浅析Android View(二)
深入理解Android View(一) View的位置参数信息
二、View的绘制过程
View的绘制过程一共分为三个部分:
- measure(测量View的大小)
- layout(确定View的位置)
- draw(画出View)
通常我们的View都是以这样的树结构呈现的,如下图
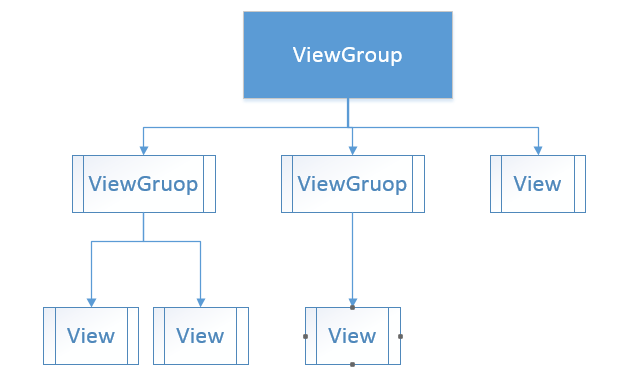
当然我们这里ViewGroup其实上面其实是放在DecorView中的,我们可以通过findViewbById(andorid.id.content)获取到顶级ViewGroup,这里的DecorView开发中一般涉及不到,这里我们不过多分析,我们只需要知道我们的绘制过程是从DecorView分发下来的即可。我们先来看ViewGroup中的一段源码
protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int size = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) {
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}这里我们可以看到在ViewGroup中的measureChildren的方法,首先获取到了所有的子View,然后调用View的measure方法进行子View的测量,这样就完成了一次测量过程,然后子View会重复父View的操作,如此返回就完成了整个View树的测量过程。通过源码我们发现一个View的大小,主要由父View的MeasureSpec和自身的LayoutParams来共同决定,LayoutParams我们应都比较熟悉了,接下来我们就来深入分析MeasureSpec,这是在View类中的一个静态内部类,看名字就能猜到它代表它的作用是一种测量标准或者说测量规格,我们先来看下它的源码
public static class MeasureSpec {
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;
private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static int makeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode) {
if (sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec) {
// 老版api
return size + mode;
} else {
return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK);
}
}
public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
}
public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
}
}
MeasureSpec代表一个32位的int值,高两位代表SpecMode,低30位代表SpecSize,Mode指测量模式,Size则指测量的大小,通过看MeasureSpec的源码也能看到,其实这里谷歌工程师非常巧妙的把Mode和Size封装到了一个int值中,非常巧妙的办法(这种设计方式可以借鉴),如果你对Java运算符不太熟的话,你可以这样理解,谷歌工程师把一个32位的int分成了两节,一节用来表示Mode,一节用来表示Size。可以看到Mode分为三种模式如下所示:
- UNSPECIFIED
父容器不对子View做任何限制,要多大给多大,一般用于系统内部,这里不用过多考虑 - EXACTLY
精准模式,一般View指定了具体的大小(dp/px)或者设置为match_parent则就是这个模式 - AT_MOST
父容器制定了一个可用的大小,子View不能大于这个值,对于wrap_content
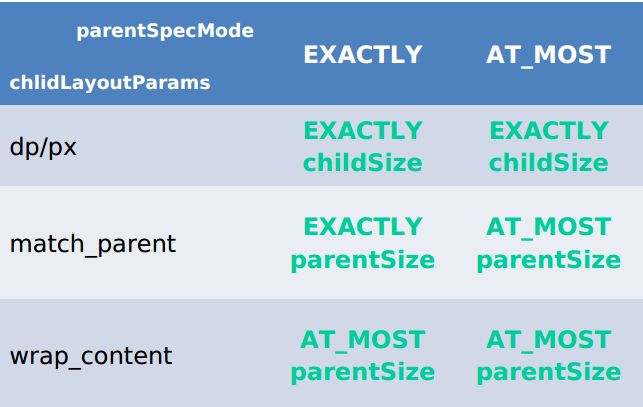
这里借用任主席博客中的一张图,UNSPECIFIED 我们不予考虑。
总结:一个View的绘制主要由父View的MeasureSpec和自身的LayoutParams决定,其关系如上表。说了这么多其实大多数时候当我自定义View时,只需要处理AT_MOST即可,通用代码如下:
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//分别获取宽高的Mode 和size
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
// 如果是精准模式则直接使用获取到的宽高,如果是AT_MOST,则使用我 们自己测量的宽高
if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mHeight);
} else if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, heightSpecSize);
} else if (heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize, mHeight);
}
}如果当前是View则直接完成测量,如果当前是ViewGruop除了完成自身绘制外,还需要遍历调用子View的measure方法。
View的layout方法和Draw方法就比较简单了,layout用于确定View的位置,原理和Measure过程类似,当一个ViewGroup的位置被确定之后,会遍历其所有子View并调用其layout方法。Draw的过程也类似,通过dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas)方法,遍历子View,通过canvas进行Draw过程,接下来我通过一个小Demo流式布局,来运用一下三个过程
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import android.content.Context; import android.util.AttributeSet; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewGroup; /** * */ public class FlowLayout extends ViewGroup { /** * 存储所有的子View */ private List<List<View>> mAllChildViews = new ArrayList<List<View>>(); /** * 存储每一行的高度 */ private List<Integer> mLineHeight = new ArrayList<Integer>(); public FlowLayout(Context context) { this(context, null); } public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs, 0); } public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) { super(context, attrs, defStyle); } @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { mAllChildViews.clear(); mLineHeight.clear(); // 