2016/1/9:深度剖析安卓Framebuffer设备驱动
忙了几天,今天在公司居然没什么活干 ,所以早上就用公司的电脑写写之前在公司编写framebuffer的使用心得体会总结,这也算是一点开发经验,不过我还没写全,精华部分还是自己藏着吧。直到下午才开始有点活干,改瑞芯微的摄像头驱动,偶滴天!!特别麻烦,摄像头的代码好几千行,果真不太好看,驱动想改也不好改
,所以早上就用公司的电脑写写之前在公司编写framebuffer的使用心得体会总结,这也算是一点开发经验,不过我还没写全,精华部分还是自己藏着吧。直到下午才开始有点活干,改瑞芯微的摄像头驱动,偶滴天!!特别麻烦,摄像头的代码好几千行,果真不太好看,驱动想改也不好改
 ,看看我的测试效果就知道了,显示的图片是反的,又到了周末了,这个问题只能留着下周上班再去解决了,今天我们就来了解一下Framebuffer设备驱动,其实Framebuffer驱动跟我这个安卓项目就挂钩了,好,我们来看看:
,看看我的测试效果就知道了,显示的图片是反的,又到了周末了,这个问题只能留着下周上班再去解决了,今天我们就来了解一下Framebuffer设备驱动,其实Framebuffer驱动跟我这个安卓项目就挂钩了,好,我们来看看:
记住!没有简单的程序,只有头脑简单的程序员!![]()
![]()
开篇之前,我们来介绍一下什么是framebuffer?
FrameBuffer其实就是,帧缓冲。
Frame帧:你所看到的屏幕的图像,或者在一个窗口中的图像,就叫一帧。
Buffer缓冲:一段RAM,用来暂存图像数据,这些数据会被直接写入到显示设备。
帧缓冲就相当于介于 图形操作 和 图像输出中间的一个中间人。将程序对图形数据的处理操作,反馈到显示输出上。
显卡(显存中的数据) <-> 帧缓冲(程序对其中的数据进行处理) <-> 显示器(输出图像)
帧缓冲可用于,实现原先视频卡并不支持的分辨率。
显卡可能并不支持你当前某个更大分辨率的显示器,但是可以通过帧缓冲获取显卡的显存中的数据,处理之后,实现更大的分辨率的图像,然后将数据直接输出到显示器上。
好了,现在我们已经了解什么是framebuffer了,接下来我们来分析framebuffer在linux下的几个重要的驱动数据结构。
1、Framebuffer帧缓冲设备
Framebuffer 驱动在 Linux 中是标准的显示设备的驱动。对于 PC 系统,它是显卡的驱动 ; 对于嵌入式SOC处理器系统,
它是LCD控制器或者其他显示控制器的驱动。同时该设备属于一个字符设备,在文件系统中设备节点是/dev/fbx.
一个系统可以有多个显示设备,最常见的有 /dev/fb0 /dev/fb1 ,如果在/dev目录下没有发现这个文件,那么需要去修改
Linux系统中相应的配置脚本。
在安卓系统中,Framebuffer设备驱动的主设备号通常为29 ,次设备号递增而生成。
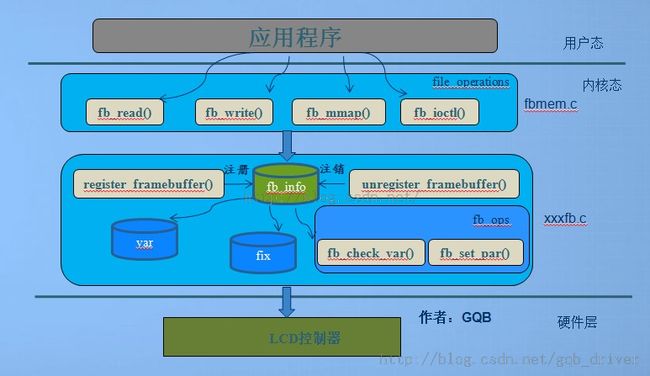
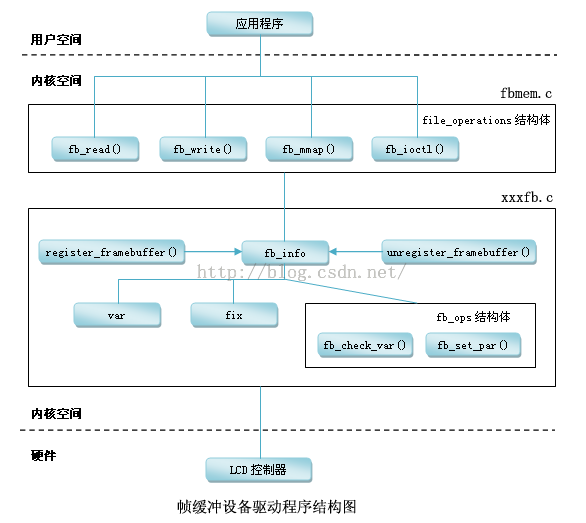
在此,我借用某内核驱动大牛GQB做的驱动框架图做分析,如有侵权,请联系我删除,谢谢!

在此,我借用某内核驱动大牛GQB做的驱动框架图做分析,如有侵权,请联系我删除,谢谢!
Framebuff的结构框架和实现:
我们可以先来看看在framebuffer驱动框架中相关的重要数据结构:
struct fb_ops {
struct module *owner;
//检查可变参数并进行设置
int (*fb_check_var)(struct fb_var_screeninfo *var, struct fb_info *info);
//根据设置的值进行更新,使之有效
int (*fb_set_par)(struct fb_info *info);
//设置颜色寄存器
int (*fb_setcolreg)(unsigned regno, unsigned red, unsigned green,
unsigned blue, unsigned transp, struct fb_info *info);
//显示空白
int (*fb_blank)(int blank, struct fb_info *info);
//矩形填充
void (*fb_fillrect) (struct fb_info *info, const struct fb_fillrect *rect);
//复制数据
void (*fb_copyarea) (struct fb_info *info, const struct fb_copyarea *region);
//图形填充
void (*fb_imageblit) (struct fb_info *info, const struct fb_image *image);
};
从设备驱动程序结构看,这个驱动主要跟fb_info结构体有相应的关系,这个结构体记录了这个设备驱动的全部相关的信息,
其中就包括设备的设置参数,状态,还有对应底层硬件操作的回调函数。在Linux中,每一个帧缓冲设备都必须对应一个fb_info,fb_info在/linux/fb.h中:
上面的fp_ops这个结构体就是常用的非常重要的一个。
和其它的内核代码中的字符驱动类似,同样,如果你要使用这个驱动,你必须去注册这个设备驱动。
打开linux3.5的内核代码,显示驱动的分析都是由 drivers/video/fbmem.c开始 。我们
可以查阅到fbmem.c里定义 register_framebuffer这个函数。通过 查看这个函数,我们可以发现其实这个函数在drivers/video/s3c-fb.c中的probe函数中调用了 register_framebuffer,在s3c-fb.c这个文件注册了一个平台总线
可以查阅到fbmem.c里定义 register_framebuffer这个函数。通过 查看这个函数,我们可以发现其实这个函数在drivers/video/s3c-fb.c中的probe函数中调用了 register_framebuffer,在s3c-fb.c这个文件注册了一个平台总线
设备的驱动程序。这里要注意了,所谓的平台总线驱动其实是由linux内核本身去实现的,是一种总线驱动的机制。
以下是fb_info结构体:
struct fb_info {
int node;
struct fb_var_screeninfo var; /* Current var */
struct fb_fix_screeninfo fix; /* Current fix */
struct fb_videomode *mode; /* current mode */
struct fb_ops *fbops;
struct device *device; /* This is the parent */
struct device *dev; /* This is this fb device */
char __iomem *screen_base; /* Virtual address */
unsigned long screen_size; /* Amount of ioremapped VRAM or 0 */
…………
};
在这个info结构体中,我们看到结构体中有结构体,所以这个给刚学过C语言和数据结构的伙伴来看是很头疼的,正所谓这是一点经验性的东西,所以不是那么简单。
首先,我们分析一下这个结构体里的几个关键的参数,其它的往后用到了我再做相应的分析:
1、node这个 参数,实质上,node这个参数指的是专用的freambuffer,说白点那就是驱动的次设备号。
2、struct fb_var_screeninfo var;结构体成员记录用户可修改的显示控制器参数,包括屏幕分辨率还有每个像素点的位数。
struct fb_var_screeninfo {
__u32 xres; /* visible resolution */
__u32 yres;
__u32 xoffset; /* offset from virtual to visible */
__u32 yoffset; /* resolution */
__u32 bits_per_pixel; /* bits/pixel */
__u32 pixclock; /* pixel clock in ps (pico seconds) */
__u32 left_margin; /* time from sync to picture */
__u32 right_margin;/* time from picture to sync */
__u32 hsync_len; /* length of horizontal sync */
__u32 vsync_len; /* length of vertical sync */
…………
};
在这个结构体中,xres表示你需要定义的LCD屏的一行包含多少个像素点,bits_per_pixel表示每个像素点需要用多少个字节去描述它。
这里面还有其它的参数,比如时间的设置,偏移量等等,太多了我就不说了,有兴趣自己慢慢去看慢慢去研究。
3、
struct fb_fix_screeninfo fix;
这个结构体记录了用户不能去修改的LCD控制器的一些相关的参数。
例如:屏幕缓冲区的物理地址,长度。当对帧缓冲设备进行映射操作的时候,就是从fb_fix_screeninfo中取得缓冲区物理地址的。
看看相应的英文注释很快就会弄懂。
struct fb_fix_screeninfo {
char id[16];
unsigned long smem_start; /* 开始的framebuffer内存,这里是物理地址要注意 */
__u32 smem_len; /* 物理地址的长度 */
unsigned long mmio_start; /* 开始的物理地址映射 */
__u32 mmio_len; /* IO内存映射的长度 */
…………
};
4、struct fb_videomode *mode 这个结构体主要是设置LCD相应的模式,看看我写的注释就清楚了。
struct fb_videomode {
const char *name; /* optional */
u32 refresh; /* optional */
u32 xres; // x分辨率
u32 yres; // y分辨率
u32 pixclock; // 像素时钟频率,即每个时钟周期显示一个像素点
u32 left_margin; // 行扫描开始脉冲到一行像素数据开始输出的延迟 hsync<==>DEN
u32 right_margin; // 一行像素数据输出完毕到下一行的行扫描开始脉冲间的延迟 DEN <==>hsync
u32 upper_margin; // 帧扫描开始脉冲到第一行像素数据开始输出的延迟 vsync<==>DEN(1st line)
u32 lower_margin; // 最后一行像素数据输出结束到下一帧的那帧扫描开始脉冲间的延迟DEN(last line)<==>vsync
u32 hsync_len; // 行扫描脉冲宽度,单位为pixclock
u32 vsync_len; // 帧扫描脉冲宽度,单位为line
u32 sync; // 各同步信号的极性定义,如hsync、vsync、DEN的极性等。
u32 vmode; // 显示模式,逐行还是隔行扫描
u32 flag; // 一般为0
};
5、struct fb_ops *fbops; 这个结构体是LCDframebuffer操作中最重要的一个,也就是说上面做了LCD的相关设置那只是在设置LCD中的硬件寄存器,
如果你想点亮LCD屏顺便操作它,那么这个结构体必不可少。
struct fb_ops {
int (*fb_open)(struct fb_info *info, int user);
int (*fb_release)(struct fb_info *info, int user);
ssize_t (*fb_read)(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *ppos);
ssize_t (*fb_write)(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count,
loff_t *ppos);
int (*fb_set_par)(struct fb_info *info);
int (*fb_setcolreg)(unsigned regno, unsigned red, unsigned green,
unsigned blue, unsigned transp, struct fb_info *info);
int (*fb_setcmap)(struct fb_cmap *cmap, struct fb_info *info)
int (*fb_mmap)(struct fb_info *info, struct vm_area_struct *vma);
……………
}
以前我的文章曾写过如何写一个简单的字符设备驱动程序,这里为就不对这个结构体进行解释了,就是定义一个可以供上层调用的文件操作结构体。
进而当你对驱动进行读,写,内存映射操作时,通过你的一系列的操作,内核就会根据你编写上层的程序去相应调用到这样的一个结构体从而操作LCD
设备。
说了这么多,好像都是废话一大堆对吧?那LCD屏幕到底要怎么点亮呢?我参考了网上大牛的博客
 lantianyu520.blog.chinaunix.net总结了几个可以点亮LCD的步骤:
lantianyu520.blog.chinaunix.net总结了几个可以点亮LCD的步骤:
1.参考LCD datasheet修改fb_videomode结构体的参数。
2.配置GPIO,点亮LCD背光。
3.参考LCD datasheet看这个LCD是否需要spi总线发送命令进行初始化,一般厂商给datasheet时也会给一份初始化代码,不过有些参数是错误的,需 要调整,发送不正确的命令会导致LCD白屏。
4.用示波器测试从LCD控制器出来的Hsync, Vsync, DE, PCLK是否正确,用万用表测量Vio, Vci是否正常。
5.有的LCD Driver需要LCD控制器发出一个CS片选使能信号。
6.用万用表测量LCD的栅压是否正常,一般为9.2V。
7.如果上述步骤后还出不来,再检查LCD初始化命令是否正确,spi时序是否符合。
如果出现图像异常的情况,那么请改:
图像异常处理:
1.驱动问题
上下抖动,左右没对齐:调整left/right/upper/lower margin值
2.LCD初始化命令问题
有纹波:调整VDD/AVDD/VGL/VGH电压
色彩失真:看LCD的RGB模式设置和LCD控制器出来的RGB模式是否一致
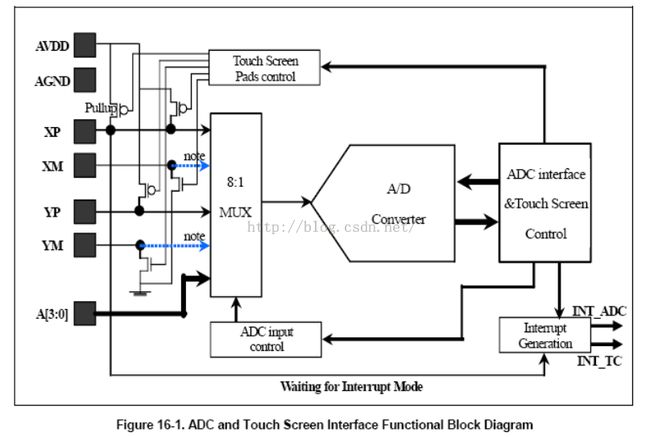
上面说的步骤仅仅只是点亮开发板屏幕的相关步骤,如果你想要像玩触屏手机一样可以触屏,那么你要配置触屏的相关驱动,触屏一般使用I2C总线协议,触屏的原理就非常复杂了,你在屏幕上按下,
屏幕上就会产生相应的电压值,因为触摸屏下面有很多电容,可以储存电荷,也就产生了相应的电压,这时候我们就可以用ADC接口,根据电压值判断你按下的X,Y横纵坐标的位置。现在触摸屏基本上支持多点触摸了,
所以使用的触摸芯片的等级也会越来越高,对于我们驱动工程师调试触摸屏的程序也会越来越难。我们的辛苦,消费者的开心,呜呜......

从触摸屏被按下到系统相应的过程如下:
(1) 当触摸屏感觉到触摸,触发IRQ_TC中断,然后读取触摸屏控制寄存器的值,判断是否被按下,如果被按下,启动定时器,执行touch_timer_fire()函数启动ADC转换。
(2) ADC转换完成后,会触发IRQ_ADC中断,执行相应的中断处理函数,如果ADC转换次数小于4,再次启动ADC转换;如果ADC转换次数为4,则启动一个系统滴答定时器,执行touch_timer_fire()函数
(3) 执行定时器服务程序时,如果此时触摸屏仍被按下,则上报事件和坐标数据,重复(2);如果没有被按下,上报时间和坐标数据,将触摸屏控制寄存器设置为中断等待状态
可见,触摸屏驱动的服务是一个封闭的循环过程。

驱动分析到此为止,中间穿插了一点触摸屏的概念,其实还有很多我没分析到的,因为太多了,一篇文章写不完。为了更好的去理解Framebuffer驱动,我们直接利用linux内核为我们写好的freamebuffer设备驱动进行操作。
认真看过上面分析的数据结构的话,你应该会知道,我要操作的是什么。
有了framebuffer的底层驱动,那在上层操作它那就太太太简单了,一点难度都没有。这里,我们用linuxX86的平台来实现这个上层程序的编写。请记住,我写的这个程序是在用户态,不在内核态。
而且,你写完上层的程序执行后是没有任何反应的,你需要切换到linux下的其它的运行级别。需要按ALT+F1进入字符界面模式。
罗嗦一下,编写framebuffer用户态程序需要以下步骤:
1、初始化framebuffer
2、向framebuffer写数据
3、退出framebuffer
好,我们直接上代码:

#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#define RGB(r,g,b)((r<<16)|(g<<8)|b)
#define WIDTH 1280
#define HIGHT 1024
static int Frame_fd ;
static int *FrameBuffer = NULL ;
static int W , H ;
//写framebuffer
int Write_FrameBuffer(const char *buffer);
int main(void)
{
1、设置长宽,打开fb设备
W = 1024 ;
H = 768 ;
Frame_fd = open("/dev/fb0" , O_RDWR);
if(-1 == Frame_fd){
perror("open frame buffer fail");
return -1 ;
}
2、对framebuffer进行内存映射mmap
//头文件 <sys/mman.h>
//函数原型:void* mmap(void* start,size_t length,int prot,int flags,int fd,off_t offset);
//start:映射区的开始地址,设置为0时表示由系统决定映射区的起始地址。
//length:映射区的长度。//长度单位是 以字节为单位,不足一内存页按一内存页处理
//prot:期望的内存保护标志,不能与文件的打开模式冲突。是以下的某个值,可以通过or运算合理地组合在一起
//flags:相关的标志,就跟open函数的标志差不多的,自己百度去查
//fd:有效的文件描述词。一般是由open()函数返回,其值也可以设置为-1,此时需要指定flags参数中的MAP_ANON,表明进行的是匿名映射。
//off_toffset:被映射对象内容的起点。
//PROT_READ //页内容可以被读取
//PROT_WRITE //页可以被写入
//MAP_SHARED //与其它所有映射这个对象的进程共享映射空间。对共享区的写入,相当于输出到文件。直到msync()或者munmap()被调用,文件实际上不会被更新。
FrameBuffer = mmap(0, 1280*1024*4 , PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE , MAP_SHARED , Frame_fd ,0 );
if(FrameBuffer == (void *)-1){
perror("memory map fail");
return -2 ;
}
3、对framebuffer写数据
char buffer[WIDTH*HIGHT*3]; //我们要写入的数据
while(1) {
Write_FrameBuffer(buffer);
printf("count:%d \n" , count++);
}
4、退出framebuffer
munmap(FrameBuffer , W*H*4); //解除内存映射
close(Frame_fd); //关闭文件描述符
return 0 ;
}
//写framebuffer
int Write_FrameBuffer(const char *buffer)
{
int row , col ;
char *p = NULL ;
//遍历分辨率1024*1280的所有像素点
for(row = 0 ; row <1024 ; row++){
for(col = 0 ; col < 1280 ; col++){
if((row < H) && (col < W)){
p = (char *)(buffer + (row * W+ col ) * 3);
//转RGB格式
FrameBuffer[row*1280+col] = RGB((unsigned char)(*(p+2)),(unsigned char)(*(p+1)),(unsigned char )(*p));
}
}
}
return 0 ;
}
至此,我们的framebuffer上层调用程序就写完了,当然这个程序你看不到什么图片,只能看到一块被映射的区域,然后printf不断的在打印数据。
如果你有兴趣,可以写一个图片数据进去,这时候要用到bmp,yuyv格式的图片知识,让图片可以显示在屏幕上,同时你也可以写一个摄像头,
让摄像头的视频流数据显示到framebuffer上,那些所谓的软件,比如车位监控,智能监控,还有小米那个智能摄像头,其实用的多半就是
这个原理,只不过他们做了拓展,可以跟TCP/IP,wifi进行结合,进而能够在互联网传输视频数据,摄像头的常用的驱动叫V4L2,
也是一个类似frambuffer驱动一样非常复杂的驱动,用到很多的知识点,我也在不断的努力学习中,往后若是有碰到,我也尽量拿出来跟大家一起
学习和分享我自己的看法。
驱动的学习是痛苦的 ,当然痛苦中就必有甘甜,如果你会写驱动程序了,那么软件层次的调用实质上就是函数传参的原理,太简单了,所以搞驱动
的工程师其实是可以往上层去发展的,因为他懂硬件也懂软件,相反,纯软件转底层开发,那就没那么容易了,你要了解很多硬件的知识和原理。
,当然痛苦中就必有甘甜,如果你会写驱动程序了,那么软件层次的调用实质上就是函数传参的原理,太简单了,所以搞驱动
的工程师其实是可以往上层去发展的,因为他懂硬件也懂软件,相反,纯软件转底层开发,那就没那么容易了,你要了解很多硬件的知识和原理。
今天就到此为止,这是我对framebuffer的理解,或许理想某些地方并不到位,如有高手,欢迎指正,共同探讨这个问题。
今天就到此为止,这是我对framebuffer的理解,或许理想某些地方并不到位,如有高手,欢迎指正,共同探讨这个问题。
我的CSDN博客: http://blog.csdn.net/morixinguan/article/month/2015/12