索引开始将Queue<T>元素复制到现有一维Array 中。
public void CopyTo(T[] array, int arrayIndex);
//移除并返回位于Queue<T>开始处的对象。
//从Queue<T>的开头移除的对象。
public T Dequeue();
//返回位于Queue<T>开始处的对象但不将其移除。
public T Peek();
//将Queue<T>元素复制到新数组。
public T[] ToArray();
//如果元素数小于当前容量的90%,
//将容量设置为Queue<T> 中的实际元素数。
public void TrimExcess();
}
队列通常记为:Q= (a1,a2,…,an),a1为队头元素,an为队尾元素。元素按照a1,a2,…,an的次序依次入队,出队的次序与入队相同,即a1第一个出队,an最后一个出队。所以,对列的操作是按照先进先出(First In First Out)或后进后出( Last In Last Out)的原则进行的,因此,队列又称为FIFO表或LILO表。
队列的常用操作有:
1、构造一个空队列:InitQueue()//在C#中可以使用构造函数来实现
2、清空队列:ClearQueue()
3、判断队列是否为空:IsEmpty()
4、判断队列是否已满:IsFull()
5、求队列长度:QueueLength()
6、入队操作:In()
7、出队操作:Out()
8、得到队头元素:GetHead()
下面给出一个实现顺序队列的源代码:
实例1:
using System;
class Queue
{
object[] data; //数据元素
int maxsize; //最大容量
int front; //指向队头
int rear; //指向队尾
//初始化队列
public Queue(int size)
{
this.maxsize = size;
data = new object[size];
front = rear = -1;
}
//最大容量属性
public int MaxSize
{
get
{
return this.maxsize;
}
set
{
this.maxsize = value;
}
}
//队尾属性
public int Rear
{
get
{
return this.rear;
}
}
//队头属性
public int Front
{
get
{
return this.front;
}
}
//数据属性
public object this[int index]
{
get
{
return data[index];
}
}
//获得队列的长度
public int GetQueueLength()
{
return rear-front;
}
//判断队列是否满
public bool IsFull()
{
if(GetQueueLength() == maxsize)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//判断队列是否为空
public bool IsEmpty()
{
if(rear==front)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//清空队列
public void ClearQueue()
{
rear = front = -1;
}
//入队
public void In(object e)
{
if(IsFull())
{
Console.WriteLine("Queue is full!");
return;
}
data[++rear]=e;
}
//出队
public object Out()
{
if(IsEmpty())
{
Console.WriteLine("Queue is empty!");
return null;
}
if(rear-front>0)
{
object tmp = data[++front];
return tmp;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("All queue numbers are dequeued!");
ClearQueue();
return null;
}
}
//获得队头元素
public object GetHead()
{
if(IsEmpty())
{
Console.WriteLine("Queue is empty!");
return null;
}
return data[front+1];
}
}
class Test
{
static void Main()
{
Queue q = new Queue(1);
int rdNum;
Random rd = new Random();
while(!q.IsFull())
{
rdNum = rd.Next(10,100);
q.In(rdNum);
Console.WriteLine("{0} Enqueue,the numbers of the queue is:{1}",rdNum,q.GetQueueLength());
}
Console.WriteLine("***************************");
while (!q.IsEmpty())
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} Dequeue, the number of the queue is:{1}", q.Out(), q.GetQueueLength());
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
实例2:
演示了C#内置的队列如何进行添加,移除等功能。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Example
{
public static void Main()
{
Queue<string> numbers = new Queue<string>();
numbers.Enqueue("one");
numbers.Enqueue("two");
numbers.Enqueue("three");
numbers.Enqueue("four");
numbers.Enqueue("five");
// A queue can be enumerated without disturbing its contents.
foreach( string number in numbers )
{
Console.WriteLine(number);
}
Console.WriteLine("\nDequeuing '{0}'", numbers.Dequeue());
Console.WriteLine("Peek at next item to dequeue: {0}",
numbers.Peek());
Console.WriteLine("Dequeuing '{0}'", numbers.Dequeue());
// Create a copy of the queue, using the ToArray method and the
// constructor that accepts an IEnumerable<T>.
Queue<string> queueCopy = new Queue<string>(numbers.ToArray());
Console.WriteLine("\nContents of the first copy:");
foreach( string number in queueCopy )
{
Console.WriteLine(number);
}
// Create an array twice the size of the queue and copy the
// elements of the queue, starting at the middle of the
// array.
string[] array2 = new string[numbers.Count * 2];
numbers.CopyTo(array2, numbers.Count);
// Create a second queue, using the constructor that accepts an
// IEnumerable(Of T).
Queue<string> queueCopy2 = new Queue<string>(array2);
Console.WriteLine("\nContents of the second copy, with duplicates and nulls:");
foreach( string number in queueCopy2 )
{
Console.WriteLine(number);
}
Console.WriteLine("\nqueueCopy.Contains(\"four\") = {0}",
queueCopy.Contains("four"));
Console.WriteLine("\nqueueCopy.Clear()");
queueCopy.Clear();
Console.WriteLine("\nqueueCopy.Count = {0}", queueCopy.Count);
}
}
/* This code example produces the following output:
one
two
three
four
five
Dequeuing 'one'
Peek at next item to dequeue: two
Dequeuing 'two'
Contents of the copy:
three
four
five
Contents of the second copy, with duplicates and nulls:
three
four
five
queueCopy.Contains("four") = True
queueCopy.Clear()
queueCopy.Count = 0
*/
实例3:过链表实现队列的方法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Queue_test
{
public class Node
{
public int Data
{ get; set; }
public Node Next { get; set; }
public Node(int data)
{ this.Data = data; }
}
public class Queue
{
private Node _head;
private Node _tail;
private int _count = 0;
public Queue() { }
public void Enqueue(int data)
{
Node _newNode = new Node(data);
if (_head == null)
{
_head = _newNode;
_tail = _head;
}
else
{
_tail.Next = _newNode;
_tail = _tail.Next;
}
_count++;
}
public int Dequeue()
{
if (_head == null)
{
throw new Exception("Queue is Empty");
}
int _result = _head.Data;
_head = _head.Next;
return _result;
}
public int Count
{
get { return this._count; }
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Queue numbers = new Queue();
numbers.Enqueue(123);
numbers.Enqueue(234);
numbers.Enqueue(345);
int num= numbers.Count;
Console.WriteLine(num);
numbers.Dequeue();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
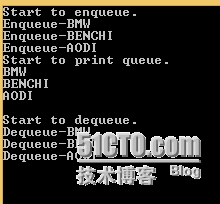
实例4:C#队列Queue用法实例分析
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication4
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string[] cars = new string[] { "BMW", "BENCHI", "AODI" };
Console.WriteLine("Start to enqueue.");
Queue<string> que = new Queue<string>();
foreach (string str in cars)
{
que.Enqueue(str);
Console.WriteLine("Enqueue-{0}", str);
}
//Print the queue
PrintQueue(que);
//Console.WriteLine("Start to print queue.");
//foreach (string str in que)
//{
// Console.WriteLine(str);
//}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Start to dequeue.");
while (que.Count > 0)
{
string str = que.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine("Dequeue-{0}", str);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
private static void PrintQueue(Queue<string> list)
{
Console.WriteLine("Start to print queue.");
foreach (string str in list)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
}
}
}
result:
参考:
http://www.jb51.net/article/65151.htm
http://www.cnblogs.com/Richet/archive/2008/10/20/1315192.html
http://www.biye5u.com/article/Csharp/methprog/2013/6074_2.html