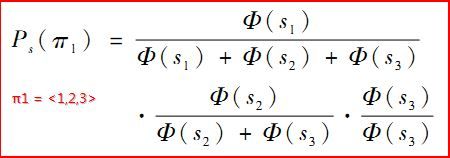【学习排序】 Learning to Rank 中Listwise关于ListNet算法讲解及实现
前一篇文章"Learning to Rank中Pointwise关于PRank算法源码实现"讲述了基于点的学习排序PRank算法的实现.该篇文章主要讲述Listwise Approach和基于神经网络的ListNet算法及Java实现.包括:
1.基于列的学习排序(Listwise)介绍
2.ListNet算法介绍
3.ListNet算法Java实现
LTR中单文档方法是将训练集里每一个文档当做一个训练实例,文档对方法是将同一个查询的搜索结果里任意两个文档对作为一个训练实例,文档列方法是将一个查询里的所有搜索结果列表作为一个训练实例.
一. 基于列的学习排序(Listwise)介绍
Listwise方法将一个查询对应的所有搜索结果评分作为一个实例,训练得到一个最优的评分函数.在给出如下数据集中:(数据集介绍详见上一篇文章)
下面介绍一种基于搜索结果排序组合的概率分布情况来训练.如下图:
参考《这就是搜索引擎:核心技术详解 by:张俊林》第5章
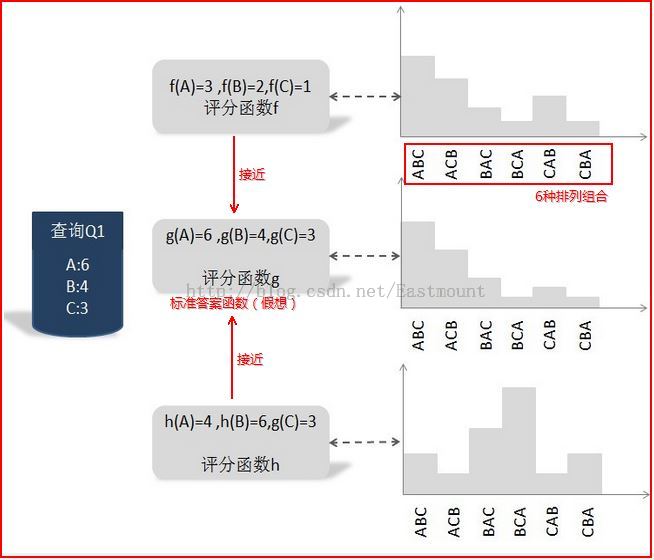
我们可以把函数g设想成最优评分函数(人工打分),对查询Q1来说:文档A得6分,文档B得4分,文档C得3分;我们的任务是找到一个函数,使得其对Q1的搜索结果打分顺序尽可能的接近标准函数g.其中函数f和h就是实际的评分函数,通过比较两个概率之间的KL距离,发现f比h更接近假想的最优函数g.故选择函数f为搜索的评分函数.
Listwise主要的算法包括:AdaRank、SVM-MAP、ListNet、LambdaMART等.
二. ListNet算法介绍
Pointwise学习排序是将训练集中的每个文档看作一个样本获取Rank函数,主要解决办法是把分类问题转换为单个文档的分类和回归问题,如PRank.
Pairwise学习排序(下篇介绍)是将同一个查询中不同的相关标注的两个文档看作一个样本,主要解决思想是把Rank问题转换为二值分类问题,如RankNet.
Listwise学习排序是将整个文档序列看作一个样本,主要是通过直接优化信息检索的评价方法和定义损失函数两种方法实现.ListNet算法将Luce模型引入到了排序学习方法中来表示文档序列,同时大多数基于神经网络的排序学习算法都是基于Luce模型(Luce模型就是将序列的任意一种排序方式表示成一个概率值)来表示序列的排序方式的.
ListNet算法参考:
《Learning to Rank: From Pairwise Approach to Listwise Approach》
《基于神经网络的Listwise排序学习方法的研究》 By:林原

1.首先输入训练集train.txt数据.{x,y}表示查询号对应的样本文档,包括标注等级Label=y(46维微软数据集共3个等级:0-不相关,1-部分相关,2-全部相关),x表示对应的特征和特征值,需要注意的是x(m)表示m个qid数,每个x(m)中有多个样本文档.
2.初始化操作.迭代次数T(设置为30次)和Learning rate(ita可以为0.003、0.001、0.03、0.01等),同时初始化权重w.
3.两层循环操作.第一层是循环迭代次数:for t = 1 to T do;第二层循环是迭代查询总数(qid总数):for i = 1 to m do.
4.计算该行分数用当前权重w.注意权重w[46]是一维数组,分别对应46个特征值,同时f(w) = w * x.

三. ListNet算法Java实现
(PS:该部分代码非常感谢我的组长XP和MT,他们在整个编程路上对我帮助是一生的.同时自己也希望以后工作中能找到更多的老师和挚友指导我前行~)
代码中有详细的注释,按照每个步骤完成.左图是主函数,它主要包括:读取文件并解析数据、写数据、学习排序模型和打分预测,右图是学习排序的核心算法.


package listNet_xiuzhang;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class listNet {
//文件总行数(标记数)
private static int sumLabel;
//特征值 46个 (标号1-46)
private static double feature[][] = new double[100000][48];
//特征值权重 46个 (标号1-46)
private static double weight [] = new double[48];
//相关度 其值有0-2三个级别 从1开始记录
private static int label [] = new int[1000000];
//查询id 从1开始记录
private static int qid [] = new int[1000000];
//每个Qid的doc数量
private static int doc_ofQid[] = new int[100000];
private static int ITER_NUM=30; //迭代次数
private static int weidu=46; //特征数
private static int qid_Num=0; //Qid数量
private static int tempQid=-1; //临时Qid数
private static int tempDoc=0; //临时doc数
/**
* 函数功能 读取文件
* 参数 String filePath 文件路径
*/
public static void ReadTxtFile(String filePath) {
try {
String encoding="GBK";
File file=new File(filePath);
if(file.isFile() && file.exists()) { //判断文件是否存在
InputStreamReader read = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file), encoding);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(read);
String lineTxt = null;
sumLabel =1; //初始化从1记录
//按行读取数据并分解数据
while((lineTxt = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
String str = null;
int lengthLine = lineTxt.length();
//获取数据 字符串空格分隔
String arrays[] = lineTxt.split(" ");
for(int i=0; i<arrays.length; i++) {
//获取每行样本的Label值
if(i==0) {
label[sumLabel] = Integer.parseInt(arrays[0]);
}
else if(i>=weidu+2){ //读取至#跳出 0-label 1-qid 2:47-特征
continue;
}
else {
String subArrays[] = arrays[i].split(":"); //特征:特征值
if(i==1) { //获取qid
//判断是否是新的Qid
if(tempQid != Integer.parseInt(subArrays[1])) {
if(tempQid != -1){ //不是第一次出现新Qid
//赋值上一个为qid_Num对应的tempDoc个文档
doc_ofQid[qid_Num]=tempDoc;
tempDoc=0;
}
//当tempQid不等于当前qid时下标加1
//相等则直接跳至Doc加1直到不等
qid_Num++;
tempQid=Integer.parseInt(subArrays[1]);
}
tempDoc++; //新的文档
qid[sumLabel] = Integer.parseInt(subArrays[1]);
}
else { //获取46维特征值
int number = Integer.parseInt(subArrays[0]); //判断特征
double value = Double.parseDouble(subArrays[1]);
feature[sumLabel][number] = value; //number数组标号:1-46
}
}
}
sumLabel++;
}
doc_ofQid[qid_Num]=tempDoc;
read.close();
} else {
System.out.println("找不到指定的文件\n");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("读取文件内容出错");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 学习排序
* 训练模型得到46维权重
*/
public static void LearningToRank() {
//变量
double index [] = new double[1000000];
double tao [] = new double[1000000];
double yita=0.00003;
//初始化
for(int i=0;i<weidu+2;i++) { //从1到136为权重,0和137无用
weight[i] = (double) 1.0; //权重初值
}
System.out.println("training...");
//计算权重 学习算法
for(int iter = 0; iter<ITER_NUM; iter++) //迭代ITER_NUM次
{
System.out.println("---迭代次数:"+iter);
int now_doc=0; //全局文档索引
for(int i=1; i<=qid_Num; i++) //总样qid数 相当于两层循环T和m
{
double delta_w[] = new double[weidu+2]; //46个梯度组成的向量
int doc_of_i=doc_ofQid[i]; //该Qid的文档数
//得分f(w),一个QID有多个文档,一个文档为一个分,所以一个i对应一个分数数组
double fw[] = new double[doc_of_i+2];
/* 第一步 算得分数组fw fin */
for(int k=1;k<=doc_of_i;k++) { //初始化
fw[k]=0.0;
}
for(int k=1;k<=doc_of_i;k++) { //每个文档的得分
for(int p=1;p<=weidu;p++) {
fw[k]=fw[k]+weight[p]*feature[now_doc+k][p]; //算出这个文档的分数
}
}
/*
* 第二步 算梯度delta_w向量
* a=Σp*x,a是向量
* b=Σexpf(x),b是数字
* c=expf(x)*x,c是向量
* 最终结果delta_w是向量
*/
double[] a=new double[weidu+2],c=new double[weidu+2];
for(int k=0;k<weidu+2;k++){a[k]=0.0;} //初始化
for(int k=0;k<weidu+2;k++){c[k]=0.0;} //初始化
double b=0.0;
//算a:----
for(int k=1; k<=doc_of_i; k++) {
double p=1.0; //先不topK
double[] temp=new double[48];
for(int q=1;q<=weidu;q++) {
//算P: ----第q个向量排XX的概率是多少
//分母:
double fenmu=0.0;
for(int m=1;m<=doc_of_i;m++) {
fenmu=fenmu+Math.exp(fw[m]); //所有文档得分
}
//top-1 exp(s1) / exp(s1)+exp(s2)+..+exp(sn)
for(int m=1;m<=doc_of_i;m++) {
p=p*(Math.exp(fw[m])/fenmu);
}
//算积
temp[q]=temp[q]+p*feature[now_doc+k][q];
}
for(int q=1; q<=weidu; q++){
a[q]=a[q]+temp[q];
}
} //End a
//算b:---- fin.
for(int k=1; k<=doc_of_i; k++){
b=b+Math.exp(fw[k]);
}
//算c:----
for(int k=1; k<=doc_of_i; k++){
double[] temp=new double[weidu+2];
for(int q=1; q<=weidu; q++){
temp[q]=temp[q]+Math.exp(fw[k])*feature[now_doc+k][q];
}
for(int q=1; q<=weidu; q++){
c[q]=c[q]+temp[q];
}
}
//算梯度:delta_x=-a+1/b*c
for(int q=1; q<=weidu; q++){
delta_w[q]= (-1)*a[q] + ((1.0/b)*c[q]);
}
//**********
/* 第三步 更新权重 fin. */
for(int k=1; k<=weidu; k++){
weight[k]=weight[k]-yita*delta_w[k];
}
now_doc=now_doc+doc_of_i; //更新当前文档索引
}
} //End 迭代次数
//输出权重
for(int i=1;i<=weidu;i++) //从1到136为权重,0和137无用
{
System.out.println(i+"wei:"+weight[i]);
}
}
/**
* 输出权重到文件fileModel
* @param fileModel
*/
