CC2541 BLE源码阅读知识积累之OSAL小结
本文均属自己阅读源码的点滴总结,转账请注明出处谢谢。
欢迎和大家交流。qq:1037701636 email:[email protected],[email protected]
写在前面的话:
最近一段时间由于项目需要,便开始在阅读TI的cc2541的BLE Stack源码,对于蓝牙4.0这块知识基本是小白,所以几乎从0开始。在没接触蓝牙之前,就知道该部分的内容较为复杂(涉及到通信等协议栈),所以本着只有会使用为目的开始了BLE的学习(哎,一直都站在别人的肩膀上),学到点新的知识就积累一点,以免忘记。
看CC2541的开源BLE,一开始还以为51单片机结构会相当的简单,未曾想过TI的大牛们进行了软件架构的封装(OSAL+HAL,一种比较类似于但非操作系统的架构)。的确,对于我们这些小鸟来说,这样的设计对于我们可能很复杂,但是对于TI的开发人员来说却带来了更多的方便,移植简单化,改点配置就又用到别的处理器上。这都有点类似于Linux了,这套框架我还是比较佩服的,下面和大家分享一些OSAL+HAL在BLE中的使用,和大家解析一些函数。
由于这部分内容,网上也可以看到很多,本人也学习很多,喜欢开源的世界,所以就和大家分享自己深入看过的内容。
1.OSAL和HAL的好处
HAL:硬件抽象层,典型的操作系统硬件封装架构,远点的类似于Linux中常见的BSP,Android中的HAL等,都可以见到。相比于之前我所记得的51编程,在HAL里面各种宏定义,将所有可以操作的寄存器都进行封装,连中断都不放过,让搞裸驱的突然会有点不适应。
OSAL:操作系统抽象层,在cc2541的世界里,OSAL主要用于应用程序的开发,API大行其道,看看API手册就能完成编码。
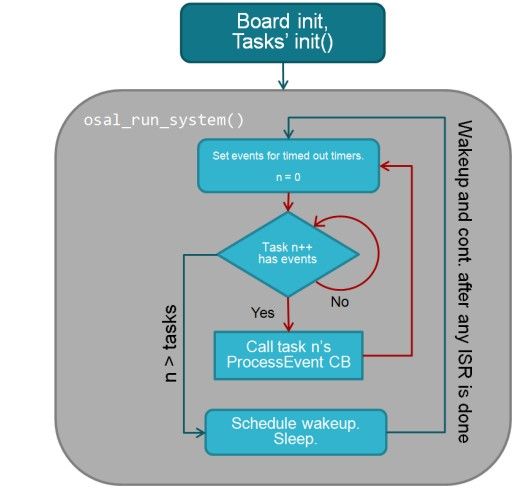
整套类操作系统围绕着:Event任务,Task事件,Message消息来进行。事件发生,由该事件对应的任务来处理,任务有时会将消息做为另一个事件从而去触发别的任务进行消息的处理。
2.OSAL中的时间API函数
因为OSAL的资源比较多,这里和大家讲讲自己看到时间相关的API,主要是osal_run_system中的osalTimeUpdate()函数,该函数会做2件主要的事情:更新系统运行的时间和更新各个软件定时器。
void osalTimeUpdate( void )//得到消逝时间的整数和小数,小数以余数形式存在
{
uint16 tmp;
uint16 ticks625us; //微妙
uint16 elapsedMSec = 0;//毫秒
// Get the free-running count of 625us timer ticks ,一个计数代表625us
tmp = ll_McuPrecisionCount();
if ( tmp != previousLLTimerTick )
{
// Calculate the elapsed ticks of the free-running timer.
ticks625us = tmp - previousLLTimerTick;
// Store the LL Timer tick count for the next time through this function.
previousLLTimerTick = tmp;
/* It is necessary to loop to convert the usecs to msecs in increments so as
* not to overflow the 16-bit variables.
*/
while ( ticks625us > MAXCALCTICKS ) //主要是防止数据过大转换为毫秒时发生溢出,MAXCALCTICKS = 13105,13105是就会溢出从0开始重新计数
{
ticks625us -= MAXCALCTICKS;
elapsedMSec += MAXCALCTICKS * 5 / 8; //滴答数us转换为ms单位8190ms
remUsTicks += MAXCALCTICKS * 5 % 8; //余数为5,0.625ms
}
// update converted number with remaining ticks from loop and the
// accumulated remainder from loop
tmp = (ticks625us * 5) + remUsTicks;//将余数加上去
// Convert the 625 us ticks into milliseconds and a remainder ( 余数)
elapsedMSec += tmp / 8;
remUsTicks = tmp % 8;//计算出整个时间后,进行取整和余数
// Update OSAL Clock and Timers
if ( elapsedMSec )//前后两次调用该函数时已经过去的时间值,该值只是ms位,有余数未计入
{
osalClockUpdate( elapsedMSec );//更新整个系统的时间,UTCTime以秒为单位记录
osalTimerUpdate( elapsedMSec );//传入过去流逝的时间值,进一步更新每个软件定时器,减去一定的时间
}
}
}
整个系统的时间都由LL(Link Layer)层的一个16位硬件定时器来维护,没深入去看因为是在BLE栈协议中,源码没有公开。这部分代码在获得当前LL Timer的计数值后进行时间计算,主要包括计算elapsed(逝去的)时间,该定时器,1个tick就代表625us,相对于频率1.6MHz。该us时间转换为ms的理想状况是Tms=Num*5/8,NUM为前后两次的tick之差,但是需要考虑的时,NUM如果很大,使得上面程序的temp一下就溢出,因此需要把握在Num到13015之内,超过部分直接获得其消逝的时间值和余数,当然为了精确这里不抛弃余数部分,在下次轮询到时继续加入进去,保证系统时间的精确,也正是remUsTicks = tmp % 8;出现的原因。
下面两个函数,前者是维护整个系统系统,保存到一个全局变量中,所有时间以s为单位记录。
osalClockUpdate( elapsedMSec );//更新整个系统的时间,UTCTime以秒为单位记录
void osalTimerUpdate( uint32 updateTime )
{
halIntState_t intState;
osalTimerRec_t *srchTimer;
osalTimerRec_t *prevTimer;
osalTime_t timeUnion;
timeUnion.time32 = updateTime;
HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION( intState ); // Hold off interrupts.
// Update the system time
osal_systemClock += updateTime;
HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION( intState ); // Re-enable interrupts.
// Look for open timer slot
if ( timerHead != NULL )
{
// Add it to the end of the timer list
srchTimer = timerHead;
prevTimer = (void *)NULL;
// Look for open timer slot
while ( srchTimer )
{
osalTimerRec_t *freeTimer = NULL;
HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION( intState ); // Hold off interrupts.
