信息安全系统设计基础第十一周学习总结
第十一周实践代码总结
exec1.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
char *arglist[3];
arglist[0] = "ls";
arglist[1] = "-l";
arglist[2] = 0 ;//NULL
printf("* * * About to exec ls -l\n");
execvp( "ls" , arglist );
printf("* * * ls is done. bye");
return 0;
}头文件:#include
定义函数:int execvp(const char file, char const argv []);
函数说明:execvp()会从PATH 环境变量所指的目录中查找符合参数file 的文件名, 找到后便执行该文件, 然后将第二个参数argv 传给该欲执行的文件。
返回值 如果执行成功则函数不会返回,执行失败则直接返回-1,失败原因存于errno中。
此处执行的execvp("ls",arglist);就会从PATH环境变量所指的目录中寻找ls的文件名,找到后执行ls,然后将-l传给该文件。
跟ls -l命令相比,发现exec1的结果并未将可执行文件、文件夹与文件区分开来。
exec2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
char *arglist[3];
arglist[0] = "ls";
arglist[1] = "-l";
arglist[2] = 0 ;
printf("* * * About to exec ls -l\n");
execvp( arglist[0] , arglist );
printf("* * * ls is done. bye\n");
}与exec1.c执行的功能是一样的,仅仅是在调用execvp函数时,用arglist[0]替换"ls",实现用数组传参。
-
exec3.c
include
include
int main()
{
char arglist[3];
char myenv[3];
myenv[0] = "PATH=:/bin:";
myenv[1] = NULL;arglist[0] = "ls";
execlp("ls", "ls", "-l", NULL);
arglist[1] = "-l";
arglist[2] = 0 ;
printf("* * * About to exec ls -l\n");
// execv( "/bin/ls" , arglist );
// execvp( "ls" , arglist );
// execvpe("ls" , arglist, myenv);
printf("* * * ls is done. bye\n");
} 该程序运用了execlp函数
表头文件 #include
定义函数 int execlp(const char * file,const char * arg,……);
函数说明 execlp()会从PATH 环境变量所指的目录中查找符合参数file的文件名,找到后便执行该文件,然后将第二个以后的参数当做该文件的argv[0]、argv[1]……,最后一个参数必须用空指针(NULL)作结束。
返回值 如果执行成功则函数不会返回,执行失败则直接返回-1,失败原因存于errno 中。
所以execlp("ls", "ls", "-l", NULL)等同于execvp( "ls" , arglist ),其中arglist[0] = "ls";arglist[1] = "-l"; arglist[2] = 0 ;
forkdemo1.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
int ret_from_fork, mypid;
mypid = getpid();
printf("Before: my pid is %d\n", mypid);
ret_from_fork = fork();
sleep(1);
printf("After: my pid is %d, fork() said %d\n",
getpid(), ret_from_fork);
return 0;
}- getpid()用来取得目前进程的进程识别码。
- 先打印当前的进程识别码
- 用fork()函数运行父进程,打印父进程识别码,然后再打印子进程识别码,因为子进程返回值为0,所以打印ret_from_fork=0;
- 结果如下:

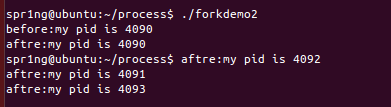
forkdemo2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
printf("before:my pid is %d\n", getpid() );
fork();
fork();
printf("aftre:my pid is %d\n", getpid() );
return 0;
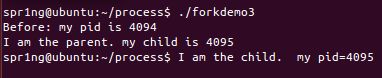
}forkdemo3.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
int fork_rv;
printf("Before: my pid is %d\n", getpid());
fork_rv = fork(); /* create new process */
if ( fork_rv == -1 ) /* check for error */
perror("fork");
else if ( fork_rv == 0 ){
printf("I am the child. my pid=%d\n", getpid());
exit(0);
}
else{
printf("I am the parent. my child is %d\n", fork_rv);
exit(0);
}
return 0;
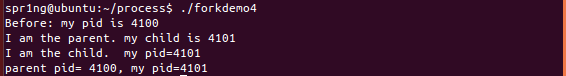
}forkdemo4.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
int fork_rv;
printf("Before: my pid is %d\n", getpid());
fork_rv = fork(); /* create new process */
if ( fork_rv == -1 ) /* check for error */
perror("fork");
else if ( fork_rv == 0 ){
printf("I am the child. my pid=%d\n", getpid());
printf("parent pid= %d, my pid=%d\n", getppid(), getpid());
exit(0);
}
else{
printf("I am the parent. my child is %d\n", fork_rv);
sleep(10);
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}- getppid()用来取得目前进程的父进程识别码。
- 先打印一个Before,显示当前进程识别码。
- 进行父进程,打印其对应子进程的识别码。
再进行子进程,打印子进程当前的识别码与其对应的父进程的识别码。
运行结果:
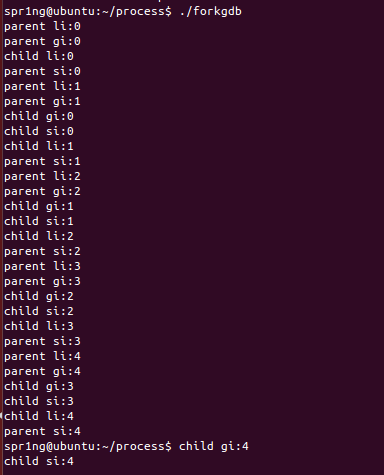
forkgdb.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int gi=0;
int main()
{
int li=0;
static int si=0;
int i=0;
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid == -1){
exit(-1);
}
else if(pid == 0){
for(i=0; i<5; i++){
printf("child li:%d\n", li++);
sleep(1);
printf("child gi:%d\n", gi++);
printf("child si:%d\n", si++);
}
exit(0);
}
else{
for(i=0; i<5; i++){
printf("parent li:%d\n", li++);
printf("parent gi:%d\n", gi++);
sleep(1);
printf("parent si:%d\n", si++);
}
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}psh1.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define MAXARGS 20
#define ARGLEN 100
int execute( char *arglist[] )
{
execvp(arglist[0], arglist);
perror("execvp failed");
exit(1);
}
char * makestring( char *buf )
{
char *cp;
buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';
cp = malloc( strlen(buf)+1 );
if ( cp == NULL ){
fprintf(stderr,"no memory\n");
exit(1);
}
strcpy(cp, buf);
return cp;
}
int main()
{
char *arglist[MAXARGS+1];
int numargs;
char argbuf[ARGLEN];
numargs = 0;
while ( numargs < MAXARGS )
{
printf("Arg[%d]? ", numargs);
if ( fgets(argbuf, ARGLEN, stdin) && *argbuf != '\n' )
arglist[numargs++] = makestring(argbuf);
else
{
if ( numargs > 0 ){
arglist[numargs]=NULL;
execute( arglist );
numargs = 0;
}
}
}
return 0;
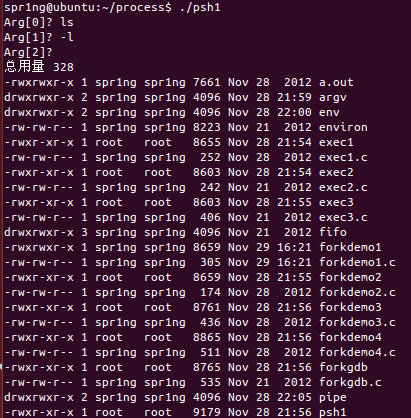
}该函数的功能为输入命令,用回车表示结束命令的输入,然后将它们传入arglist之中,利用execute来调用执行命令。
运行结果:
psh2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#define MAXARGS 20
#define ARGLEN 100
char *makestring( char *buf )
{
char *cp;
buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';
cp = malloc( strlen(buf)+1 );
if ( cp == NULL ){
fprintf(stderr,"no memory\n");
exit(1);
}
strcpy(cp, buf);
return cp;
}
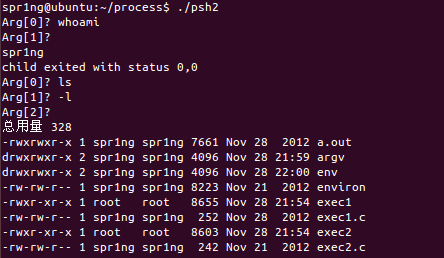
void execute( char *arglist[] )
{
int pid,exitstatus;
pid = fork();
switch( pid ){
case -1:
perror("fork failed");
exit(1);
case 0:
execvp(arglist[0], arglist);
perror("execvp failed");
exit(1);
default:
while( wait(&exitstatus) != pid )
;
printf("child exited with status %d,%d\n",
exitstatus>>8, exitstatus&0377);
}
}
int main()
{
char *arglist[MAXARGS+1];
int numargs;
char argbuf[ARGLEN];
numargs = 0;
while ( numargs < MAXARGS )
{
printf("Arg[%d]? ", numargs);
if ( fgets(argbuf, ARGLEN, stdin) && *argbuf != '\n' )
arglist[numargs++] = makestring(argbuf);
else
{
if ( numargs > 0 ){
arglist[numargs]=NULL;
execute( arglist );
numargs = 0;
}
}
}
return 0;
}testbuf1.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello");
fflush(stdout);
while(1);
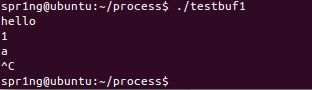
}- 输出hello,而后一直空循环,不退出程序的执行。
- fflush(stdout)跟fflush(stdin)类似,是对标准输出流的清理,但是它并不是把数据丢掉,而是及时地打印数据到屏幕上.
- 运行结果:
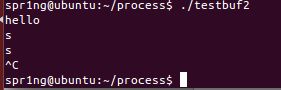
testbuf2.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello\n");
while(1);
}testbuf3.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
fprintf(stdout, "1234", 5);
fprintf(stderr, "abcd", 4);
}- 将1234以标准输出流输出,将abcd以标准错误流输出。
- 运行结果:
testpid.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int main()
{
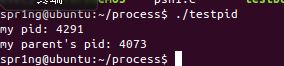
printf("my pid: %d \n", getpid());
printf("my parent's pid: %d \n", getppid());
return 0;
}- getpid得到当前进程的标识码
- getppid得到当前进程父进程的标识码
- 运行结果:
testpp.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
char **pp;
pp[0] = malloc(20);
return 0;
}- 运行结果:
段错误 一般是非法访问内存造成的
核心已转储 (core dump) -- 内存清除,早期的内存用磁芯存储器
testsystem.c
#include <stdlib.h>
int main ( int argc, char *argv[] )
{
system(argv[1]);
system(argv[2]);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
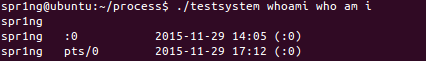
}- system()会调用fork()产生子进程,由子进程来调用/bin/sh-c
- string来执行参数string字符串所代表的命令,此命令执行完后随即返回原调用的进程。在调用system()期间SIGCHLD 信号会被暂时搁置,SIGINT和SIGQUIT 信号则会被忽略。
- 返回值 如果system()在调用/bin/sh时失败则返回127,其他失败原因返回-1。若参数string为空指针(NULL),则返回非零值。
- 运行两个命令
- 运行结果:
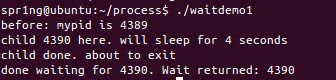
waitdemo1.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define DELAY 4
void child_code(int delay)
{
printf("child %d here. will sleep for %d seconds\n", getpid(), delay);
sleep(delay);
printf("child done. about to exit\n");
exit(17);
}
void parent_code(int childpid)
{
int wait_rv=0; /* return value from wait() */
wait_rv = wait(NULL);
printf("done waiting for %d. Wait returned: %d\n",
childpid, wait_rv);
}
int main()
{
int newpid;
printf("before: mypid is %d\n", getpid());
if ( (newpid = fork()) == -1 )
perror("fork");
else if ( newpid == 0 )
child_code(DELAY);
else
parent_code(newpid);
return 0;
}- wait()会暂时停止目前进程的执行,直到有信号来到或子进程结束。如果在调用wait()时子进程已经结束,则wait()会立即返回子进程结束状态值。子进程的结束状态值会由参数status 返回,而子进程的进程识别码也会一快返回。如果不在意结束状态值,则参数 status可以设成NULL。
- 返回值 如果执行成功则返回子进程识别码(PID),如果有错误发生则返回-1。失败原因存于errno中。
- 将子进程停止,如果执行成功则返回子进程识别码。
- 运行结果:
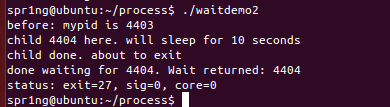
waitdemo2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define DELAY 10
void child_code(int delay)
{
printf("child %d here. will sleep for %d seconds\n", getpid(), delay);
sleep(delay);
printf("child done. about to exit\n");
exit(27);
}
void parent_code(int childpid)
{
int wait_rv;
int child_status;
int high_8, low_7, bit_7;
wait_rv = wait(&child_status);
printf("done waiting for %d. Wait returned: %d\n", childpid, wait_rv);
high_8 = child_status >> 8; /* 1111 1111 0000 0000 */
low_7 = child_status & 0x7F; /* 0000 0000 0111 1111 */
bit_7 = child_status & 0x80; /* 0000 0000 1000 0000 */
printf("status: exit=%d, sig=%d, core=%d\n", high_8, low_7, bit_7);
}
int main()
{
int newpid;
printf("before: mypid is %d\n", getpid());
if ( (newpid = fork()) == -1 )
perror("fork");
else if ( newpid == 0 )
child_code(DELAY);
else
parent_code(newpid);
} - 输出子进程结束的状态(exit、sig、core)。
- 运行结果:
argv文件夹
- 包含函数argtest.c argv.h freemakeargv.c makeargv.c
- 类似于psh1的用法,在运行程序时需要加上要运行的代码。
- 运行结果:
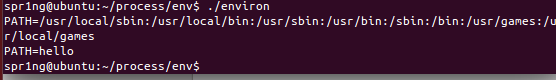
environ.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
printf("PATH=%s\n", getenv("PATH"));
setenv("PATH", "hello", 1);
printf("PATH=%s\n", getenv("PATH"));
#if 0
printf("PATH=%s\n", getenv("PATH"));
setenv("PATH", "hellohello", 0);
printf("PATH=%s\n", getenv("PATH"));
printf("MY_VER=%s\n", getenv("MY_VER"));
setenv("MY_VER", "1.1", 0);
printf("MY_VER=%s\n", getenv("MY_VER"));
#endif
return 0;
}- getenv()用来取得参数name环境变量的内容。参数name为环境变量的名称,如果该变量存在则会返回指向该内容的指针。环境变量的格式为name=value。
- setenv()用来改变或增加环境变量的内容。参数name为环境变量名称字符串。
- 运行结果:
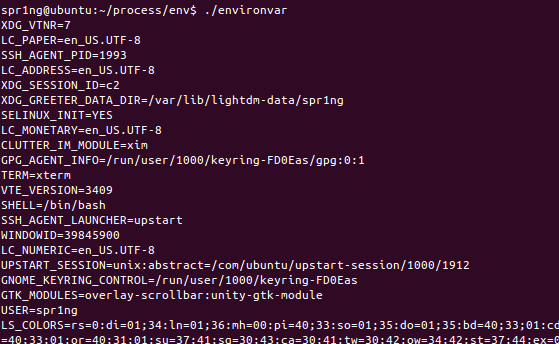
environvar.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
extern char **environ;
int i;
for(i = 0; environ[i] != NULL; i++)
printf("%s\n", environ[i]);
return 0;
}- 简单打印环境变量表
- 指针变量environ,它指向的是包含所有的环境变量的一个列表。
- 运行结果:
consumer.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#define FIFO_NAME "/tmp/myfifo"
#define BUFFER_SIZE PIPE_BUF
int main()
{
int pipe_fd;
int res;
int open_mode = O_RDONLY;
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE + 1];
int bytes = 0;
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
printf("Process %d opeining FIFO O_RDONLY \n", getpid());
pipe_fd = open(FIFO_NAME, open_mode);
printf("Process %d result %d\n", getpid(), pipe_fd);
if (pipe_fd != -1) {
do {
res = read(pipe_fd, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE);
bytes += res;
} while (res > 0);
close(pipe_fd);
} else {
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Process %d finished, %d bytes read\n", getpid(), bytes);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}- memset:作用是在一段内存块中填充某个给定的值,它是对较大的结构体或数组进行清零操作的一种最快方法。
- void memset(void s, int ch, size_t n);
- 函数解释:将s中前n个字节替换为ch并返回s;
- 运行结果:
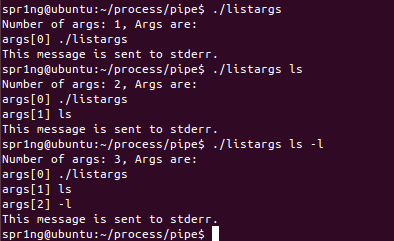
listargs.c
#include <stdio.h>
main( int ac, char *av[] )
{
int i;
printf("Number of args: %d, Args are:\n", ac);
for(i=0;i<ac;i++)
printf("args[%d] %s\n", i, av[i]);
fprintf(stderr,"This message is sent to stderr.\n");
}- 运行结果:
pipedemo.c
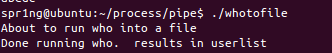
- 输入一个数据,将返回一个一模一样的数据。
- 运行结果
whotofile.c
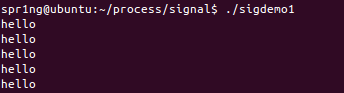
sigdemo2.c
- 一直输出hello
- 通过ctrl+z强制停止
- 运行结果:
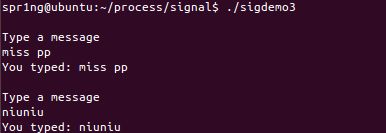
sigdemo3.c
- 输入什么打印什么
- 运行结果:
参考文献
- ITEDU函数辅助 http://www.iteedu.com/os/linux/linuxprgm/linuxcfunctions/process/fprintf.php
- 《fflush(stdin)和fflush(stdout)》 http://blog.csdn.net/yeyuangen/article/details/6743416
实践体会
结果是明白了,但是有些代码还是弄不懂,我没有粘出代码的就是我不懂的。希望先通过与同学的交流来学习不懂的部分,再不行就只能麻烦老师了。