public static void WriteFileModel(String fileModel) {
//输出权重到文件
try {
System.out.println("write start.总行数:"+sumLabel);
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(fileModel);
//写数据
fileWriter.write("## ListNet");
fileWriter.write("\r\n");
fileWriter.write("## Epochs = "+ITER_NUM);
fileWriter.write("\r\n");
fileWriter.write("## No. of features = 46");
fileWriter.write("\r\n");
fileWriter.write("1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ... 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46");
fileWriter.write("\r\n");
fileWriter.write("0");
fileWriter.write("\r\n");
for(int k=0; k<weidu; k++){
fileWriter.write("0 "+k+" "+weight[k+1]);
fileWriter.write("\r\n");
}
fileWriter.close();
System.out.println("write fin.");
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("写文件内容出错");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 预测排序
* 正规应对test.txt文件进行打分排序
* 但我们是在Hadoop实现该打分排序步骤 此函数仅测试train.txt打分
*/
public static void PredictRank(String fileScore) {
//输出得分
try {
System.out.println("write start.总行数:"+sumLabel);
String encoding = "GBK";
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(fileScore);
//写数据
for(int k=1; k<sumLabel; k++){
double score=0.0;
for(int j=1;j<=weidu;j++){
score=score+weight[j]*feature[k][j];
}
fileWriter.write("qid:"+qid[k]+" score:"+score+" label:"+label[k]);
fileWriter.write("\r\n");
}
fileWriter.close();
System.out.println("write fin.");
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("写文件内容出错");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 主函数
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
String fileInput = "Fold1\\train.txt"; //训练
String fileModel = "model_weight.txt"; //输出权重模型
String fileScore = "score_listNet.txt"; //输出得分
//第1步 读取文件并解析数据
System.out.println("read...");
ReadTxtFile(fileInput);
System.out.println("read and write well.");
//第2步 排序计算
LearningToRank();
//第3步 输出模型
WriteFileModel(fileModel);
//第4步 打分预测排序
PredictRank(fileScore);
}
/*
* End
*/
}
四. 总结
上面的代码我更希望你关注的是ListNet在训练模型过程中的代码,也就是通过train.txt获取得到46维的权重的模型.通过该模型你可以对test.txt进行打分(权重*特征值)排序,而上面的代码仅是对train.txt进行了简单的打分操作,那时因为我们的作业是基于Hadoop或Spark分布式处理基础上的.所以该部分由其他同学完成.
同时你也可以通过开源的RankLib或罗磊同学的ListNet算法进行学习,地址如下:
http://sourceforge.net/projects/minorthird/
http://code.google.com/p/learning-to-rank-listnet/
http://people.cs.umass.edu/~vdang/ranklib.html
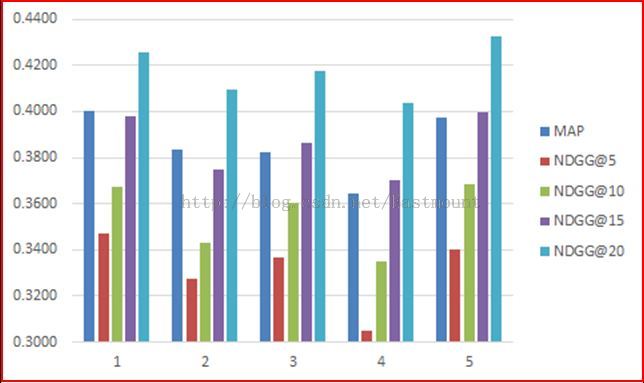
最后我们使用开源的MAP和NDCG@r简单对该算法进行了性能评估,同时附上Hadoop上的运行截图(MapReduce只找到了PRank的一张截图).


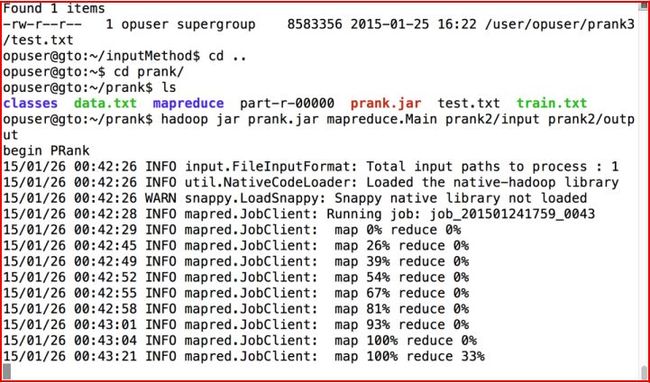
(By:Eastmount 2015-2-5 夜10点 http://blog.csdn.net/eastmount/article/)