初探linux子系统集之i2c子系统(二)
大概也是前年了,一直没有把那个i2c的子系统讲解完,这里偷个懒,把以前整理的i2c相关的知识再梳理一下,做个了结,然后再去学习timer子系统。
先看下i2c在内核中的代码分布:
obj-$(CONFIG_I2C_BOARDINFO) += i2c-boardinfo.o obj-$(CONFIG_I2C) += i2c-core.o obj-$(CONFIG_I2C_SMBUS) += i2c-smbus.o obj-$(CONFIG_I2C_CHARDEV) += i2c-dev.o obj-$(CONFIG_I2C_MUX) += i2c-mux.o obj-y += algos/ busses/ muxes/i2c的核心是i2c-core.c实现了i2c核心功能,i2c-dev.c实现了应用的交互接口。至于algos里面那主要实现的是总线适配,busses主要就是一些控制器相关的和gpio模拟的i2c,之后我们会详细介绍gpio模拟的i2c的代码。
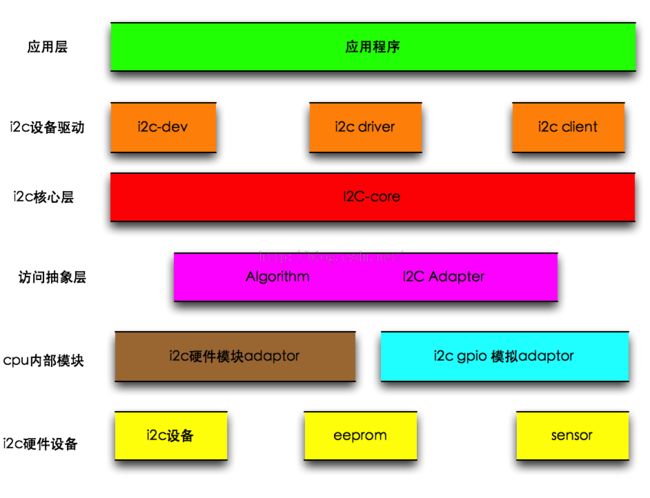
既然看了代码分布,那么还是先要了解下i2c的框架了:
其中adaptor是i2c的总线驱动,dev和driver,client是i2c的设备驱动。一般如果要实现芯片的i2c驱动,那么就需要实现总线驱动,而设备驱动一般都是通用的。
好了,既然已经知道了i2c的基本框架,那么就来看看他的数据结构了:
struct i2c_msg; struct i2c_algorithm; struct i2c_adapter; struct i2c_client; struct i2c_driver; union i2c_smbus_data; struct i2c_board_info;I2C 的 driver
struct i2c_driver {
unsigned int class;//I2C设备类型
/* Notifies the driver that a new bus has appeared or is about to be
* removed. You should avoid using this, it will be removed in a
* near future.
*/
int (*attach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *) __deprecated;
int (*detach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *) __deprecated;
/* Standard driver model interfaces */
int (*probe)(struct i2c_client *, const struct i2c_device_id *);
int (*remove)(struct i2c_client *);
/* driver model interfaces that don't relate to enumeration */
void (*shutdown)(struct i2c_client *);
int (*suspend)(struct i2c_client *, pm_message_t mesg);
int (*resume)(struct i2c_client *);
/* Alert callback, for example for the SMBus alert protocol.
* The format and meaning of the data value depends on the protocol.
* For the SMBus alert protocol, there is a single bit of data passed
* as the alert response's low bit ("event flag").
*/
void (*alert)(struct i2c_client *, unsigned int data);
/* a ioctl like command that can be used to perform specific functions
* with the device.
*/
int (*command)(struct i2c_client *client, unsigned int cmd, void *arg);
struct device_driver driver;
const struct i2c_device_id *id_table;
/* Device detection callback for automatic device creation */
int (*detect)(struct i2c_client *, struct i2c_board_info *);
const unsigned short *address_list; //要检测的I2C地址
struct list_head clients;
};
I2C的client
识别单个设备连接到一个总线上。
struct i2c_client {
unsigned short flags; /* div., see below */
unsigned short addr; /* chip address - NOTE: 7bit */
/* addresses are stored in the */
/* _LOWER_ 7 bits */
char name[I2C_NAME_SIZE]; //设备名
struct i2c_adapter *adapter; /* the adapter we sit on *///I2C主控制器
struct i2c_driver *driver; /* and our access routines *///I2C设备驱动
struct device dev; /* the device structure */从机的驱动类型设备节点
int irq; /* irq issued by device */ //中断号
struct list_head detected;
};
I2C的board_info
struct i2c_board_info {
char type[I2C_NAME_SIZE]; //I2C设备名
unsigned short flags; //i2c_client.flags的初始化
unsigned short addr; //设备地址
void *platform_data;
struct dev_archdata *archdata;
struct device_node *of_node;
int irq; //设备中断号
};
I2C的algorithm
所有的驱动时序都是在算法中实现的
struct i2c_algorithm {
/* If an adapter algorithm can't do I2C-level access, set master_xfer
to NULL. If an adapter algorithm can do SMBus access, set
smbus_xfer. If set to NULL, the SMBus protocol is simulated
using common I2C messages */
/* master_xfer should return the number of messages successfully
processed, or a negative value on error */
int (*master_xfer)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs,
int num);
int (*smbus_xfer) (struct i2c_adapter *adap, u16 addr,
unsigned short flags, char read_write,
u8 command, int size, union i2c_smbus_data *data);
/* To determine what the adapter supports */
u32 (*functionality) (struct i2c_adapter *);
};
I2C的adapter
主控制器,用以鉴定i2c总线
struct i2c_adapter {
struct module *owner;
unsigned int class; /* classes to allow probing for */
const struct i2c_algorithm *algo; /* the algorithm to access the bus */
void *algo_data;
/* data fields that are valid for all devices */
struct rt_mutex bus_lock;
int timeout; /* in jiffies */
int retries;
struct device dev; /* the adapter device */
int nr;
char name[48];
struct completion dev_released;
struct mutex userspace_clients_lock;
struct list_head userspace_clients;
};.
I2C的msg
在调用i2c_transfer的时候发送或者接收数据
struct i2c_msg {
__u16 addr; /* slave address*/
__u16 flags; //读写等的标志
#define I2C_M_TEN 0x0010 /* this is a ten bit chip address */
#define I2C_M_RD 0x0001 /* read data, from slave to master */
#define I2C_M_NOSTART 0x4000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_REV_DIR_ADDR 0x2000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK 0x1000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_NO_RD_ACK 0x0800 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_RECV_LEN 0x0400 /* length will be first received byte */
__u16 len; /* msg length *//发送和接收的buf的长度/
__u8 *buf; /* pointer to msg data*///发送或者接收的buf
};
I2C 的 gpio 模拟用的 platform_data
struct i2c_gpio_platform_data {
unsigned int sda_pin;
unsigned int scl_pin;
int udelay;
int timeout;
unsigned int sda_is_open_drain:1;
unsigned int scl_is_open_drain:1;
unsigned int scl_is_output_only:1;
};
主要数据结构就是这些,接下去的话在下一篇文章中简单介绍下gpio模拟的i2c的流程。