8.Linux文件编程
8.Linux文件编程
文件描述符:
在Linux系统中,所有打开的文件对应一个数字,这个数字我们称为:文件描述符。
下面我们通过下面的几个函数来入门:
打开文件:
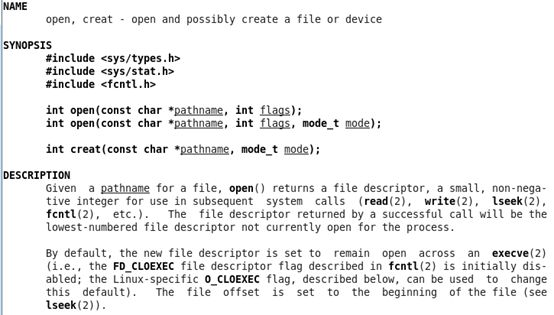
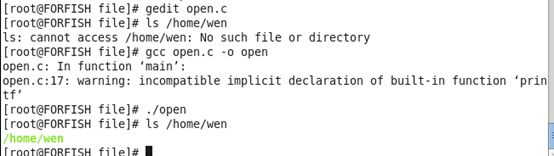
在命令行执行:man open.得到下面的信息。
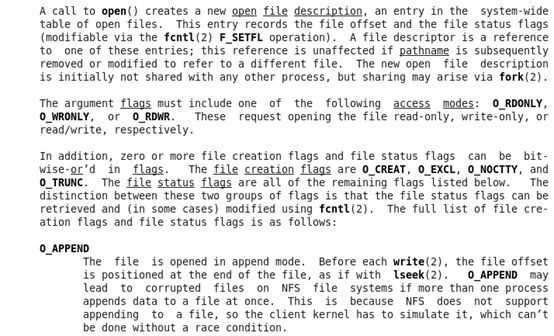
我们从帮助文档知道:open函数的功能是:open and possibly create a file or device.该函数有两种形式存在:
int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
使用该函数需要包含的头文件:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
open() 函数的返回值:the new file descriptor or -1 if an error occurred.
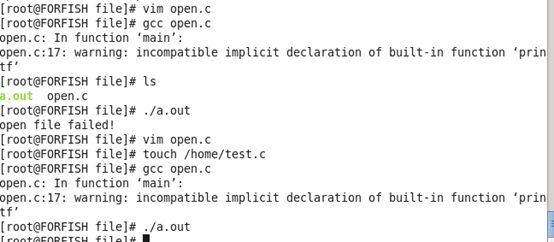
代码:open.c:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
void main(){
int fd;
fd = open("/home/test.c",O_RDWR);
if(fd<0){
printf("open file failed!\n");
}
}
编译过程:
如果文件不存在则创建:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
void main(){
int fd;
fd = open("/home/wen",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0755);
if(fd<0){
printf("open file failed!\n");
}
}
创建文件:
我们从帮助文档知道:creat函数的功能是:open and possibly create a file or device.该函数有两种形式存在:
int creat(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);使用该函数需要包含的头文件:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
creat 函数的返回值:the new file descriptor or -1 if an error occurred.
代码creat.c:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
void main(){
int fd;
fd = creat("/home/wen",0755);
if(fd<0){
printf("create file failed!\n");
}
}
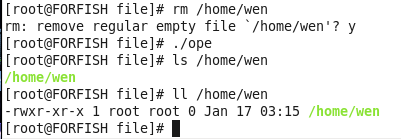
运行结果:
关闭文件:
先在命令行执行:man close.部分截图如下。
我们从上面的帮助文档知道,close函数的功能是close a file descriptor。函数的有一个参数就是文件描述符fd。使用该函数需要包含头文件unistd.h。至于该函数的返回值:返回0表示关闭成功。返回-1表示关闭异常。Appropriately:适当的,合适的。
close.c文件的代码:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void main(){
int fd;
int fod;
fd = creat("/home/wen",0755);
if(fd<0){
printf("create file failed!\n");
}
fod = open("/home/wen",O_RDWR);
if(fod<0){
printf("open file failed!\n");
}
close(fod);
}
读文件:
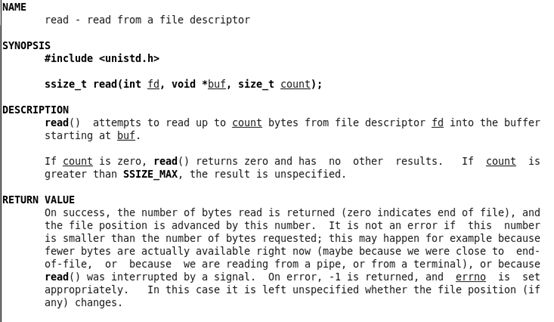
在命令行执行:man 2 read得到下面的信息:
我们从帮助文档知道read函数的功能是在一个文件描述符中读取内容。使用read函数需要包含unistd.h头文件。该函数有三个参数:
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
第一个个参数是文件描述符,第二个参数是读入的地方,第三个参数是读入的大小。如果读入的大小是0则返回0,如果读入的内容大于count,则返回的大小不确定,成功就返回读入的字节数,大小是count,放在缓冲区buf。
read.c的代码:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void main(){
int fd;
char buf[12];
fd = open("/home/wen",O_RDWR);
if(fd<0){
printf("open file failed!\n");
}
read(fd,buf,7);
buf[7] = "\0";
printf("buf is %s\n",buf);
close(fd);
}
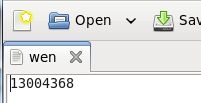
文件/home/wen的内容:
![]()
运行结果:
写文件
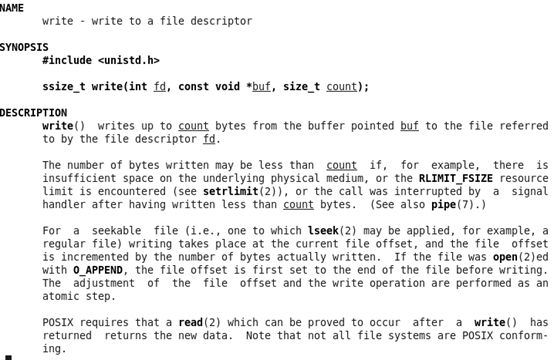
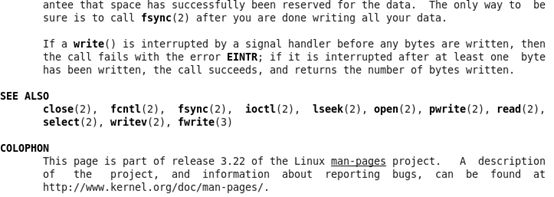
在命令行执行man 2 write,得到下面的信息:
从上面知道wirte的功能是向一个打开的文件写入数据,他的原型是:
ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);需要包含的头文件unistd.h。如果写失败返回-1.功能是从buf里取出count个字节,写入到fd的文件描述符里。
write.c的代码:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void main(){
int fd;
char *buf = "1300436815";
fd = open("/home/wen",O_RDWR);
if(fd<0){
printf("open file failed!\n");
}
write(fd,buf,8);
close(fd);
}
运行结果:
上面我们已经学习了对文件的读和写的两种操作,那么下面的这个函数能不能把我们写入的内容读出来呢?代码如下:
运行的结果:
我们看到,读出的内容根本不是我们想象的。这是因为文件读写指针的问题。因为我们是先写操作,此时执行完写后,文件读写指针已经在文件内容的末尾,再往下读,读出来就是我们想不到的。这就是我接下来要学习的了。
定位文件:
在命令行man 2 lseek得到下面的内容:
我们从上面的帮助文档知道lseek的功能是重新定位文件读写指针。原型:
