基于Visual C++2010 与office2010开发办公自动化(27)-实现Office晚期自动化绑定
Office Word 2010
Office Word 2010 增强了 Navigation Pane 特性,用户可在 Navigation Pane 中快速切换至任何一章节的开头(根据标题样式判断),同时也可在输入框中进行即时搜索,包含关键词的章节标题会高亮显示。例如
Office Word 2010 也增加了在线实时协作功能,用户可以从 Office Word Web App 中启动 Word 2010 进行在线文档的编辑,并可在左下角看到同时编辑的其他用户(包括其他联系方式、IM 等信息,需要 Office Communicator)。而当其他用户修改了某处后,Word 2010 会提醒当前用户进行同步。(注:此功能也存在于部分其他 Office 2010 程序中)
另外,用户可在 Office Word 2010, Office PowerPoint 2010 以及 Office OneNote 2010 等 Office 2010 程序中直接插入其他正在运行的软件的截图。
Office Excel 2010
Office Excel 2010 新增了 Sparklines 特性,可根据用户选择的数据直接在单元格内画出折线图、柱状图等,并配有 Sparklines 设计面板供自定义样式。
Office PowerPoint 2010
Office PowerPoint 2010 除了新增更多幻灯片切换特效、图片处理特效之外,还增加了更多视频功能,用户可直接在 PowerPoint 2010 中设定(调节)开始和终止时间剪辑视频,也可将视频嵌入之 PowerPoint 文件中。
PowerPoint 2010 左侧的幻灯片面板也新增了分区特性,用户可将幻灯片分区归类,也可对整个区内的所有幻灯片进行操作。见下图中的 Default Section 和 LiveSino Section。
PowerPoint 2010 也增加了类似格式刷的工具 – Animation Painter,可将动画效果应用至其他对象,用法同格式刷。另外就是上次我提到的 Broadcast Slide Show 在线幻灯片播放功能。
Office Web Applications 2010
Office Web Applications 2010 包含 Word Web App, Excel Web App, PowerPoint Web App 以及 OneNote Web App,支持简单的编辑及实时协作功能,支持 IE, Firefox, 和 Safari
Office Mobile 2010
Office Mobile 2010 包含新版 Word Mobile, Excel Mobile, PowerPoint Mobile, OneNote Mobile 以及支持对话模式的 Outlook Mobile
绑定
在使应用程序(如 Microsoft Office 应用程序)自动运行时,对 Office 应用程序对象的属性和方法的调用必须以某种方式连接到这些对象。将属性和方法调用连接到实现这些属性和方法的对象的过程通常称为绑定。在 Visual C++ 中,有两种类型的绑定,分别是早期绑定 和晚期绑定。所选择的绑定类型可以影响程序的许多方面,包括性能、灵活性和可维护性。
早期绑定
采用早期绑定时,Visual C++.net 使用有关所涉及的 Office 应用程序的可用类型信息直接绑定到它需要使用的方法或属性。编译器可以执行类型和语法检查,以确保传递到方法或属性的参数的数量和类型正确无误,并且返回的值是所期望的类型。由于早期绑定在运行时调用属性或方法所需的工作量较小,因此有时速度较快。然而,虽然早期绑定可能速度较快,但与晚期绑定之间的性能差异通常不大。
晚期绑定
与早期绑定不同,晚期绑定要等到运行时才会将属性和方法调用绑定到它们的对象。为此,目标对象必须实现一个特殊的 COM 接口:IDispatch。利用 IDispatch::GetIDsOfNames 方法,Visual C++.net可以询问对象支持哪些方法和属性,然后,IDispatch::Invoke 方法允许 Visual C++.net 调用这些方法和属性。这种晚期绑定的优点是:它消除了早期绑定所固有的某些版本依赖性。然而,它也有以下缺点:省略了对自动化代码完整性的编译时检查,也不提供“智能感知”功能(该功能可提供有助于正确调用方法和属性的提示)。
好了,下面我来举例说明如何创建使用Office晚期自动化绑定的步骤:
1.启动VS2010
2.创建一个CLR项目如下,在窗体中插入若干相关空间和文本,插入背景,详情参看下图:
3.在Form1.h中插入以下代码,详细见代码分析与注释
#pragma once namespace Yincheng { using namespace System; using namespace System::ComponentModel; using namespace System::Collections; using namespace System::Windows::Forms; using namespace System::Data; using namespace System::Drawing; /// <summary> /// Form1 摘要 /// /// 警告: 如果更改此类的名称,则需要更改 /// 与此类所依赖的所有 .resx 文件关联的托管资源编译器工具的 /// “资源文件名”属性。否则, /// 设计器将不能与此窗体的关联 /// 本地化资源正确交互。 /// </summary> public ref class Form1 : public System::Windows::Forms::Form { public: Form1(void) { InitializeComponent(); // //TODO: 在此处添加构造函数代码 // } protected: /// <summary> /// 清理所有正在使用的资源。 /// </summary> ~Form1() { if (components) { delete components; } } private: System::Windows::Forms::RichTextBox^ richTextBox1; protected: private: System::Windows::Forms::Button^ button1; private: System::Windows::Forms::Button^ button2; private: /// <summary> /// 必需的设计器变量。 /// </summary> System::ComponentModel::Container ^components; #pragma region Windows Form Designer generated code /// <summary> /// 设计器支持所需的方法 - 不要 /// 使用代码编辑器修改此方法的内容。 /// </summary> void InitializeComponent(void) { System::ComponentModel::ComponentResourceManager^ resources = (gcnew System::ComponentModel::ComponentResourceManager(Form1::typeid)); this->richTextBox1 = (gcnew System::Windows::Forms::RichTextBox()); this->button1 = (gcnew System::Windows::Forms::Button()); this->button2 = (gcnew System::Windows::Forms::Button()); this->SuspendLayout(); // // richTextBox1 // this->richTextBox1->Location = System::Drawing::Point(104, 81); this->richTextBox1->Name = L"richTextBox1"; this->richTextBox1->Size = System::Drawing::Size(388, 186); this->richTextBox1->TabIndex = 0; this->richTextBox1->Text = L"在使应用程序(如 Microsoft Office 应用程序)自动运行时,对 Office 应用程序对象的属性和方法的调用必须以某种方式连接到这些对象。将属性和方" L"法调用连接到实现这些属性和方法的对象的过程通常称为绑定。在 Visual C++.net 中,有两种类型的绑定,分别是早期绑定 和晚期绑定。所选择的绑定类型可以" L"影响程序的许多方面,包括性能、灵活性和可维护性。"; // // button1 // this->button1->Location = System::Drawing::Point(144, 276); this->button1->Name = L"button1"; this->button1->Size = System::Drawing::Size(141, 38); this->button1->TabIndex = 1; this->button1->Text = L"启动Excel软件"; this->button1->UseVisualStyleBackColor = true; this->button1->Click += gcnew System::EventHandler(this, &Form1::button1_Click); // // button2 // this->button2->Location = System::Drawing::Point(313, 276); this->button2->Name = L"button2"; this->button2->Size = System::Drawing::Size(141, 38); this->button2->TabIndex = 2; this->button2->Text = L"关闭应用程序"; this->button2->UseVisualStyleBackColor = true; this->button2->Click += gcnew System::EventHandler(this, &Form1::button2_Click); // // Form1 // this->AutoScaleDimensions = System::Drawing::SizeF(6, 12); this->AutoScaleMode = System::Windows::Forms::AutoScaleMode::Font; this->BackColor = System::Drawing::SystemColors::ActiveCaptionText; this->BackgroundImage = (cli::safe_cast<System::Drawing::Image^ >(resources->GetObject(L"$this.BackgroundImage"))); this->ClientSize = System::Drawing::Size(592, 386); this->Controls->Add(this->button2); this->Controls->Add(this->button1); this->Controls->Add(this->richTextBox1); this->Name = L"Form1"; this->StartPosition = System::Windows::Forms::FormStartPosition::CenterScreen; this->Text = L"CSDN著名技术专家尹成-演示如何实现Office晚期自动化绑定"; this->ResumeLayout(false); } #pragma endregion //关闭应用程序 private: System::Void button2_Click(System::Object^ sender, System::EventArgs^ e) { this->Close(); } //启动Excel软件 private: System::Void button1_Click(System::Object^ sender, System::EventArgs^ e) { Object^ MyApp; Object^ MyBook; Object^ MyBooks; Object^ MySheet; Object^ MySheets; Object^ MyRange; array<System::Object^,1>^ MyParameters; array<System::Object^,1>^ MyArray; String^ MyInfo; System::Type^ MyClassType; System::Reflection::Binder^ MyBinder; try { // 获取Excel类型 MyClassType=Type::GetTypeFromProgID("Excel.Application"); MyApp=Activator::CreateInstance(MyClassType); //获取workbooks集合 MyBooks=MyApp->GetType()->InvokeMember("Workbooks",System::Reflection::BindingFlags::GetProperty,MyBinder, MyApp,MyArray); //新增workbook. MyBook=MyBooks->GetType()->InvokeMember("Add",System::Reflection::BindingFlags::InvokeMethod,MyBinder, MyBooks,MyArray); //获取worksheets集合 MySheets=MyBook->GetType()->InvokeMember("Worksheets",System::Reflection::BindingFlags::GetProperty,MyBinder, MyBook,MyArray); //获取第一个 worksheet. MyParameters=gcnew array<System::Object^,1>(1); MyParameters[0]=1; MySheet=MySheets->GetType()->InvokeMember("Item",System::Reflection::BindingFlags::GetProperty,MyBinder, MySheets, MyParameters ); //获取A1单元格所在区域 MyParameters=gcnew array<System::Object^,1>(2) ; MyParameters[0]="A1"; MyParameters[1]= System::Reflection::Missing::Value; MyRange=MySheet->GetType()->InvokeMember("Range",System::Reflection::BindingFlags::GetProperty,MyBinder, MySheet, MyParameters ); //在A1单元格中填充数据. MyParameters=gcnew array<System::Object^,1>(1) ; MyParameters[0]=this->richTextBox1->Text; MyRange->GetType()->InvokeMember("Value",System::Reflection::BindingFlags::SetProperty,MyBinder, MyRange, MyParameters ); MyParameters=gcnew array<System::Object^,1>(1) ; //启动 Excel MyParameters[0]=true; MyApp->GetType()->InvokeMember("Visible",System::Reflection::BindingFlags::SetProperty,MyBinder, MyApp, MyParameters ); MyApp->GetType()->InvokeMember("UserControl",System::Reflection::BindingFlags::SetProperty,MyBinder, MyApp, MyParameters ); } catch (Exception^ MyEx) { MessageBox::Show(MyEx->Message, "信息提示", MessageBoxButtons::OK, MessageBoxIcon::Information); } } }; }
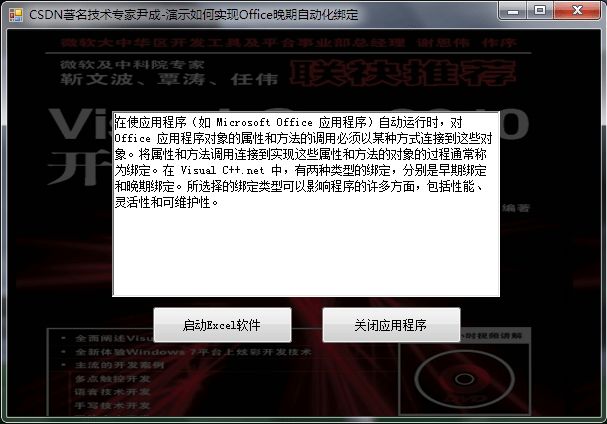
5.启动调试运行如下:
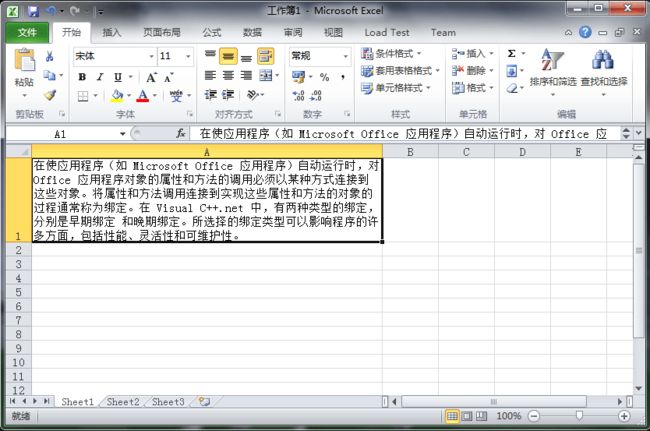
点击”启动Excel软件“Excel中同步数据显示,如下所示: