Trie树的常见应用大总结(面试+附代码实现)
(一)Trie的简介
Trie树,又称字典树,单词查找树或者前缀树,是一种用于快速检索的多叉树结构,如英文字母的字典树是一个26叉树,数字的字典树是一个10叉树。他的核心思想是空间换时间,空间消耗大但是插入和查询有着很优秀的时间复杂度。
(二)Trie的定义
和插入操作相仿,若查询途中某一个结点并不存在,则直接就return返回。否则继续下去,当字符串结束时,trie树上也有结束标志,那么证明此字符串存在,return true;
(1)统计前缀出现的次数
这是Trie最基本的应用,每个结点的字母使用count记录出现的次数即可。
这里提供一道题目,hdu 1251供大家练习。
给定一组字符串s,k我们输入k则需要翻译成s,也就是说两者是映射关系。接下来我们给出一段话,让你翻译出正常的文章。用map固然简便,但是Trie的效率更加高。只需要在k的结尾结点出记录下s即可。
这里也提供一道题目,hdu 1075。(被注释的是我原来的程序,wa了,有大神看出来麻烦告诉我一下,谢谢)。
我的初步想法是和(1)类似,对(1)中的trie进行先序遍历,将字符串和出现次数存进一个结构体,最后对这个数组进行快速排序,时间复杂度为O(nlogn),看网上说可以利用分治+trie
+最小堆,我还没有仔细搞清楚,以后研究完在添加。
(4)输入自动补全
其实原理都差不多,把字符串结尾处的结点当作root,进行先序遍历,即可得出所有以输入的字符串为前缀的答案。
Trie树,又称字典树,单词查找树或者前缀树,是一种用于快速检索的多叉树结构,如英文字母的字典树是一个26叉树,数字的字典树是一个10叉树。他的核心思想是空间换时间,空间消耗大但是插入和查询有着很优秀的时间复杂度。
(二)Trie的定义
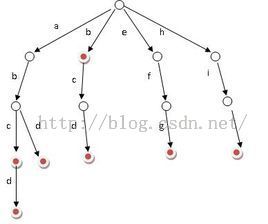
Trie树的键不是直接保存在节点中,而是由节点在树中的位置决定。一个节点的所有子孙都有相同的前缀(prefix),从根节点到当前结点的路径上的所有字母组成当前位置的字符串,结点可以保存当前字符串、出现次数、指针数组(指向子树)以及是否是结尾标志等等。
typedef struct Trie_Node
{
char count[15]; //单词前缀出现的次数
struct Trie_Node* next[MAXN]; //指向各个子树的指针
bool exist; //标记结点处是否构成单词
}Trie;
Trie树可以利用字符串的公共前缀来节约存储空间,如下图所示:

它有3个基本性质:
(1) 根节点不包含字符,除根节点外每一个节点都只包含一个字符。
(2) 从根节点到某一节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,为该节点对应的字符串。
(3) 每个节点的所有子节点包含的字符都不相同。
(三)Trie树的基本操作
(1)插入操作
按下标索引逐个插入字母,若当前字母存在则继续下一个,否则new出当前字母的结点,所以插入的时间复杂度只和字符串的长度n有关,为O(n)。
void Insert(Trie *root, char* s,char *add)
{
Trie *p=root;
while(*s!='\0')
{
if(p->next[*s-'a']==NULL)
{
p->next[*s-'a']=createNode();
}
p=p->next[*s-'a'];
// p->count=add;
++s;
}
p->exist=true;
strcpy(p->count,add);
}(2)查询操作
和插入操作相仿,若查询途中某一个结点并不存在,则直接就return返回。否则继续下去,当字符串结束时,trie树上也有结束标志,那么证明此字符串存在,return true;
int Search(Trie* root,const char* s)
{
Trie *p=root;
while(*s!='\0')
{
p=p->next[*s-'a'];
if(p==NULL)
return 0;
++s;
}
return p->count;
}
(3)删除操作
一般来说,对Trie单个结点的删除操作不常见,所以我在这里也只提供递归删除整个树的操作
void del(Trie *root)
{
for(int i=0;i<MAXN;i++)
{
if(root->next[i]!=NULL)
{
del(root->next[i]);
}
}
// free(root);
delete root;
}
(4)遍历操作
如果我们想要将trie中的字符串排序输出,直接先序遍历即可。
void Print(Trie *root)
{
Trie *p=root;
if(p->exist)
cout<<p->name<<": "<<p->count<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<26;i++)
{
if(p->next[i]!=NULL){
Print(p->next[i]);
}
}
}
(四)Trie树的具体应用
(1)统计前缀出现的次数
这是Trie最基本的应用,每个结点的字母使用count记录出现的次数即可。
这里提供一道题目,hdu 1251供大家练习。
//hdu 1251 统计前缀出现次数
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=26;
typedef struct Trie_Node
{
int count; //单词前缀出现的次数
struct Trie_Node* next[MAXN]; //指向各个子树的指针
bool exist; //标记结点处是否构成单词
}Trie;
Trie* createNode()
{
//Trie* p =(Trie*)malloc(sizeof(Trie));
Trie *p=new Trie;
p->count=0;
p->exist=false;
memset(p->next,0,sizeof(p->next));
return p;
}
void Insert(Trie *root, const char* s)
{
Trie *p=root;
while(*s!='\0')
{
if(p->next[*s-'a']==NULL)
{
p->next[*s-'a']=createNode();
}
p=p->next[*s-'a'];
p->count+=1;
++s;
}
p->exist=true;
}
int Search(Trie* root,const char* s)
{
Trie *p=root;
while(*s!='\0')
{
p=p->next[*s-'a'];
if(p==NULL)
return 0;
++s;
}
return p->count;
}
void del(Trie *root)
{
for(int i=0;i<MAXN;i++)
{
if(root->next[i]!=NULL)
{
del(root->next[i]);
}
}
// free(root);
delete root;
}
int main()
{
char s[15];
bool flag=false;
Trie* root=createNode();
while(gets(s))
{
if(flag)
{
int ans=Search(root,s);
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
else
{
if(strlen(s)!=0)
Insert(root,s);
}
if(strlen(s)==0)
flag=true;
}
del(root);
return 0;
}(2)翻译(密码,明文)
给定一组字符串s,k我们输入k则需要翻译成s,也就是说两者是映射关系。接下来我们给出一段话,让你翻译出正常的文章。用map固然简便,但是Trie的效率更加高。只需要在k的结尾结点出记录下s即可。
这里也提供一道题目,hdu 1075。(被注释的是我原来的程序,wa了,有大神看出来麻烦告诉我一下,谢谢)。
/*
//hdu 1075映射
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=26;
typedef struct Trie_Node
{
char count[15]; //单词前缀出现的次数
struct Trie_Node* next[MAXN]; //指向各个子树的指针
bool exist; //标记结点处是否构成单词
}Trie;
Trie* createNode()
{
Trie* p =(Trie*)malloc(sizeof(Trie));
p->exist=false;
memset(p->next,0,sizeof(p->next));
return p;
}
void Insert(Trie *root, char* s,char *add)
{
Trie *p=root;
while(*s!='\0')
{
if(p->next[*s-'a']==NULL)
{
p->next[*s-'a']=createNode();
}
p=p->next[*s-'a'];
// p->count=add;
++s;
}
p->exist=true;
strcpy(p->count,add);
}
void Search(Trie* root, const char* s)
{
Trie *p=root;
while(*s!='\0')
{
if(p->next[*s-'a']==NULL)
{
printf("%s",s);
return ;
}
p=p->next[*s-'a'];
++s;
}
if(p->exist)
printf("%s",p->count);
else
printf("%s",s);
}
void del(Trie *root)
{
for(int i=0;i<MAXN;i++)
{
if(root->next[i]!=NULL)
{
del(root->next[i]);
}
}
free(root);
}
int main()
{
char text[3013],from[15],to[15];
Trie* root=createNode();
scanf("%s",from);
while(scanf("%s",from),strcmp(from,"END"))
{
scanf("%s",to);
Insert(root,to,from);
}
scanf("%s",from);
getchar();
while(gets(text),strcmp(text,"END"))
{
int len=strlen(text);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if(islower(text[i]))
{
int j=0;
char temp[15];
memset(temp,'\0',sizeof(temp));
while(islower(text[i]))
temp[j++]=text[i++];
Search(root,temp);
}
if(!islower(text[i]))
printf("%c",text[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct node{
char dic[15];
node * next[26];
bool flag;
}*root;
node *build()
{
node *p=(node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
for(int i=0;i<26;i++)
p->next[i]=NULL;
p->flag=false;
return p;
}
void insert(char *earth,char *mars)
{
int len=strlen(mars);
node *p;
p=root;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if(p->next[mars[i]-'a']==NULL)
p->next[mars[i]-'a']=build();
p=p->next[mars[i]-'a'];
}
p->flag=true;
strcpy(p->dic,earth);
}
void query(char *earth)
{
int len=strlen(earth);
node *p;
p=root;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if(p->next[earth[i]-'a']==NULL)
{
printf("%s",earth);
return;
}
p=p->next[earth[i]-'a'];
}
if(p->flag)
printf("%s",p->dic);
else
printf("%s", earth);
}
int main()
{
char earth[15],mars[15],ask[3010];
scanf("%s",earth);
root=build();
while(scanf("%s",earth),strcmp(earth,"END"))
{
scanf("%s",mars);
insert(earth,mars);
}
scanf("%s",earth);
getchar();
while(gets(ask),strcmp(ask,"END"))
{
int len=strlen(ask);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if(islower(ask[i]))
{
int j=0;
memset(earth,'\0',sizeof(earth));
while(islower(ask[i]))
earth[j++]=ask[i++];
query(earth);
}
if(!islower(ask[i]))
printf("%c",ask[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}(3)实现搜索引擎的热门搜索排名
我的初步想法是和(1)类似,对(1)中的trie进行先序遍历,将字符串和出现次数存进一个结构体,最后对这个数组进行快速排序,时间复杂度为O(nlogn),看网上说可以利用分治+trie
+最小堆,我还没有仔细搞清楚,以后研究完在添加。
(4)输入自动补全
其实原理都差不多,把字符串结尾处的结点当作root,进行先序遍历,即可得出所有以输入的字符串为前缀的答案。
/ 自动补全
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=26;
typedef struct Trie_Node
{
int count; //单词出现的次数
struct Trie_Node* next[MAXN]; //指向各个子树的指针
bool exist; //标记结点处是否构成单词
char name[15];
}Trie;
Trie* createNode()
{
Trie* p =(Trie*)malloc(sizeof(Trie));
p->count=0;
p->exist=false;
memset(p->next,0,sizeof(p->next));
return p;
}
void Insert(Trie *root,char* word)
{
Trie *p=root;
char *s=word;
while(*s!='\0')
{
if(p->next[*s-'a']==NULL)
{
p->next[*s-'a']=createNode();
}
p=p->next[*s-'a'];
++s;
}
p->exist=true;
p->count+=1;
strcpy(p->name,word);
}
Trie* Search(Trie* root, char* s)
{
Trie *p=root;
while(*s!='\0')
{
p=p->next[*s-'a'];
if(p==NULL)
return 0;
++s;
}
return p;
}
void del(Trie *root)
{
for(int i=0;i<MAXN;i++)
{
if(root->next[i]!=NULL)
{
del(root->next[i]);
}
}
free(root);
}
void Print(Trie *root)
{
Trie *p=root;
if(p->exist)
cout<<p->name<<": "<<p->count<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<26;i++)
{
if(p->next[i]!=NULL){
Print(p->next[i]);
}
}
}
int main()
{
char s[15];
Trie* root=createNode();
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
cin>>s;
Insert(root,s);
}
while(cin>>s)
{
Trie *ans=Search(root,s);
if(ans)
Print(ans);
}
del(root);
return 0;
}