systemd详解(CentOS 7)
一、init进程演变
1.init的发展
CentOS 5: SysV init,串行
CentOS 6:Upstart,并行,借鉴ubantu
CentOS 7:Systemd,并行,借鉴MAC
2.Systemd新特性:
(1)系统引导时实现服务并行启动:服务间无依赖关系会并行启动
(2)按需激活进程:若服务非立刻使用,不会立刻激活,处于半活动状态,占用端口用时启动服务
(3)系统状态快照:回滚到过去某一状态
(4)基于依赖关系定义服务控制逻辑
二、systemd核心概念:unit单元
1.unit相关配置文件:
unit由其相关配置文件进行标识、识别和配置
文件中主要包含了系统服务、监听的socket、保存的快照以及其它与init相关的信息;
/usr/lib/systemd/system
/run/systemd/system
/etc/systemd/system
2.unit常见类型:
Serviceunit:文件扩展名为.service,用于定义系统服务;
Targetunit:文件扩展为.target,用于模拟实现“运行级别”;
Device unit=:文件扩展名为 .device,用于定义内核识别的设备;
Mount unit:文件扩展名为.mount,定义文件系统挂载点;
Socketunit:文件扩展名为 .socket,用于标识进程间通信用到的socket文件;
Snapshotunit:文件扩展名为 .snapshot, 管理系统快照;
Swapunit:文件扩展名为 .swap, 用于标识swap设备;
Automountunit: 文件扩展名为.automount,文件系统自动点设备;
Pathunit:文件扩展名为 .path, 用于定义文件系统中的一文件或目录;
3.unit特性:
1)基于socket的激活机制:socket与程序分离,将套接字先分配但时程序本身未启动
2)基于bus的激活机制:基于总线的请求来激活设备
3)基于device的激活机制:设备插入时候自动挂载激活设备,挂载点不存在自动创建
4)基于Path的激活机制:监控目录文件是否存在来激活服务或者进程
5)系统快照:保存各unit的当前状态信息于持久存储设备中;
6)向后兼容sysv init脚本; /etc/init.d/下的脚本也能兼容
注意:也存在不兼容情况:
1)systemctl的命令是固定不变的;
2)非由systemd启动的服务,systemctl无法与之通信;
三、syscemctl:管理systemd系统服务
syscemctl命令:控制systemd系统和服务管理
systemctl [OPTIONS...] COMMAND [NAME...]
CentOS 7上通过管理 service类型的unit文件
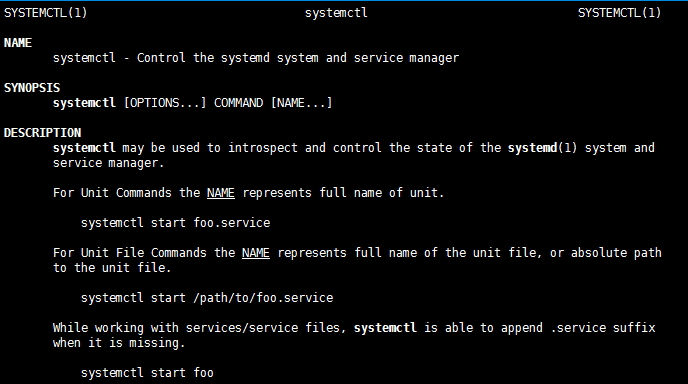
CentOS 5/6 ==>CentOS 7转换:
1.启动/关闭类
启动:service NAME start ==> systemctl start NAME.service
停止:service NAME stop ==> systemctl stop NAME.service
重启:service NAME restart ==> systemctl restart NAME.service
状态:service NAME status ==> systemctl status NAME.service
条件式重启:service NAME condrestart ==> systemctl try-restart NAME.service
重载或重启服务:systemctl reload-or-restart NAME.servcie
重载或条件式重启服务:systemctl reload-or-try-restart NAME.service
2.查看服务类
查看某服务当前激活与否的状态:systemctl is-active NAME.service
查看所有已激活的服务:systemctl list-units --type service
查看所有服务(已激活及未激活):chkconfig --lsit ==> systemctl list-units -t service --all
3.开机设置类
设置服务开机自启:chkconfig NAME on ==> systemctl enable NAME.service
禁止服务开机自启:chkconfig NAME off ==> systemctl disable NAME.service
查看某服务是否能开机自启:chkconfig --list NAME ==> systemctl is-enabled NAME.service
禁止某服务设定为开机自启:systemctl mask NAME.service
取消此禁止:systemctl unmask NAME.servcie
4.查看依赖关系类
查看服务的依赖关系:systemctl list-dependencies NAME.service
5.管理target units:
1)运行级别对应关系
0 ==> runlevel0.target, poweroff.target
1 ==> runlevel1.target, rescue.target
2 ==> runlevel2.tartet, multi-user.target
3 ==> runlevel3.tartet, multi-user.target
4 ==> runlevel4.tartet, multi-user.target
5 ==> runlevel5.target, graphical.target
6 ==> runlevel6.target, reboot.target
2)级别相关命令
级别切换:init N ==> systemctl isolate NAME.target
查看级别:runlevel ==> systemctl list-units --type target
查看所有级别:systemctl list-units -t target -a
获取默认运行级别:systemctl get-default
修改默认运行级别:systemctl set-default NAME.target
切换至紧急救援模式:systemctl rescue
切换至emergency模式:systemctl emergency
6.其它常用命令:
关机:systemctl halt, systemctl poweroff
重启:systemctl reboot
挂起:systemctl suspend
快照:systemctl hibernate
快照并挂起:systemctl hybrid-sleep
四、服务单元文件:service unit file
1./usr/lib/systemd/system和/etc/systemd/system关系
/etc...设定默认运行级别和启动时服务的运行关系,连接文件。
一般管理员可在/etc/…...下定义一些service unit file文件
2.serviceunit file文件格式
例如:[root@localhost system]# cat firewalld.service
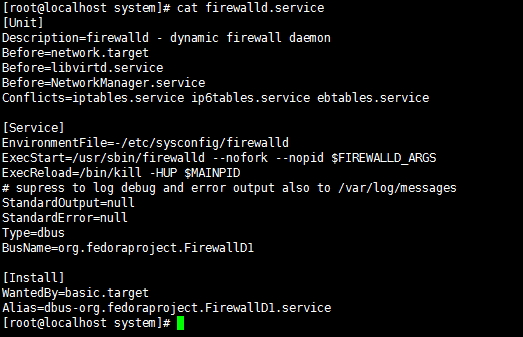
[Unit]:定义与Unit类型无关的通用选项;用于提供unit的描述信息、unit行为及依赖关系等;
[Service]:与特定类型相关的专用选项;此处为Service类型;
[Install]:定义由"systemctl enable"以及"systemctl disable"命令在实现服务启用或禁用时用到选项;
(1)Unit段的常用选项:
Description:描述信息;意义性描述;
After:定义unit的启动次序;表示当前unit应该晚于哪些unit启动;其功能与Before相反;
Requies:依赖到的其它units;强依赖,被依赖的units无法激活时,当前unit即无法激活;
Wants:依赖到的其它units;弱依赖;
Conflicts:定义units间的冲突关系;
(2)Service段的常用选项:
Type:用于定义影响ExecStart及相关参数的功能的unit进程启动类型;
类型种类:
simple:默认。由ExecStart指明的进程所启动起来进程为主进程
forking:由ExecStart所启动的进程生成的一个子进程为主,父进程退出
oneshot:一次性的启动,后续的unit进程启动后,该进程退出
dbus:仅在得到dbus之后才推出
notify:发送通知以后才能运行
idle:类似于simple
EnvironmentFile:环境配置文件,为ExecStart提供一些变量;
ExecStart:指明启动unit要运行命令或脚本;ExecStartPre, ExecStartPost
ExecStop:指明停止unit要运行的命令或脚本;
Restart:启动此项,意外终止会自动重启脚本
(3)Install段的常用选项:
Alias:当前unit的别名
RequiredBy:被哪些units所依赖;
WantedBy:被哪些units所依赖;
注意:对于新创建的unit文件或,修改了的unit文件,要通知systemd重载此配置文件;
#systemctl daemon-reload
http://xuding.blog.51cto.com/4890434/1730952