// To minimize time in this critical section, avoid 32-bit math。
//这边的计数算法总体为了节省时间。
if ((timeUnion.time16[1] == 0) && (timeUnion.time8[1] == 0))//消逝的时间数据只有1Byte
{
// If upper 24 bits are zero, check lower 8 bits for roll over
if (srchTimer->timeout.time8[0] >= timeUnion.time8[0])//定时器的时间还没有到0
{
// 8-bit math
srchTimer->timeout.time8[0] -= timeUnion.time8[0];//对软定时器进行减计时,只有一个字节且定时器数要大于消逝的时间
}
else
{
// 32-bit math
if (srchTimer->timeout.time32 > timeUnion.time32)
{
srchTimer->timeout.time32 -= timeUnion.time32;
}
else
{
srchTimer->timeout.time32 = 0;
}
}
}
else //消逝的时间至少2个Byte,16位
{
// 32-bit math
if (srchTimer->timeout.time32 > timeUnion.time32)
{
srchTimer->timeout.time32 -= timeUnion.time32;
}
else
{
srchTimer->timeout.time32 = 0;//一旦定时器时间值小于了消耗的时间值,直接定时器回0
}
}
// Check for reloading
if ( (srchTimer->timeout.time16[0] == 0) && (srchTimer->timeout.time16[1] == 0) &&
(srchTimer->reloadTimeout) && (srchTimer->event_flag) )//是否需要定时器重载
{
// Notify the task of a timeout
osal_set_event( srchTimer->task_id, srchTimer->event_flag );//事件延时事件一刀就立马让进行任务处理
// Reload the timer timeout value
srchTimer->timeout.time32 = srchTimer->reloadTimeout;
}
// When timeout or delete (event_flag == 0)
if ( ((srchTimer->timeout.time16[0] == 0) && (srchTimer->timeout.time16[1] == 0)) ||
(srchTimer->event_flag == 0) )//在定时器事件处理标志位0或者定时器计数完成,就进行下面的操作
{
// Take out of list
if ( prevTimer == NULL )
{
timerHead = srchTimer->next;//出现需要清空的定时器为头链表,则需要进行重定位
}
else
{
prevTimer->next = srchTimer->next;//删除链表节点,做前后的链接
}
// Setup to free memory
freeTimer = srchTimer;//记录当前需要清空的定时器
// Next
srchTimer = srchTimer->next;
}
else//无满足的定时器,就继续收索到下一个定时器节点进行操作。
{
// Get next
prevTimer = srchTimer;
srchTimer = srchTimer->next;
}
HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION( intState ); // Re-enable interrupts.
if ( freeTimer )//找到需要清除的软件定时器
{
if ( (freeTimer->timeout.time16[0] == 0) && (freeTimer->timeout.time16[1] == 0) )//定时这里意味着有事件发生
{
osal_set_event( freeTimer->task_id, freeTimer->event_flag );//触发事件,启动任务处理
}
osal_mem_free( freeTimer );//清除无用定时器(定时结束或者事件发生标志清空)
}
}
}
}
该函数是处理整个软件定时器的核心所在,设计的稍微复杂一点:之所有存在这个软件定时器,其实也是有LL Timer来完成的。它的存在是为了给某些场合提供方便,比如设备启动之后,就会设计成这样 ,延时5s都会触发一次事件的发生,以表示系统在正常运行,类似于心跳包。
osal_start_timerEx( simpleBLEPeripheral_TaskID, SBP_PERIODIC_EVT, SBP_PERIODIC_EVT_PERIOD ),该函数是OSAL内实现启动一个事件的函数类型与osal_set_event(),只是前者需要有一个延时,延时事件到后触发事件,而这个延时就是由上面的软件定时器来完成的。
OSAL维护着一个定时器全局链表timerHead,每当调用osal_start_timerEx实际再调用osalAddTimer,来创建一个新的软件Timer。
osalTimerRec_t * osalAddTimer( uint8 task_id, uint16 event_flag, uint32 timeout )
{
osalTimerRec_t *newTimer;
osalTimerRec_t *srchTimer;
// Look for an existing timer first
newTimer = osalFindTimer( task_id, event_flag );//通过对任务ID和具体的事件标志来查询定时器链表中是否已经存在
if ( newTimer )
{
// Timer is found - update it.
newTimer->timeout.time32 = timeout;//如果定时器事件对应的任务处理定时器已经存在直接更新时间
return ( newTimer );
}
else
{
// New Timer
newTimer = osal_mem_alloc( sizeof( osalTimerRec_t ) );//新分配一个软定时器内存
if ( newTimer )
{
// Fill in new timer
newTimer->task_id = task_id;
newTimer->event_flag = event_flag;
newTimer->timeout.time32 = timeout;
newTimer->next = (void *)NULL;//该定时器在定时器链表尾
newTimer->reloadTimeout = 0;
// Does the timer list already exist
if ( timerHead == NULL )
{
// Start task list
timerHead = newTimer;
}
else //定时器链表头非空
{
// Add it to the end of the timer list
srchTimer = timerHead;
// Stop at the last record
while ( srchTimer->next )
srchTimer = srchTimer->next;//找到链表尾
// Add to the list
srchTimer->next = newTimer;//将最新的定时器加入到链表尾中,其next为NULL
}
return ( newTimer );
}
else
{
return ( (osalTimerRec_t *)NULL );
}
}
}
结合上面两个函数,可以很好的理解软件定时器的工作模式,是一个减计算模式,加入了点小算法,对定时完成后的事件直接进行事件触发操作,以达到延时效果。
3.OSAL中的消息处理相关API解析
消息的出现,比如按键事件触发,引起了硬件task任务处理,处理时会调用向应用层注册的一个回调函数Callback(初始化时完成),在回调函数中将按键的ID打包,通过消息发给应用层APP,应用层再进一步做出处理。
uint8 OnBoard_SendKeys( uint8 keys, uint8 state )
{
keyChange_t *msgPtr;
if ( registeredKeysTaskID != NO_TASK_ID )
{
// Send the address to the task
msgPtr = (keyChange_t *)osal_msg_allocate( sizeof(keyChange_t) ); //其实分配的内存大小为osal_msg_hdr_t + keyChange_t
if ( msgPtr )
{
msgPtr->hdr.event = KEY_CHANGE;//事件类型按键变化
msgPtr->state = state;
msgPtr->keys = keys;
osal_msg_send( registeredKeysTaskID, (uint8 *)msgPtr );//将按键事件产生的消息发送到注册啦按键这一事件的任务
}
return ( SUCCESS );
}
else
return ( FAILURE );
在这里进行消息的发送,OSAL维护一个全局的osal_qHead队列,允许你将新的消息插入队列头或者尾,整个消息内容包括固定的链表头:
typedef struct
{
void *next;
uint16 len;
uint8 dest_id;
} osal_msg_hdr_t;
再加上相关消息需要携带的内容。在收到消息的地方,遍历链表,找到对应的消息,再会对数据进行提取。
uint8 *osal_msg_receive( uint8 task_id )
{
osal_msg_hdr_t *listHdr;
osal_msg_hdr_t *prevHdr = NULL;
osal_msg_hdr_t *foundHdr = NULL;
halIntState_t intState;
// Hold off interrupts
HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState);
// Point to the top of the queue
listHdr = osal_qHead;
// Look through the queue for a message that belongs to the asking task
while ( listHdr != NULL )
{
if ( (listHdr - 1)->dest_id == task_id )//判断消息处理函数是否就是当前接收的任务处理函数
{
if ( foundHdr == NULL )
{
// Save the first one
foundHdr = listHdr;
}
else
{
// Second msg found, stop looking
break;
}
}
if ( foundHdr == NULL )
{
prevHdr = listHdr;
}
listHdr = OSAL_MSG_NEXT( listHdr );
}
// Is there more than one?
if ( listHdr != NULL )
{
// Yes, Signal the task that a message is waiting
osal_set_event( task_id, SYS_EVENT_MSG );
}
else
{
// No more
osal_clear_event( task_id, SYS_EVENT_MSG );//清楚这个任务事件消息标志
}
// Did we find a message?
if ( foundHdr != NULL )
{
// Take out of the link list
osal_msg_extract( &osal_qHead, foundHdr, prevHdr );//解析出消息内容
}
// Release interrupts
HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState);
return ( (uint8*) foundHdr );
}
以上的过程就是整个事件触发消息,消息再打包发生,由目的任务处理函数进行进一步处理,直到完成后进行清空。
以上是部分OSAL中的内容,下次继续分析BLE中的主从机简单的工作模型。