获取当前ViewGroup的宽度 int width = getWidth(); int lineWidth = 0; int lineHeight = 0; // 记录当前行的view List<View> lineViews = new ArrayList<View>(); int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { View child = getChildAt(i); MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child .getLayoutParams(); int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight(); // 如果需要换行 if (childWidth + lineWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin > width) { // 记录LineHeight mLineHeight.add(lineHeight); // 记录当前行的Views mAllChildViews.add(lineViews); // 重置行的宽高 lineWidth = 0; lineHeight = childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin; // 重置view的集合 lineViews = new ArrayList(); } lineWidth += childWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin; lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin); lineViews.add(child); } // 处理最后一行 mLineHeight.add(lineHeight); mAllChildViews.add(lineViews); MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) this.getLayoutParams(); // 设置子View的位置 int left = 0; // 添加marginTop int top = 0 + params.topMargin; // 获取行数 int lineCount = mAllChildViews.size(); for (int i = 0; i < lineCount; i++) { // 当前行的views和高度 lineViews = mAllChildViews.get(i); lineHeight = mLineHeight.get(i); for (int j = 0; j < lineViews.size(); j++) { // 为每一列设置marginLeft if (j == 0) { left = 0 + params.leftMargin; } View child = lineViews.get(j); // 判断是否显示 if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) { continue; } MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child .getLayoutParams(); int cLeft = left + lp.leftMargin; int cTop = top + lp.topMargin; int cRight = cLeft + child.getMeasuredWidth(); int cBottom = cTop + child.getMeasuredHeight(); // 进行子View进行布局 child.layout(cLeft, cTop, cRight, cBottom); left += child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin; } left = 0; top += lineHeight; } } @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { // 父控件传进来的宽度和高度以及对应的测量模式 int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); // 如果当前ViewGroup的宽高为wrap_content的情况 int width = 0;// 自己测量的 宽度 int height = 0;// 自己测量的高度 // 记录每一行的宽度和高度 int lineWidth = 0; int lineHeight = 0; // 获取子view的个数 int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { View child = getChildAt(i); // 测量子View的宽和高 measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); // 得到LayoutParams MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) child .getLayoutParams(); // 子View占据的宽度 int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin; // 子View占据的高度 int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + params.bottomMargin + params.topMargin; // 换行时候 if (lineWidth + childWidth > sizeWidth) { // 对比得到最大的宽度 width = Math.max(width, lineWidth); // 重置lineWidth lineWidth = childWidth; // 记录行高 height += lineHeight; lineHeight = childHeight; } else { // 不换行情况 // 叠加行宽 lineWidth += childWidth; // 得到最大行高 lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight); } // 处理最后一个子View的情况 if (i == childCount - 1) { width = Math.max(width, lineWidth); height += lineHeight; } } // 这里就是关键代码 setMeasuredDimension(modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeWidth : width, modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeHeight : height); } /** * 与当前ViewGroup对应的LayoutParams */ @Override public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) { return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs); } }