安卓个人学习------ImageView,SeekBar,TableHost,ProgressBar的使用
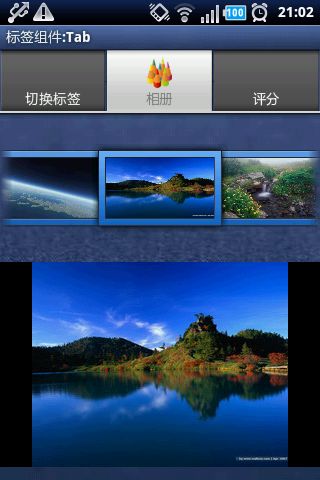
先让大家看一个效果图
怎么样,效果炫吗?
让我们来分析一下,这种效果怎么样才能实现呢?
首先我们注意一下,上方几个横着切换的功能是TabHost
TabHost
提供选项卡(Tab页)的窗口视图容器。此对象包含两个子对象:一组是用户可以选择指定Tab页的标签;另一组是FrameLayout用来显示该Tab页的内容。通常控制使用这个容器对象,而不是设置在子元素本身的值。(译者注:即使使用的是单个元素,也最好把它放到容器对象ViewGroup里)
内部类
interfaceTabHost.OnTabChangeListener
接口定义了当选项卡更改时被调用的回调函数
interface TabHost.TabContentFactory
当某一选项卡被选中时生成选项卡的内容
class TabHost.TabSpec
单独的选项卡,每个选项卡都有一个选项卡指示符,内容和tag标签,以便于记录.
公共方法
public void addTab(TabHost.TabSpec tabSpec)
新增一个选项卡
参数
tabSpec 指定怎样创建指示符和内容.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TabHost xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<LinearLayout android:id="@+id/tab1" android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<Button android:id="@+id/button" android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="切换到第3个标签" />
<ImageView android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@drawable/background" android:layout_marginTop="30dp"/>
</LinearLayout>
</TabHost>
import android.app.TabActivity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.widget.TabHost;
public class TableHostTest extends TabActivity {
private TabHost tabHost = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
tabHost = this.getTabHost();
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
/*注意true的作用*/
inflater.inflate(R.layout.tablehost, tabHost.getTabContentView(),true);
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1").setIndicator("界面1").setContent(R.id.tab1));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab2").setIndicator("界面2").setContent(new Intent(this,SeekBarDemo.class)));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3").setIndicator("界面3").setContent(new Intent(this,UITest4Activity.class)));
}
}
进度条显示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="进度条演示" />
<ProgressBar
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:max="1000"
android:progress="100"
android:id="@+id/progressbar1"
/>
<ProgressBar
style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal"
android:layout_marginTop="30dp"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:max="1000"
android:progress="500"
android:secondaryProgress="300"
android:id="@+id/progressbar2"
/>
</LinearLayout>
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.ProgressBar;
public class ProgressBarDemo extends Activity{
ProgressBar progressbar = null;
static int i = 0;
int progressbarMax = 0;
Handler handler = new Handler();
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.progressbar_layout);
findViews();
}
private void findViews() {
progressbar = (ProgressBar) this.findViewById(R.id.progressbar2);
progressbar.setMax(1000);
progressbarMax = progressbar.getMax();
new Thread(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
while(i< progressbarMax){
i=doWork();
handler.post(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
progressbar.setProgress(i);
}
});
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
}
public int doWork(){
Log.d("TAG", String.valueOf(i));
return ++i;
}
/* //不能用!!!!
public void run(){
Log.d("TAG","thread starting...");
while(i++ < progressbarMax){
progressbar.setProgress(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
*/
}
下面用ImageView实现图片预览功能
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.drawable.BitmapDrawable;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnTouchListener;
import android.widget.ImageView;
public class ImageViewDemo extends Activity implements OnTouchListener {
ImageView imageView1, imageView2;
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
this.setContentView(R.layout.imageview_layout);
findViews();
}
private void findViews() {
imageView1 = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.img1);
imageView2 = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.img2);
imageView1.setOnTouchListener(this);
}
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
float scale = 412 / 320;
int x = (int) (event.getX() * scale);
int y = (int) (event.getY() * scale);
//尝试考虑解决边界问题
int width = (int) (100 * scale);
int height = (int) (100 * scale);
BitmapDrawable bitmapDrawable = (BitmapDrawable) imageView1.getDrawable();
imageView2.setImageBitmap(Bitmap.createBitmap(bitmapDrawable.getBitmap(),
x,y, width, height));
return false;
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/img1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="#cccccc"
android:src="@drawable/pig" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/img2"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#cccccc"
android:scaleType="fitStart"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
/>
</LinearLayout>
调节音量等的控制条:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<SeekBar
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:max="1000"
android:id="@+id/seekbar"
/>
</LinearLayout>
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.SeekBar;
import android.widget.SeekBar.OnSeekBarChangeListener;
public class SeekBarDemo extends Activity implements OnSeekBarChangeListener {
SeekBar seekbar = null;
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
this.setContentView(R.layout.seekbar_layout);
findViews();
}
private void findViews() {
seekbar = (SeekBar) this.findViewById(R.id.seekbar);
seekbar.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onProgressChanged(SeekBar seekBar, int progress,
boolean fromUser) {
Log.d("TAG", "changed: "+ String.valueOf(seekBar.getProgress()));
}
@Override
public void onStartTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) {
Log.d("TAG", "start: "+ String.valueOf(seekBar.getProgress()));
}
@Override
public void onStopTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) {
Log.d("TAG", "stop: "+ String.valueOf(seekBar.getProgress()));
}
}