C++ Primer 学习笔记_47_STL剖析(二):vector源码剖析、内存分配器Allocator
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
return 0;
}
vector() _NOEXCEPT
: _Mybase()
{ // construct empty vector
}
explicit vector(const _Alloc& _Al) _NOEXCEPT
: _Mybase(_Al)
{ // construct empty vector, allocator
}
allocator() _THROW0()
{ // construct default allocator (do nothing)
}
_Vector_alloc(const _Alloc& _Al = _Alloc())
: _Mypair(_One_then_variadic_args_t(), _Al)
{ // construct allocator from _Al
_Alloc_proxy();
}
_Vector_val()
{ // initialize values
_Myfirst = pointer();
_Mylast = pointer();
_Myend = pointer();
}
pointer _Myfirst; // pointer to beginning of array
pointer _Mylast; // pointer to current end of sequence
pointer _Myend; // pointer to end of array
};
1、首先,vector 在VC 2008 中的实现比较复杂,虽然vector 的声明跟VC6.0 是一致的,如下:
template < class _Ty, class _Ax = allocator<_Ty> > //第二参数是有默认参数的 class vector;
2、但在VC2008 中vector 还有基类,如下:
// TEMPLATE CLASS vector
template < class _Ty,
class _Ax >
class vector
: public _Vector_val<_Ty, _Ax>
{
};
3、稍微来看一下基类_Vector_val:
// TEMPLATE CLASS _Vector_val
template < class _Ty,
class _Alloc >
class _Vector_val
: public _CONTAINER_BASE_AUX_ALLOC<_Alloc>
{
// base class for vector to hold allocator _Alval
protected:
_Vector_val(_Alloc _Al = _Alloc())
: _CONTAINER_BASE_AUX_ALLOC<_Alloc>(_Al), _Alval(_Al)
{
// construct allocator from _Al
}
typedef typename _Alloc::template
rebind<_Ty>::other _Alty;
_Alty _Alval; // allocator object for values
};
4、为了理解_Alty 的类型,还得看一下allocator模板类:
template<class _Ty> class allocator
{
template<> class _CRTIMP2_PURE allocator<void>
{
// generic allocator for type void
public:
template<class _Other>
struct rebind
{
// convert an allocator<void> to an allocator <_Other>
typedef allocator<_Other> other;
};
....
};
...
};
typedef typename _Alloc::template rebind<_Ty>::other _Alty; 整体来看是类型定义,假设现在我们这样使用vector<int>, 那么_Ty 即 int, _Ax 即 allocator<int>,由vector 类传递给基类Vector_val,则_Alloc 即 allocator<int> ;可以看到 allocator<void> 是allocator 模板类的特化, rebind<_Ty> 是成员模板类,other是成员模板类中自定义类型,_Ty 即是int , 那么other 类型也就是allocator<int>, 也就是说_Alty 是类型 allocator<int> 。_Alty _Alval; 即 基类定义了一个allocator<int> 类型的成员,被vector 继承后以后用于为vector 里面元素分配内存等操作。
如 iterator new_data = alloc.allocate(new_size); 注意,标准的vector::iterator 是以模板类实现的,下面的实现简单地将其等同为指针,实际上真正的iterator 类的实现是内部有一个指针成员,指向容器元素。
××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
对比list 的实现,继承它的基类_List_nod 的一个成员 allocator<_Node> _Alnod; 如下:
typename _Alloc::template rebind<_Node>::other _Alnod; // allocator object for nodes
其中 _Node有三个成员,如下:
_Nodeptr _Next; // successor node, or first element if head
_Nodeptr _Prev; // predecessor node, or last element if head
_Ty _Myval; // the stored value, unused if head
如果是list<int> ,那么_Ty 即是int 类型。双向链表在创建一个新结点时,这样实现:
_Nodeptr _Pnode = this->_Alnod.allocate(1); // 即分配一个节点的空间,返回指向这个节点的指针。
实际上list 还继承另外两个基类的两个成员,如下:
typename _Alloc::template rebind<_Nodeptr>::other _Alptr;// allocator object for pointers to nodes
typename _Alloc::template rebind<_Ty>::other _Alty _Alval; // allocator object for values stored in nodes
×××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××××
三、vector动态数组内部如何实现连续空间
1、通过跟踪一个简单的程序,观察vector的capacity分配的过程,通过调试单步执行
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
cout << v.capacity() << endl;
v.push_back(1);
cout << v.capacity() << endl;
v.push_back(1);
cout << v.capacity() << endl;
v.push_back(1);
cout << v.capacity() << endl;
v.push_back(1);
cout << v.capacity() << endl;
v.push_back(1);
cout << v.capacity() << endl;
v.push_back(1);
cout << v.capacity() << endl;
v.push_back(1);
cout << v.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}
capacity 容量的计算方式如下:容量每次增长为 原先容量 + 原先容量 / 2;
增长的源码跟踪结果如下:
size_type _Grow_to(size_type _Count) const
{ // grow by 50% or at least to _Count
size_type _Capacity = capacity();
_Capacity = max_size() - _Capacity / 2 < _Capacity
? 0 : _Capacity + _Capacity / 2; // try to grow by 50%
if (_Capacity < _Count)
_Capacity = _Count;
return (_Capacity);
}
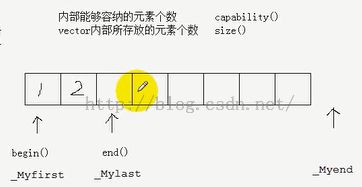
2、容量跟vector 大小的概念是不一样的,capacity >= size,如下图所示:
size 指的是_Mylast - _Myfirst 的区间;capacity 指的是 _Myend - _Myfirst 的区间;也就是说存在尚未使用的空间。
当push_back 的时候往往带有拷贝和析构多个操作,所以一下子分配比size() 大的空间capacity,可以减轻频繁操作造成的效率问题。
通常,向量缓存了一部分内存空间,用来容纳更多的元素,这样,下一次插入新元素的时候,就不必重新分配内存,提高了插入速度。
四、内存分配器Allocator
allocator 模板类:
#include <memory>
template <class T> class allocator
{
public:
T *allocate(size_t);
void deallocate(T *, size_t);
void construct(T *, size_t);
void destroy(T *);
//.......
};
当然实际的接口没实现没那么简单,但大概实现的功能差不多:
allocate 调用operator new ;deallocate 调用 operator delete; construct 调用placement new (即在分配好的内存上调用拷贝构造函数),destroy 调用析构函数。
参考:
C++ primer 第四版
Effective C++ 3rd
C++编程规范