off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence);
需要包含的头文件:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
该函数的返回值是移动后的文件指针距离文件头的位置,如果失败则返回-1.他有三个参数。第一个参数是指定文件,offset是偏移量,整数向前,负数向后。whence只有三种取值:SEEK_SET、SEEK_CUR和SEEK_END。我们通过whence参数决定了指针开始移动的位置,而通过偏移量offset可以设置移动的大小。
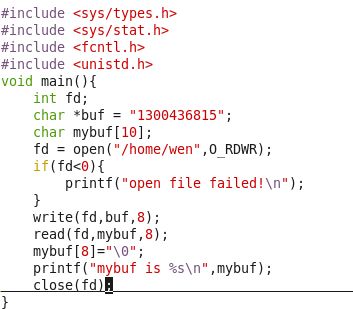
我们在上一节的代码加上,代码如下:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void main(){
int fd;
char *buf = "1300436815";
char mybuf[10];
fd = open("/home/wen",O_RDWR);
if(fd<0){
printf("open file failed!\n");
}
write(fd,buf,8);
lseek(fd,0,SEEK_SET);//locate in beginning
read(fd,mybuf,8);
mybuf[8]="\0";
printf("mybuf is %s\n",mybuf);
close(fd);
}
运行结果:
从上面的运行结果看到,我们要的效果出来了。
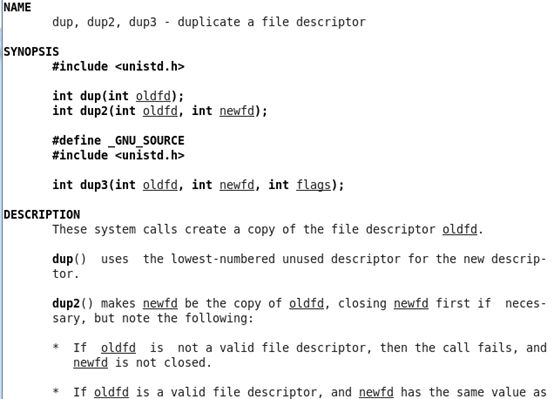
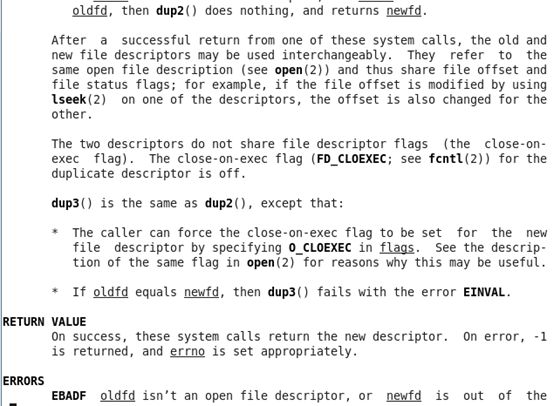
复制文件描述符:
在帮助文档里的信息:
复制文件描述符dup函数,他需要包含的头文件:
#include <unistd.h>
dup函数:
int dup(int oldfd);
int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <unistd.h>
int dup3(int oldfd, int newfd, int flags);
dup函数的功能是从一个旧的文件描述符,复制一个新的文件描述符。当我们使用的是dup()时候,如果成功返回值就是新的文件描述符,失败则是返回-1.
write.c的内容改为:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void main(){
int fd;
char *buf = "1300436815";
char mybuf[10];
fd = open("/home/wen",O_RDWR);
if(fd<0){
printf("open file failed!\n");
}
int mydup = dup(fd);
write(mydup,buf,8);
lseek(fd,0,SEEK_SET);//locate in beginning
read(fd,mybuf,8);
mybuf[8]="\0";
printf("mybuf is %s\n",mybuf);
close(fd);
}
运行的结果跟前面的一个,说明复制成功,如下:
综合实例:文件复制:
在我们的linux中复制文件的命令是:cp sofile gotfile
我们实现的步骤是:1.打开源文件 2.打开目标文件 3.读出源文件的内容 4.将读出的内容写入到目标文件。这就实现了文件的复制了。
copy.c 的代码:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void main(int argc, char **argv){
int fd_s;
int fd_t;
int count=0;
char buf[512];
//open source file
fd_s = open(argv[1],O_RDONLY);
//open target file
fd_t = open(argv[2],O_RDWR | O_CREAT,0777);
//read source file and write to the target file
while((count = read(fd_s,buf,512)) > 0){
write(fd_t,buf,count);
}
//close all file
close(fd_s);
close(fd_t);
}
执行的过程:
source.c的内容:
生成的target.c的内容: